Solution for Laminate, Sandwich, and Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) Structures
Recommended Products for Laminate, Sandwich, and CLT Structures
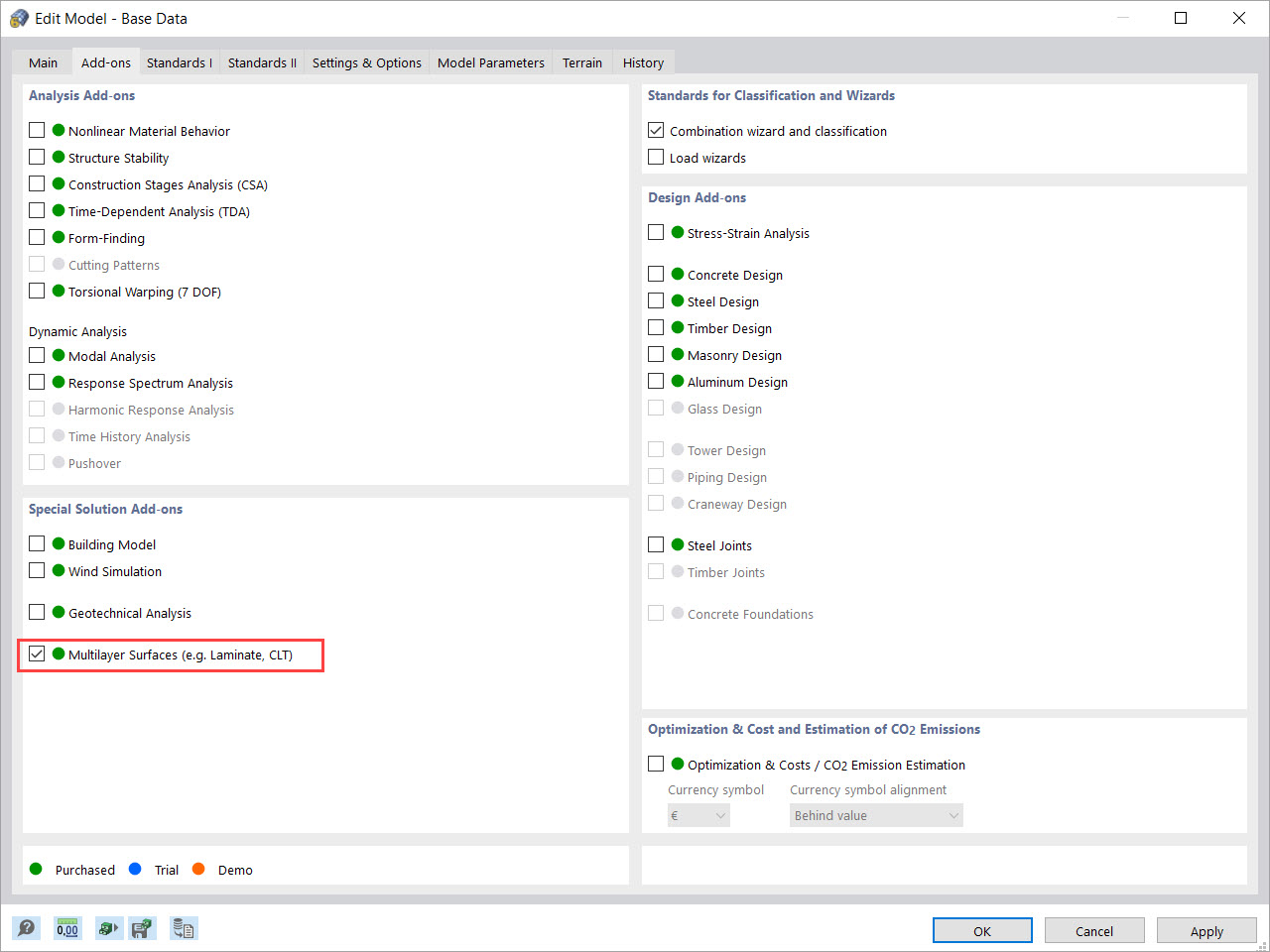
Definition of Multilayer Surfaces Such as Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
The Multilayer Surfaces add-on allows you to define multilayer surface structures. The calculation can be carried out with or without the shear coupling.
