Main Program RFEM or RSTAB
Extension Products for Structural Engineering
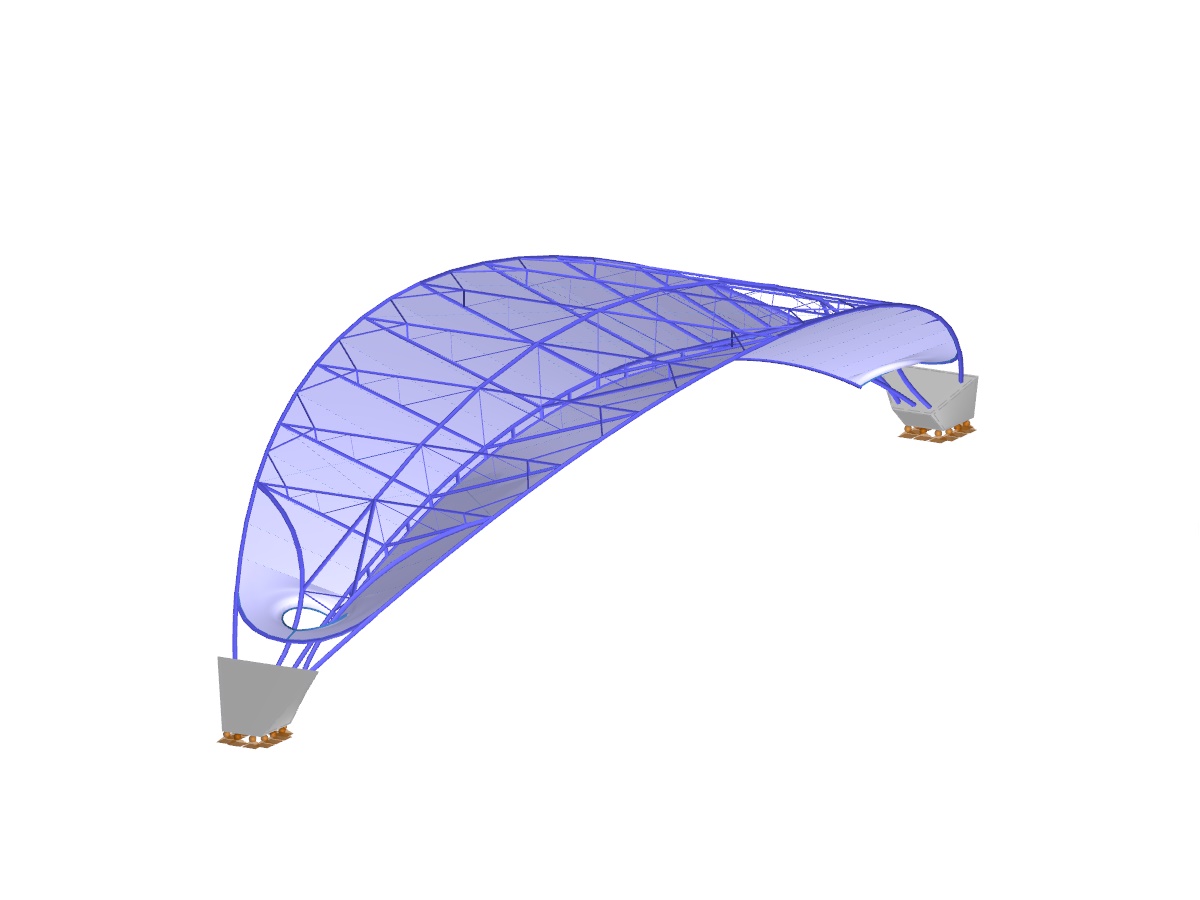
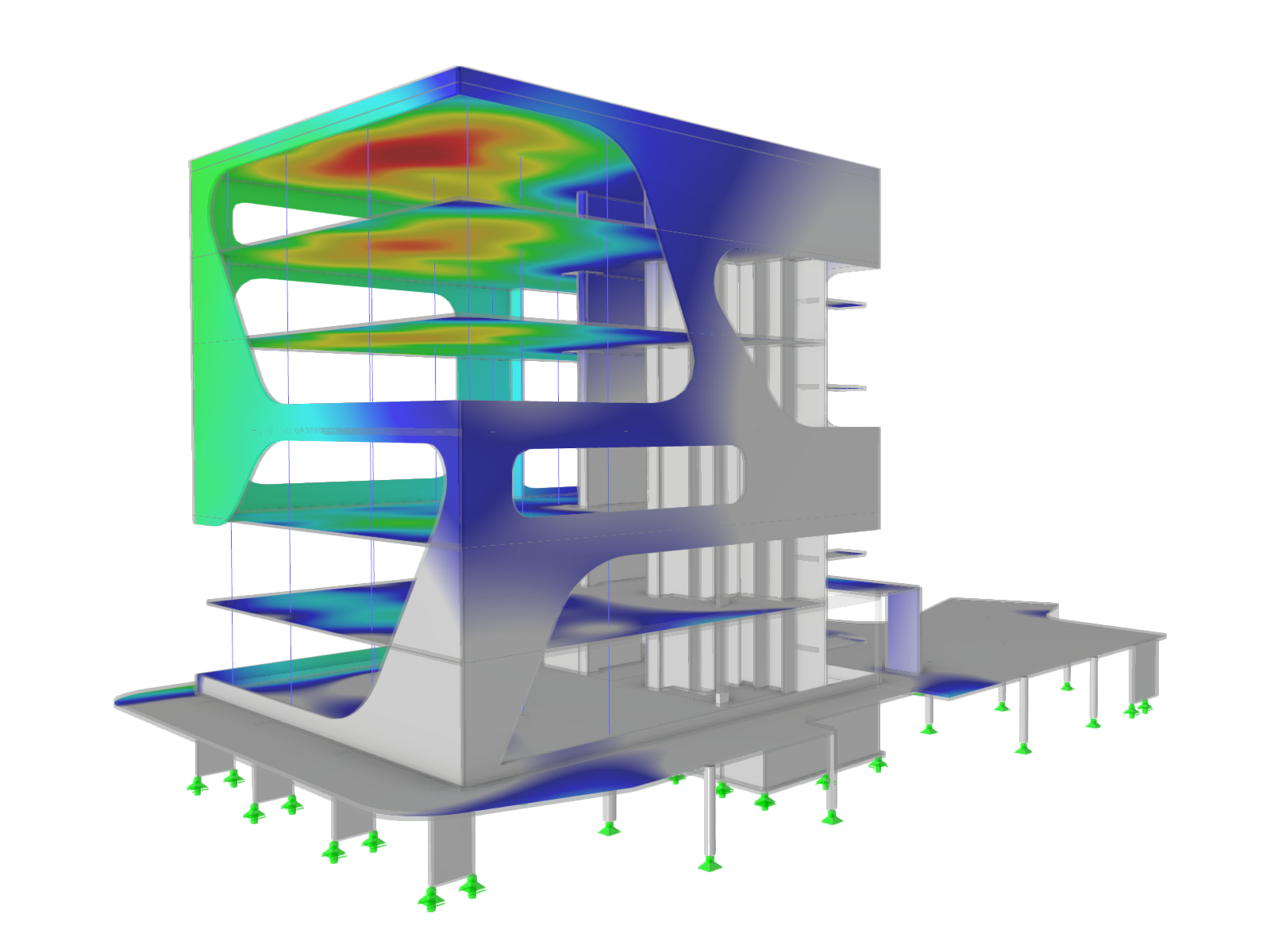
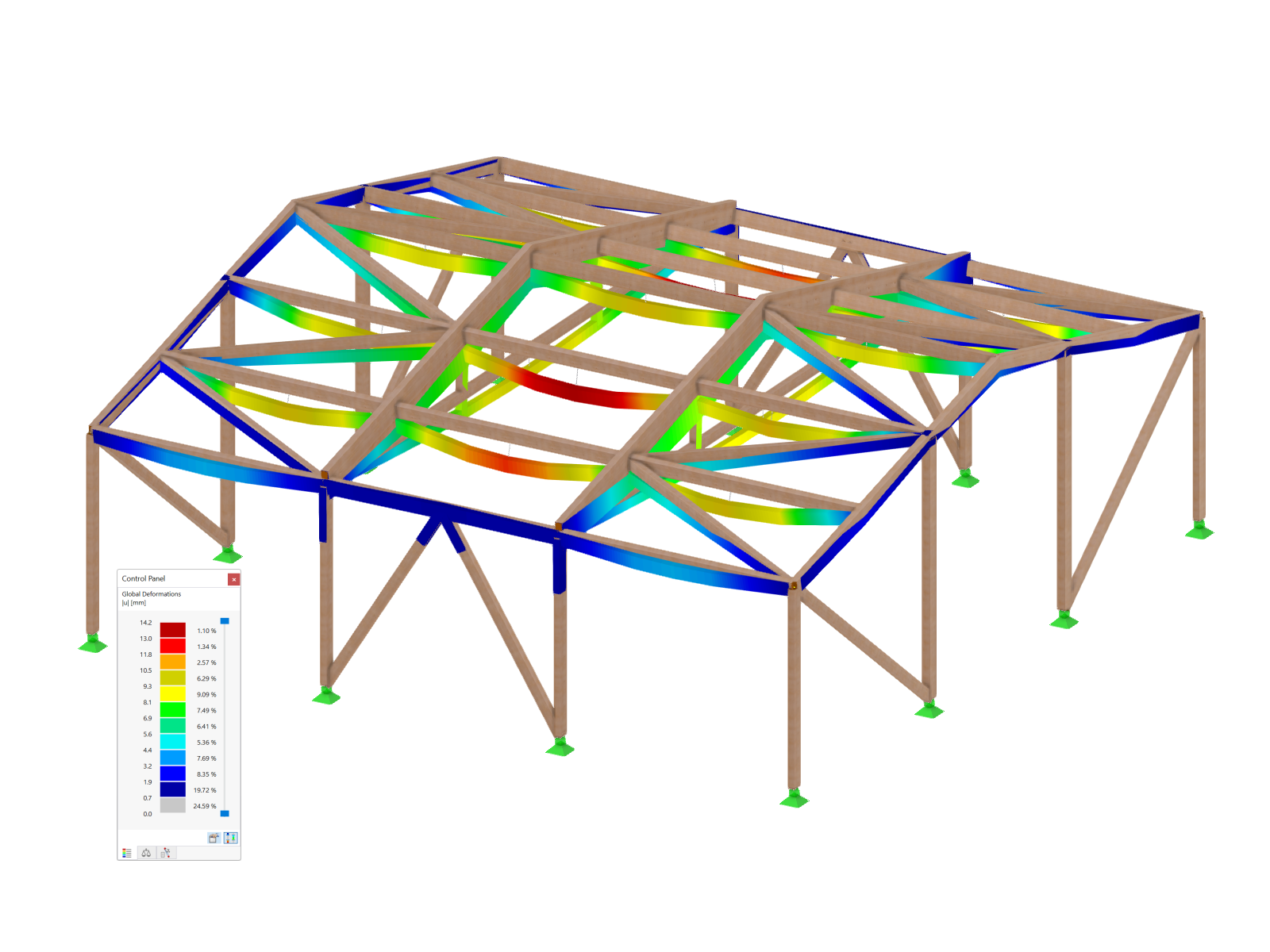
