The second moment of area, also known as the area moment of inertia, is a cross-section property used in the strengths of materials. The stiffness of a component can be defined by using the moment of inertia. It is determined by the geometry and size of a cross-section.
The formula symbol of the second moment of area is I and the unit is mm4, cm4, or m4 in the metric system, or in4, ft4, or yd4 in the imperial system (also ℓ4).
There are three types of second moments of area.
Axial Second Moment of Area
The axial second moments of area Iy and Iz describe the stiffnesses against bending about the local axes y and z. The deflection as well as the occurring stresses are smaller as soon as the second moment of area increases with a constant load. The y-axis is often referred to as the "strong" axis, because the second moment of area Iy is greater here.
|
Iy |
Flächenträgheitsmoment um die y-Achse |
|
z |
Senkrechter Abstand der y-Achse zum Element dA |
|
Iz |
Flächenträgheitsmoment um die z-Achse |
|
y |
Senkrechter Abstand der z-Achse zum Element dA |
Biaxial Moment of Area
The biaxial moment of area is often referred to as the area centrifugal moment, the moment of deviation, the moment of area deviation, or simply as the centrifugal moment. It is used to calculate deformations on asymmetrical cross-sections and to determine unsymmetrical loads on any cross-sections.
Polar Second Moment of Area
A second moment of area, which describes the resistance of a closed circular cross-section or of circular cross-sections against torsion, is referred to as the polar moment of inertia. The polar second moment of area Ip is composed of the two moments of area Iy and Iz. It is also to be equated with the torsional moment of inertia IT for circular and circular ring cross-sections, which describes the stiffness against rotation about the longitudinal axis.
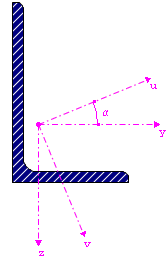
For unsymmetric cross-sections, the second moments of area are displayed around the principal axes u and v of the cross-section.