Construction Stages
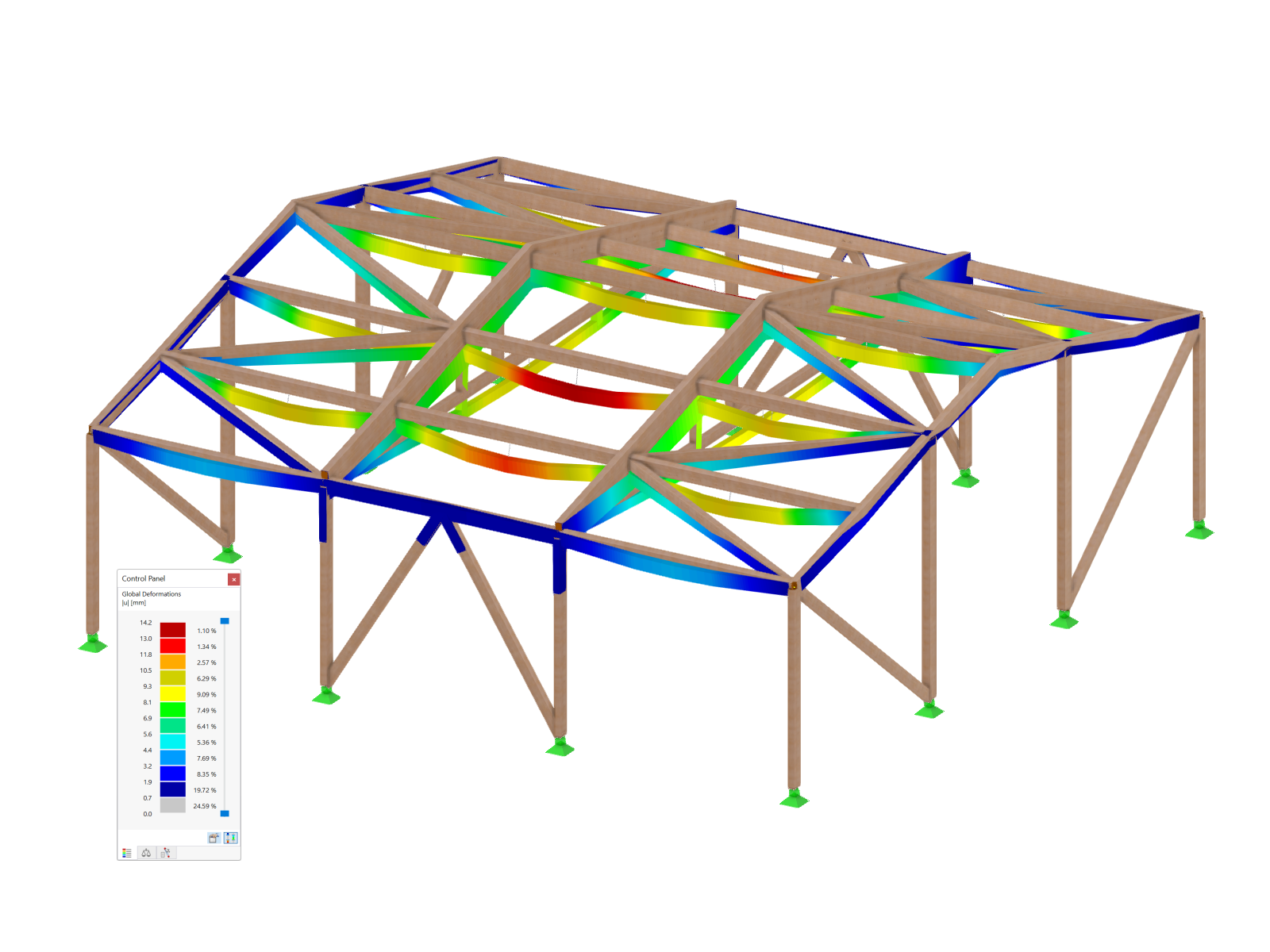
The Construction Stages Analysis (CSA) add-on allows for considering the construction process of structures (member, surface, and solid structures) in RFEM.