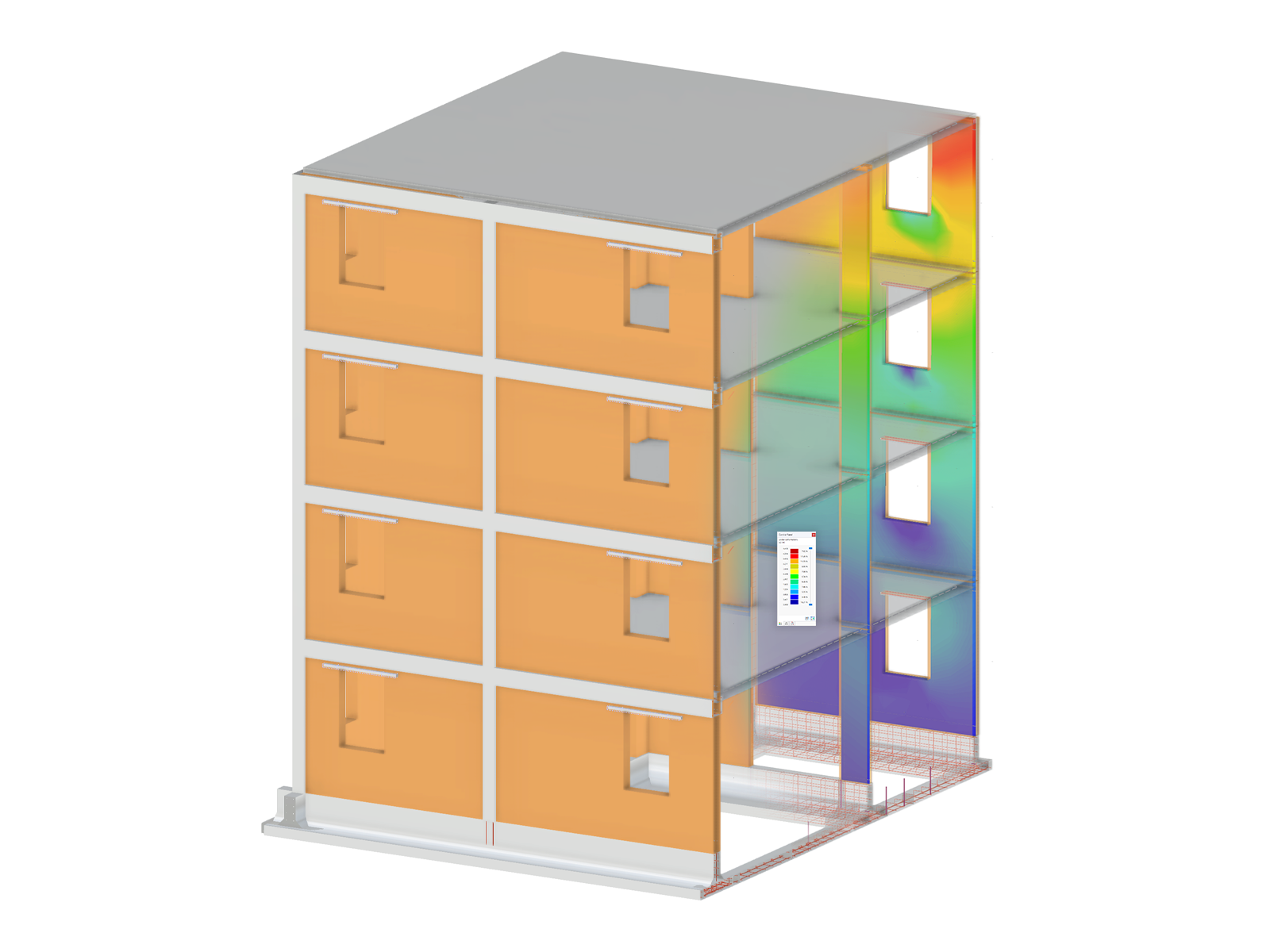
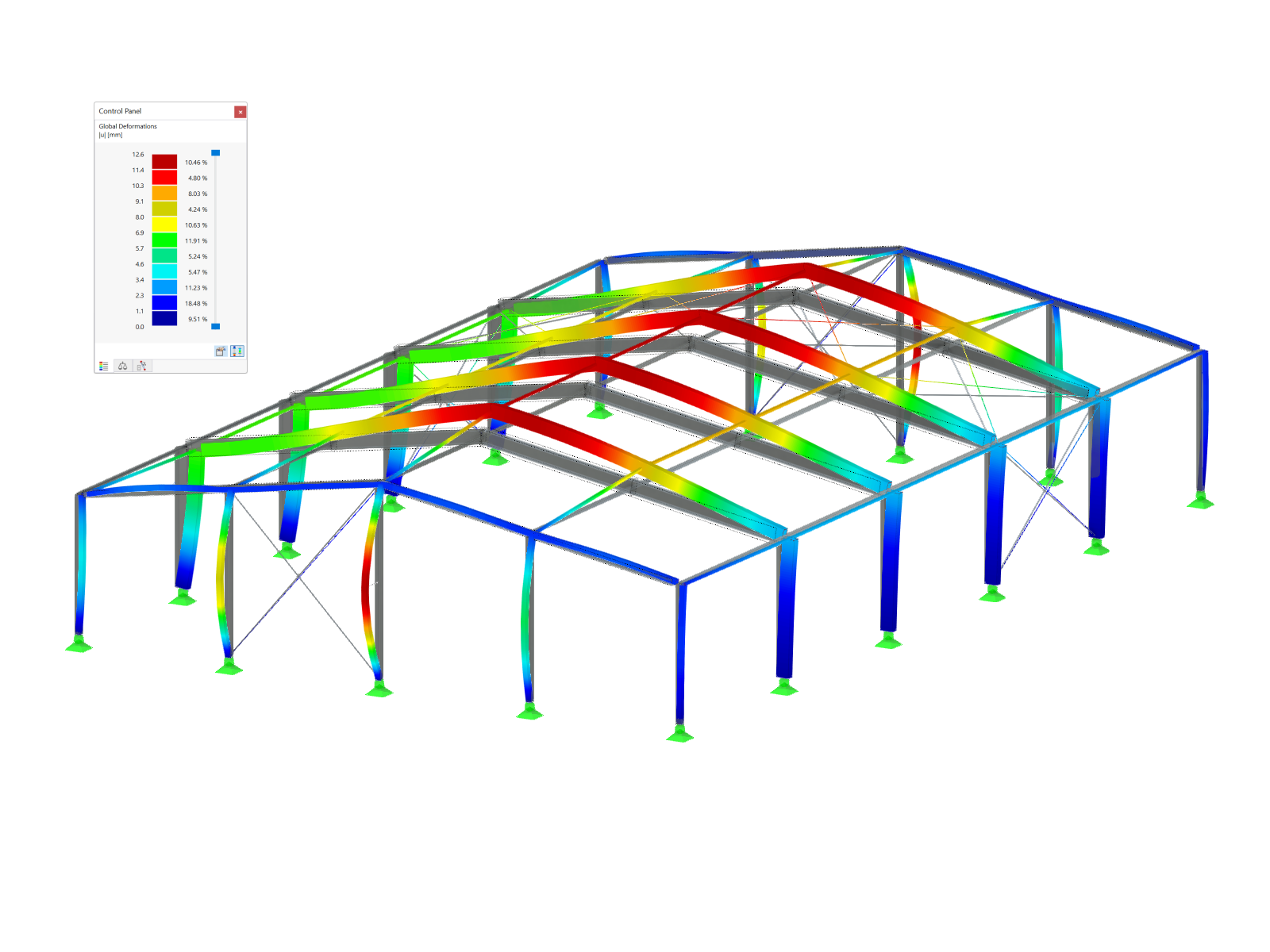
Hybrid Timber Construction with Complementary Materials
The "Building Model" add-on