Features
A beam structure consists of one-dimensional structural components that are straight or curved. A member is thus characterized by its slenderness as well as a start node and an end node. Further characteristics are the transferrable internal forces of the individual members and those of the connections in the nodes.
Application
Basically, a beam structure is used to ensure the stability of the structure/building and to safely transfer the loads. The use of members has the advantage that the planning, execution, and calculation of the entire structure is simplified by separating the (beam) structure and the facade, for example.
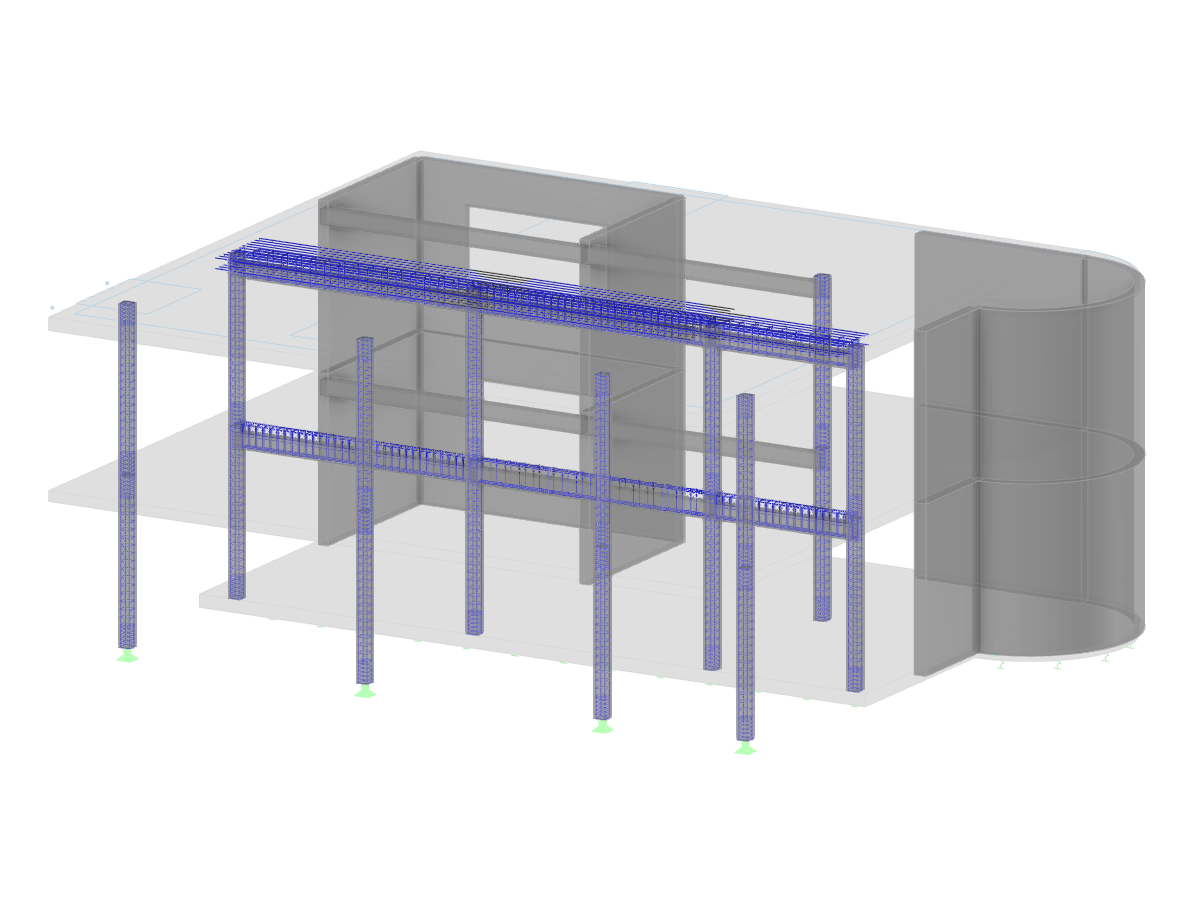
An example of a beam structure is the shell of a logistics hall made of steel sections, typically consisting of columns, beams/girders, compression pipes, and tension rods, see Image 01.