Support and Learning
We provide professional support and many services in order to help you with finding a quick and efficient solution for your projects.
Outdated Products
Technical Support | Sales Team
.png?mw=512&hash=4e74affa9ad0c7b703151c5085ac9b8e59171c23)
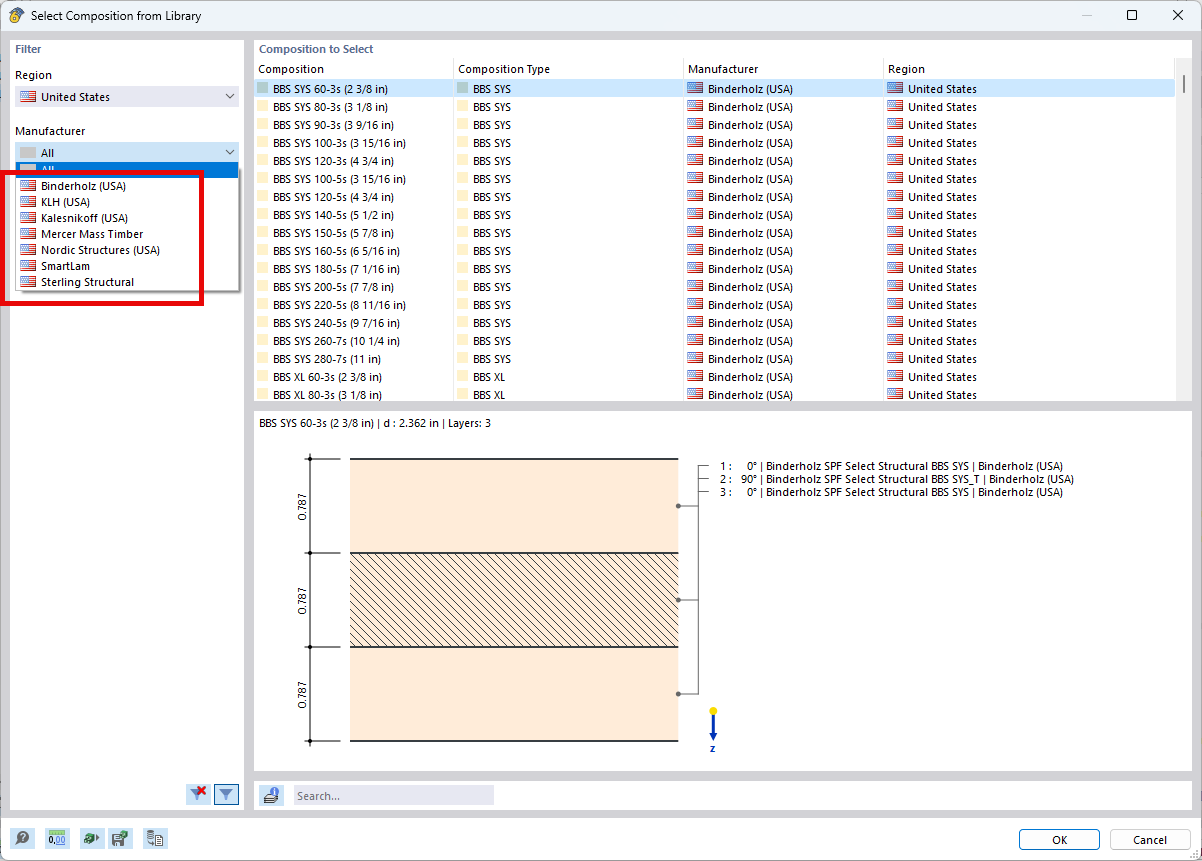
Among others, the following cross-laminated timber manufacturers are available in the layer structure library:
- Binderholz (USA)
- KLH (USA, CAN)
- Kalesnikoff (USA, CAN)
- Nordic Structures (USA, CAN)
- Mercer Mass Timber
- SmartLam
- Sterling Structural
- Superstructures listed in Lignatec Edition 32 "Cross-Laminated Timber of Swiss Production"
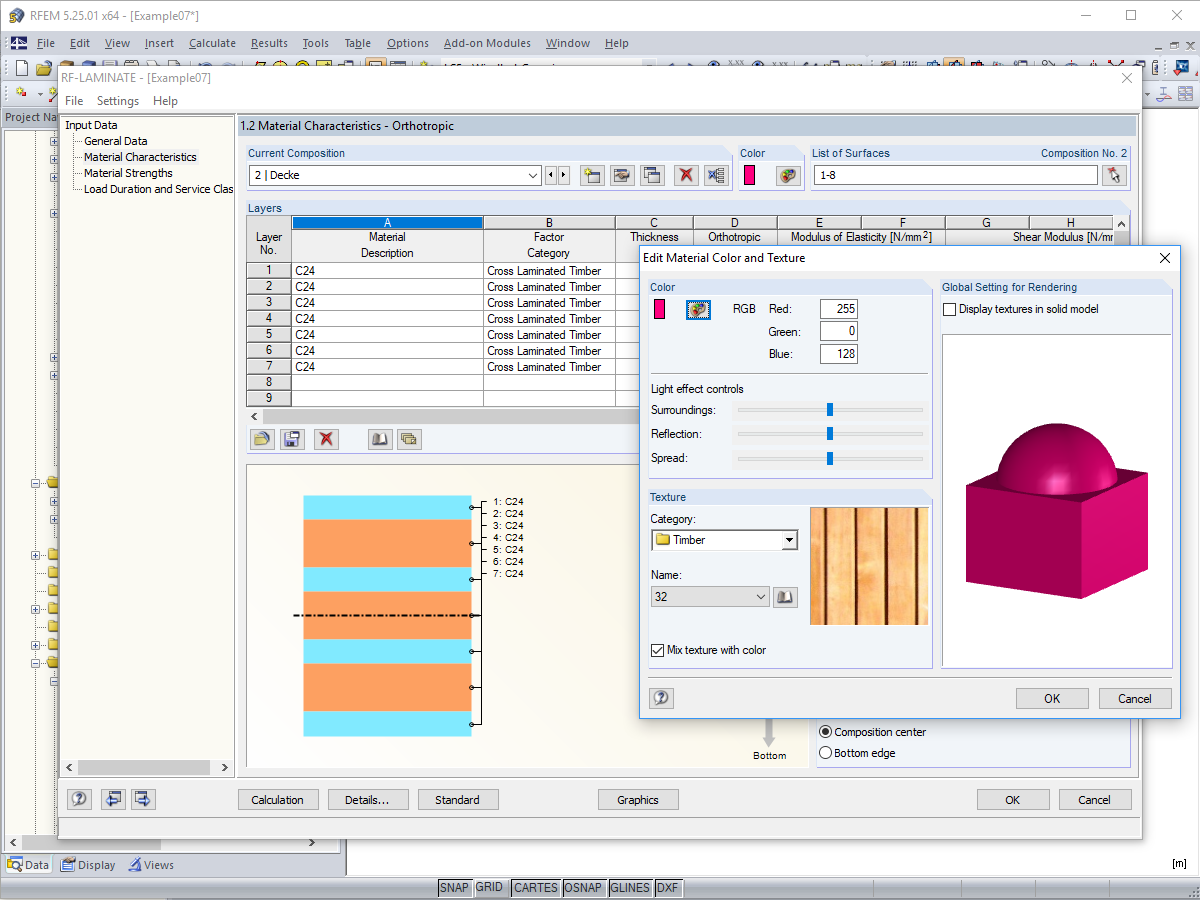
By importing a structure from the layer structure library, all relevant parameters are adopted automatically. The library is continually updated.