simplifies the modeling and analysis of timber buildings. It speeds up the creation of building models and automatizes the load generation, ideal for demanding structural timber projects.
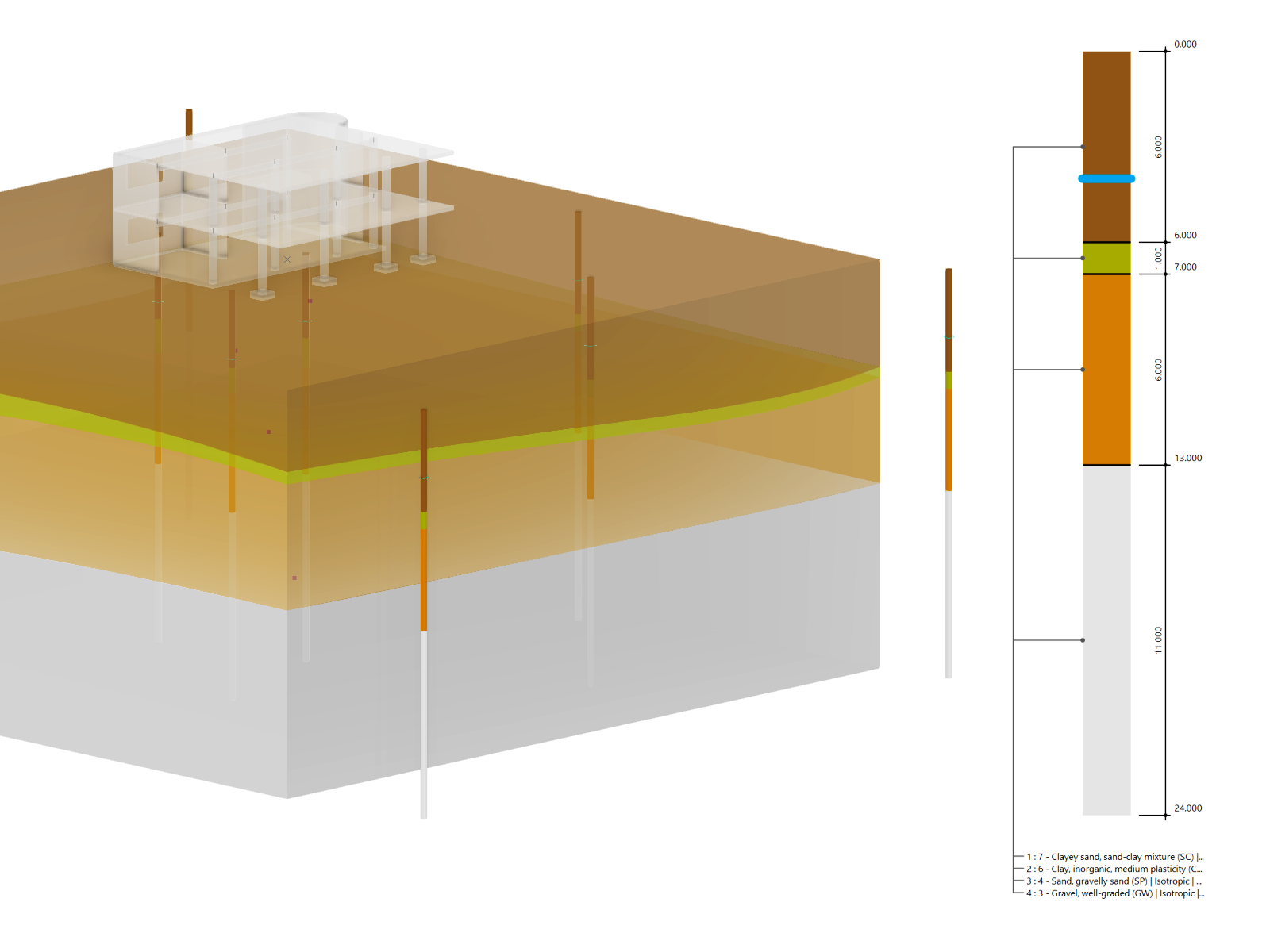
Geotechnical Analysis
In RFEM, the Geotechnical Analysis add-on uses the properties from soil samples to determine a soil body to be analyzed.