The essential part of a beam structure are the member connections of each other as well as the type of internal forces that they transfer. The rigid or hinged connections are included for the following reasons, for example:
- Limitation of the member length for transport reasons
- Direction change of a member
- Structural requirement, for example, to transfer the internal forces by means of moment hinges, shear force hinges, or axial force hinges
- Limitation of the internal forces of a single member by supporting a beam to reduce the span moment, for example
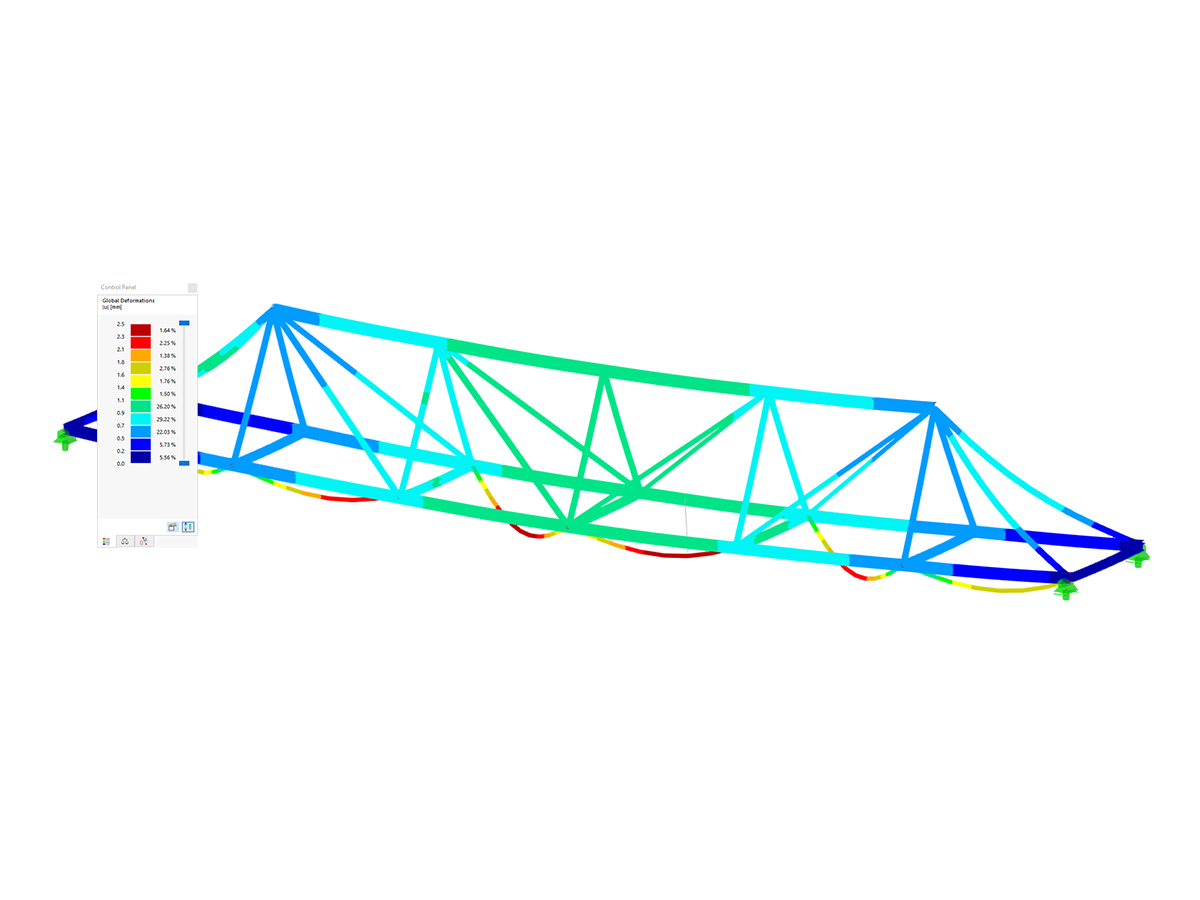
Frequently used types of member structures are, for example, trusses (Image 02) or frame structures (Image 03).
Beam Structures with Dlubal Software
Dlubal Software provides RFEM and RSTAB as main programs that allow you to intuitively model planar and spatial beam structures.
In both main programs, you can perform linear or nonlinear calculation of internal forces, deformations, and support forces.
For the cross-section design and stability analysis of the individual members, as well as for the special connection design, the corresponding add-on modules are available.
See Also
- Truss
- Frame Structure
- Arched Structure
- Cable Structure