- General stress analysis
- Graphical and numerical results of stresses and stress ratios fully integrated in RFEM
- Flexible design with different layer compositions
- High efficiency due to few entries required
- Flexibility due to detailed setting options for basis and extent of calculations
- A local overall stiffness matrix of the surface in RFEM is generated on the basis of the selected material model and the layers contained. The following material models are available:
- Orthotropic
- Isotropic
- User-defined
- Hybrid (for combinations of material models)
- Option to save frequently used layer structures in a database
- Determination of basic, shear, and equivalent stresses
- In addition to the basic stresses, the required stresses according to DIN EN 1995-1-1 and the interaction of those stresses are available as results.
- Stress analysis for structural surfaces including simple or complex shapes
- Equivalent stresses calculated according to different approaches:
- Shape modification hypothesis (von Mises)
- Shear stress hypothesis (Tresca)
- Normal stress hypothesis (Rankine)
- Principal strain hypothesis (Bach)
- Calculation of transversal shear stresses according to Mindlin or Kirchhoff, or user-defined specifications
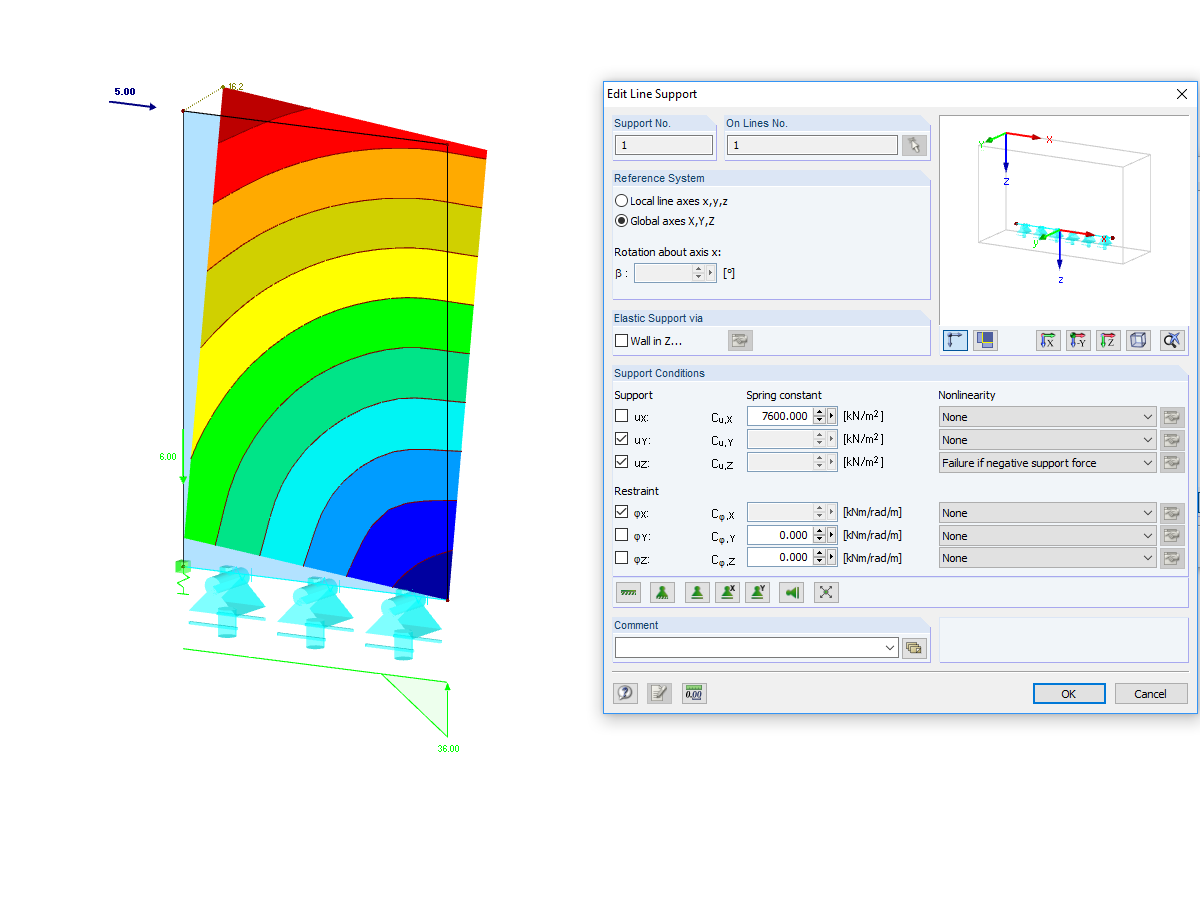
- Serviceability limit state design by checking surface displacements
- User-defined specifications of limit deflections
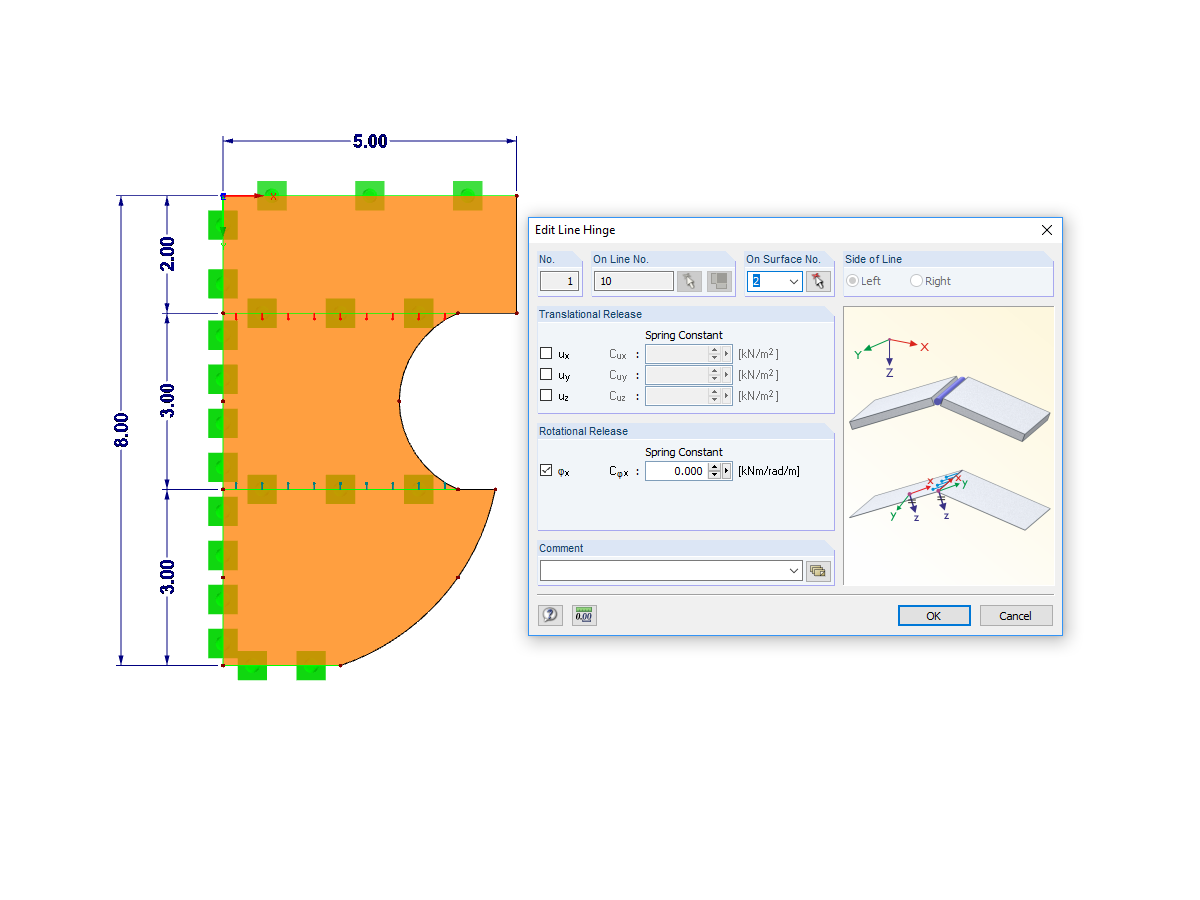
- Possibility to consider layer coupling
- Detailed results of individual stress components and ratios in tables and graphics