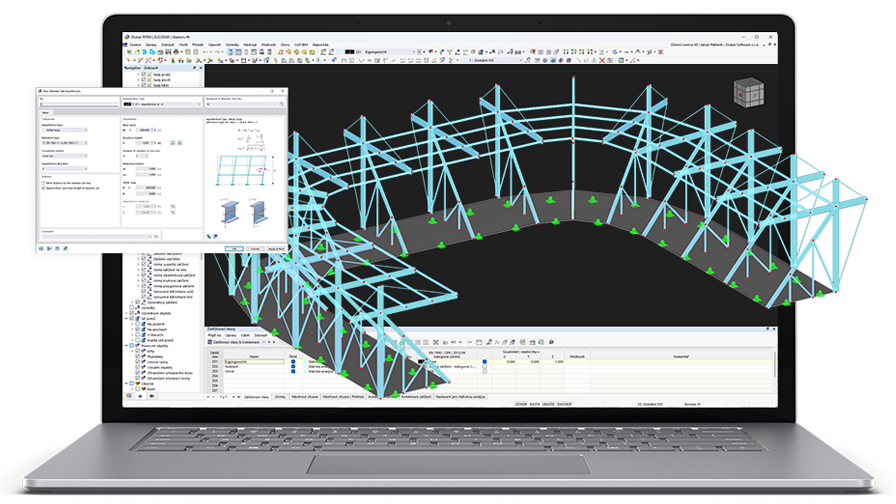
Construction Stages
The Construction Stages Analysis (CSA) add-on allows for considering the construction process of structures (member, surface, and solid structures) in RFEM.
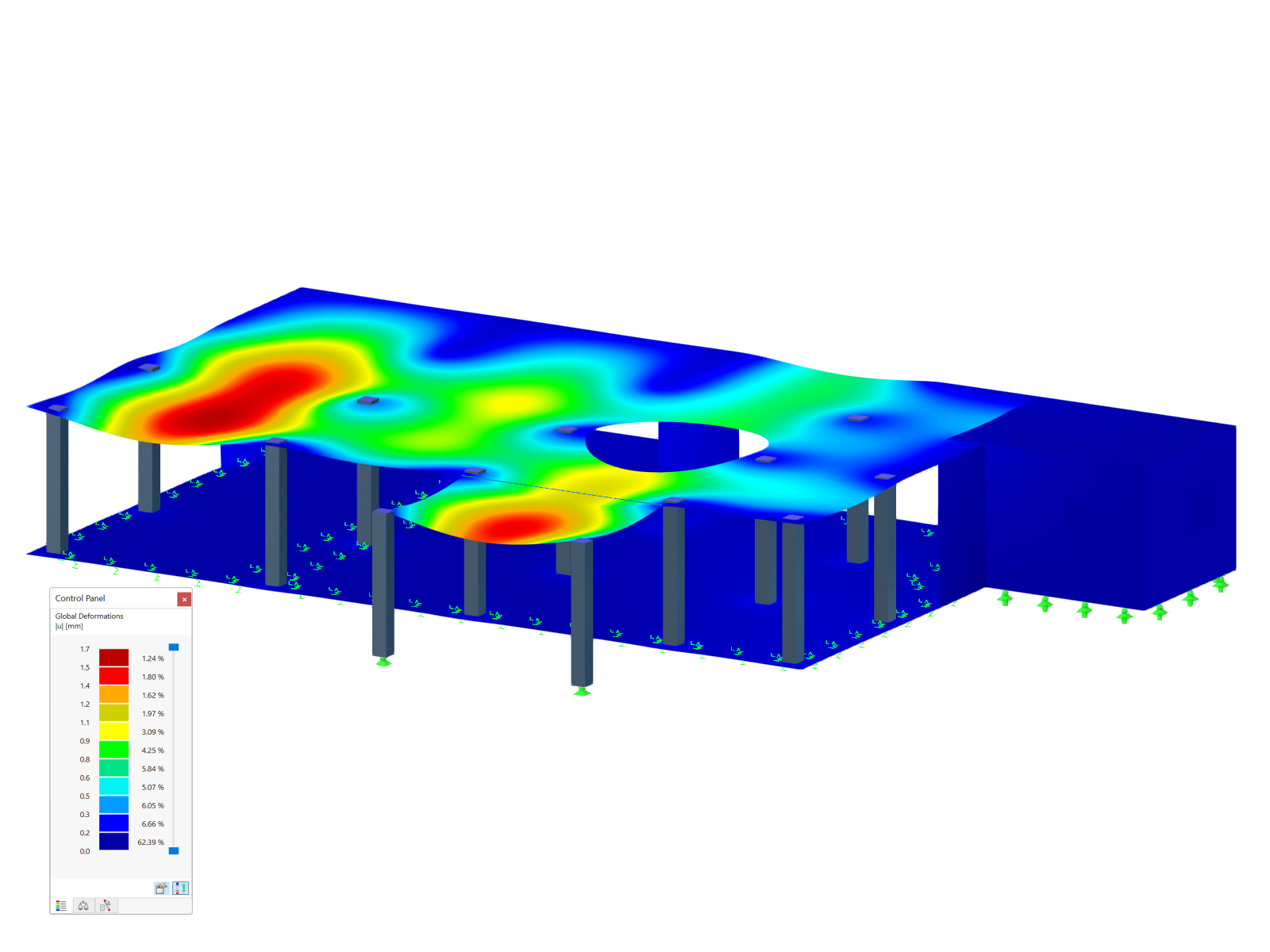
Time-Dependent Analysis (TDA)
The Time-Dependent Analysis (TDA) add-on allows you to consider the time-dependent material behavior of members and surfaces. The long-term effects, such as creep, shrinkage, and aging, can influence the distribution of internal forces, depending on the structure.