- Results of stresses for each layer in the model
- Parts list of designed surfaces
- Possible coupling of layers entirely without shear
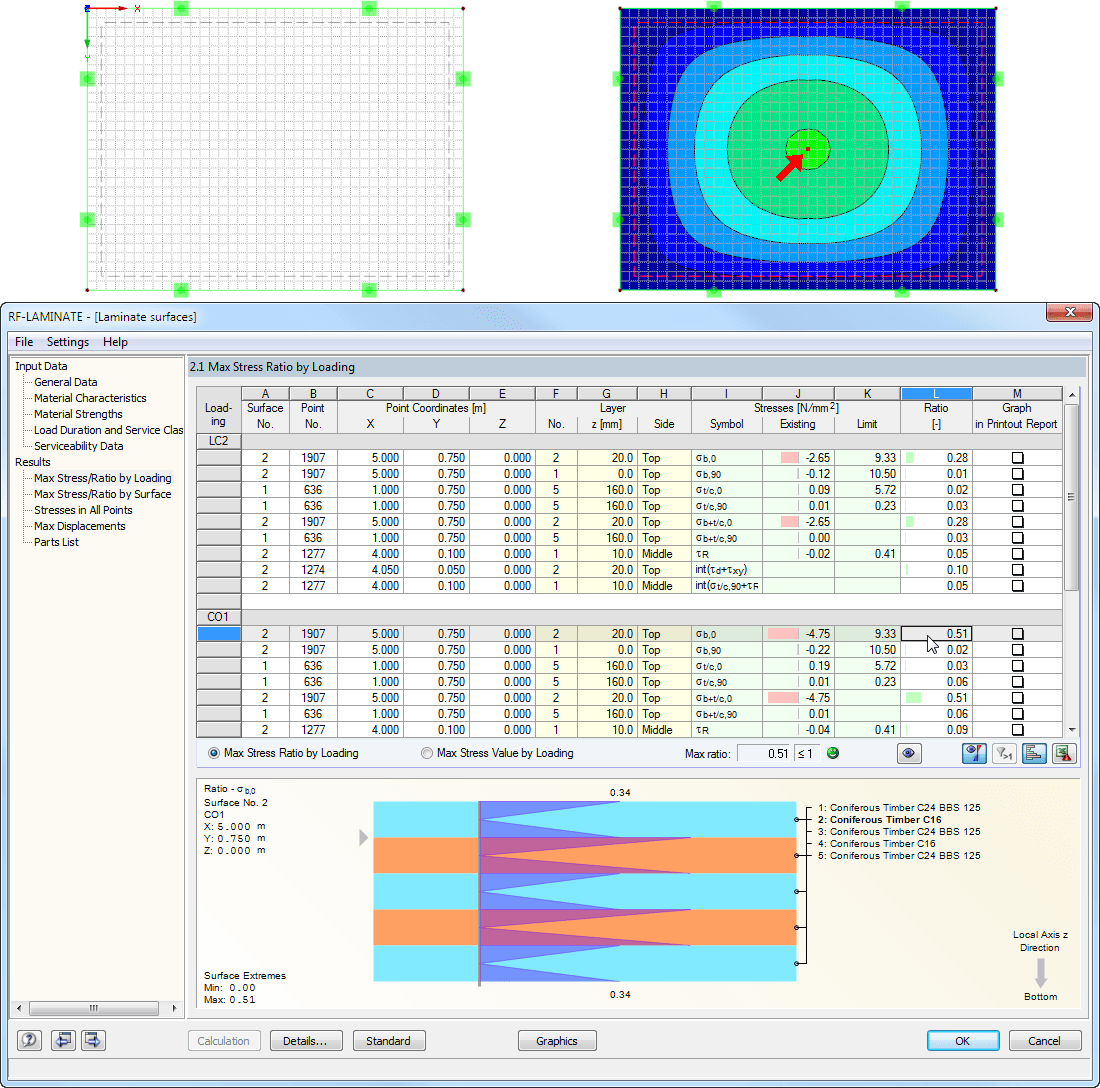
After the calculation, the maximum stresses, stress ratios, and displacements are displayed by load case, surface, or grid points. The design ratio can be related to any kind of stress type. The current location is highlighted by color in the RFEM model.
In addition to the result evaluation in tables, it is possible to display the stresses and stress ratios graphically in the RFEM work window. For this, you can adjust the colors and values assigned in the panel.
It is necessary to select load cases, load combinations, and result combinations for the ultimate and the serviceability limit state design. After selecting the surfaces to be designed, you can define the relevant material model.
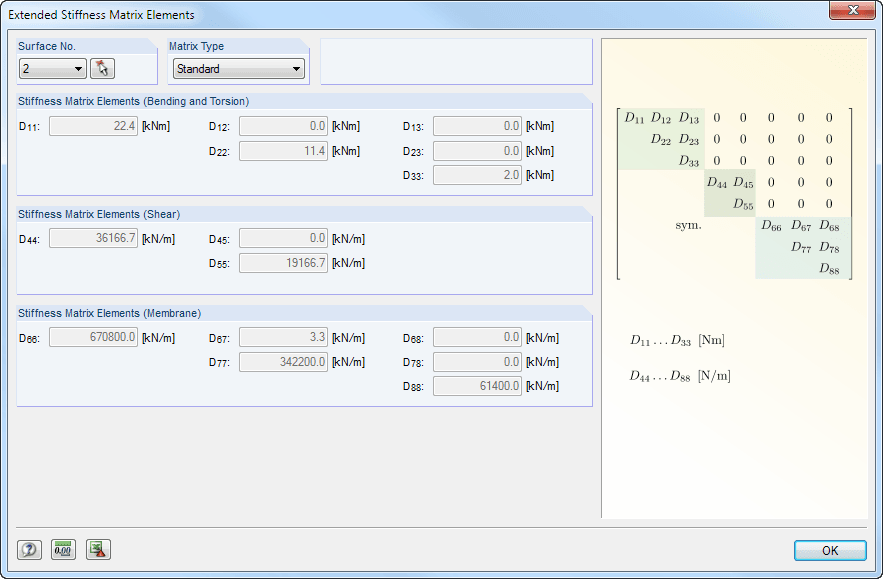
The structure of layers forming the basis for the stiffness calculation can vary. You can adjust the parameters defined by the selected material model according to your individual needs. The 3*3 matrix of the layers is modifiable as well. In this way completely free selection when generating the stiffnesses is provided.
The limit stresses of each layer are defined by the selected material. These values can be customized as well.





.png?mw=192&hash=f63e4a3f1836233005de32f60201d5392e507cf1)



.png?mw=80&hash=24e105a767cf2e175614b729c2d2fa1673e4e81b)
































.png?mw=350&hash=b023d6c658e181cb7d69028c0f3994dedab96fc5)