Response Spectrum Analysis
The Response Spectrum Analysis add-on performs seismic analysis using multi-modal response spectrum analysis. The spectra required for this can be created in compliance with the standards or can be user-defined. The equivalent static forces are generated from them. The add-on includes an extensive library of accelerograms from seismic zones that can be used to generate the response spectra.
Optimization of Model Parameters
The add-on uses particle swarm optimization (PSO) to determine optimal parameters for parameterized models based on weight, cost, or CO2 emissions.
Definition of Multilayer Surfaces Such as Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
The Multilayer Surfaces add-on allows you to define multilayer surface structures. The calculation can be carried out with or without the shear coupling.
Support and Learning
We provide professional support and many services in order to help you with finding a quick and efficient solution for your projects.
Technical Support | Sales Team



.png?mw=1024&hash=aeb4eef06592d784fa1f0dfcb514e59fd45bcb79)
Dlubal_KohlA_]_LI.jpg?mw=400&hash=b19f0b64f31f0dfc292e91d388ff4ead0b408e47)

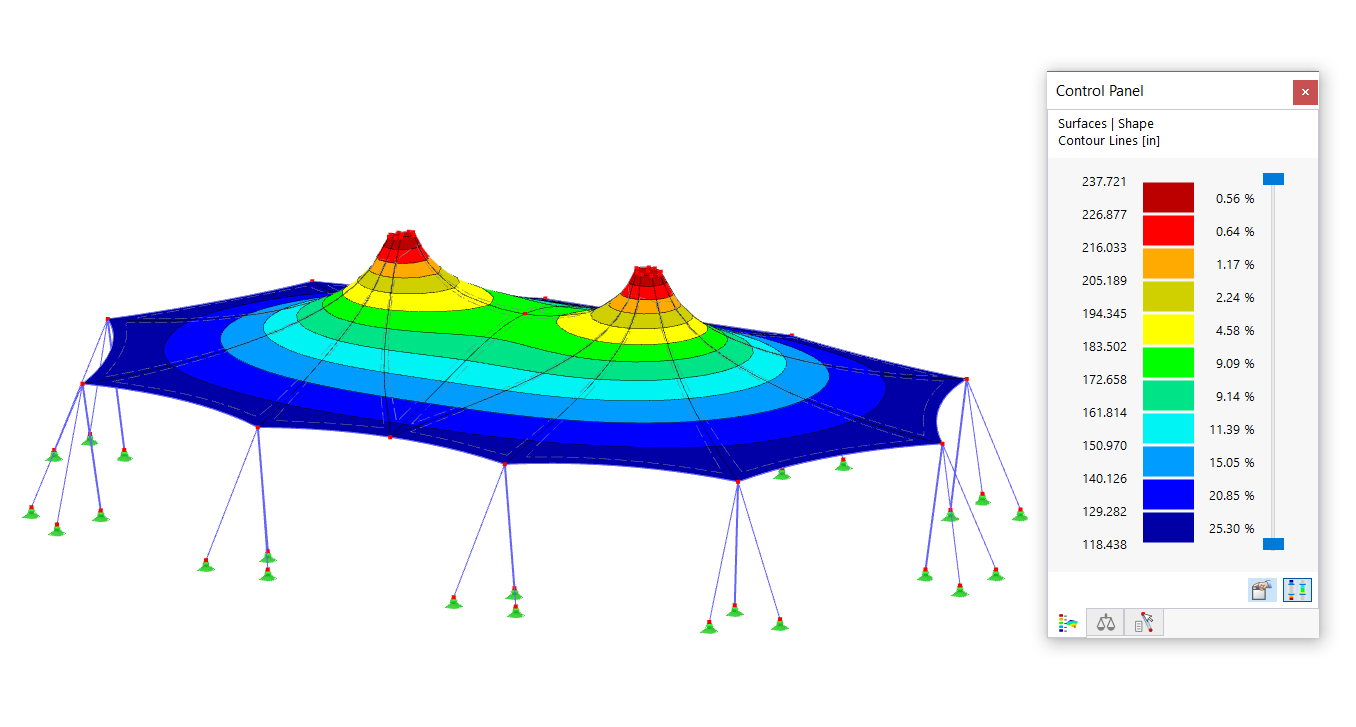
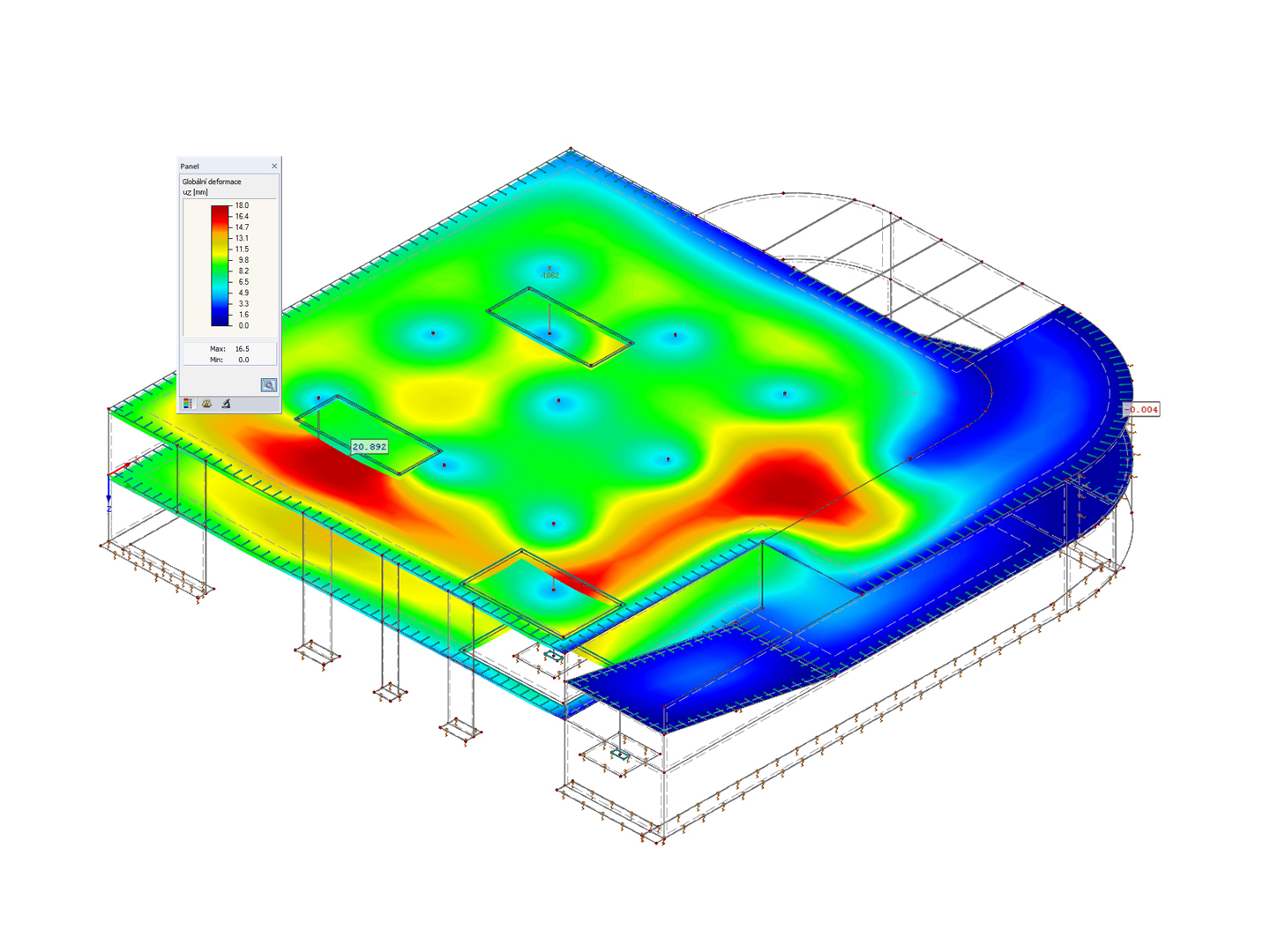
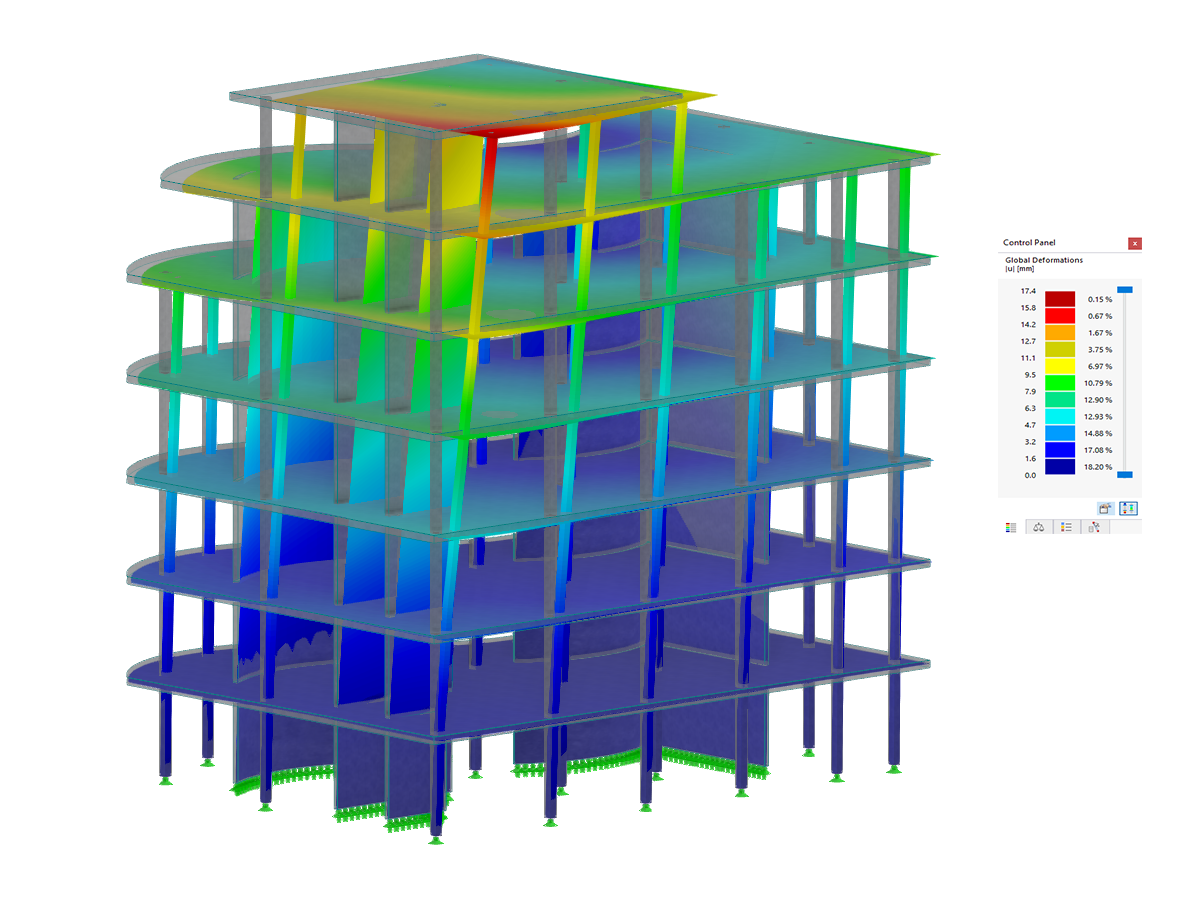
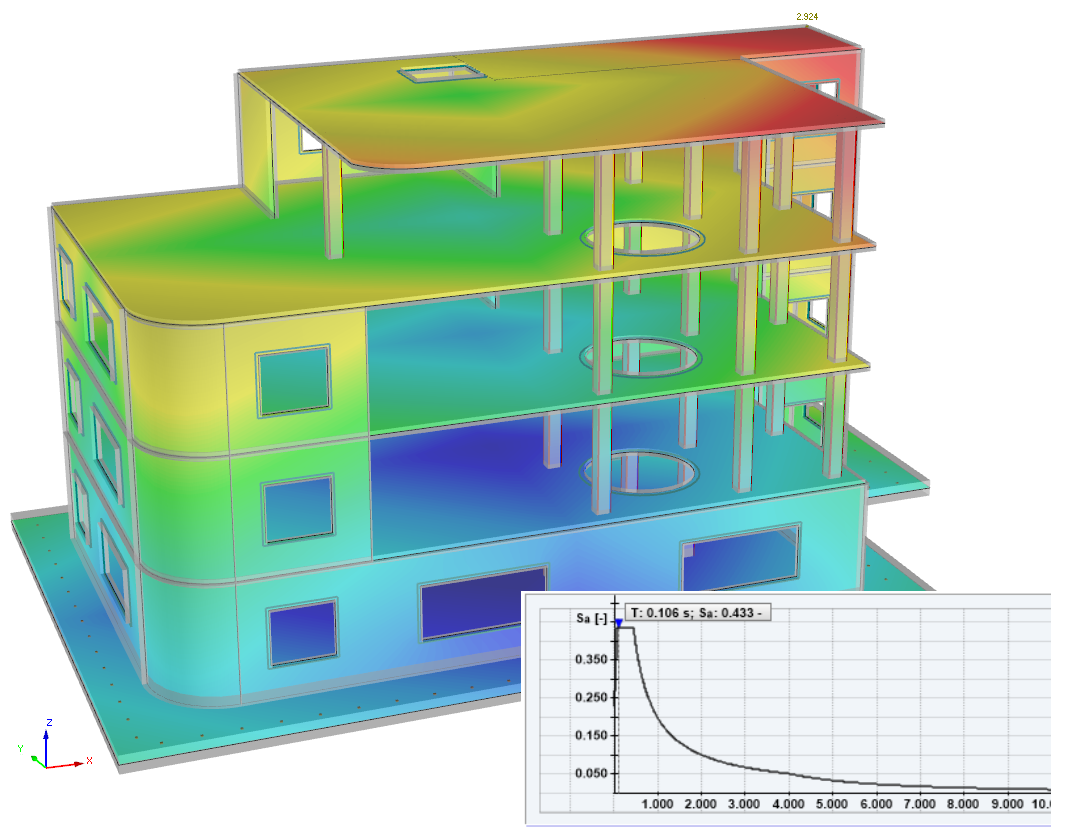


.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)

.png?mw=192&hash=f63e4a3f1836233005de32f60201d5392e507cf1)

.png?mw=80&hash=24e105a767cf2e175614b729c2d2fa1673e4e81b)