This load wizard allows you to import the reaction forces of line and nodal supports of another model and to apply them as loads. This way, models can be digitally coupled as structural models with item lists. The linked models are managed in the Dependent Models tab of the model's Base Data dialog box.
Model
In the Model tab, define the model whose support reactions you want to import. In the Load Wizard, the "source model" is referred to as "Connected model". Please note the following:
- The current model and the connected model must be in the same Project .
- Both models must have different model IDs (see the chapter Model Parameters ).
- It is not necessary to open the connected model.
- The connected model has to be saved with results. If this is not the case, it is not possible to import any support reactions.
Select the "source model" in the "Connected model" list (see the image 1Import Support Reactions). You can also make the selection in the Dlubal Center by clicking the
![]() button.
button.
Objects
In the Objects tab, you can assign the support reactions of the connected model to the nodes and lines of the current model.
Import from Supported Objects
There are two options in the list for importing the support reactions as loads:
- Manually: The nodes and lines or members must be defined by the user in the Import to Current Model's Objects section.
- Free Loads: The support forces and moments of the connected model are applied as free concentrated loads or as free line loads. In the Import to Current Model's Objects section, you only need to specify the surfaces on which these loads act.
Import from Connected Model's Objects
All objects for which support reactions are available in the connected model are included by default for the import. If you want to consider only certain objects, clear the "All" check box. Then, you can enter the numbers of the supported nodes and lines of the source model.
Import to Current Model's Objects
Specify the numbers of the nodes and lines on which the reactions of the connected model should act as loads. You can also use the
![]() button to select the objects in the work window. If you import the support reactions as free loads, specify the numbers of the target surfaces.
button to select the objects in the work window. If you import the support reactions as free loads, specify the numbers of the target surfaces.
Loading
The Loading tab manages the assignment of loads in the load cases of both the connected model and the current model.
Categories
In the "Load distribution" list, two options are available for selection:
- Uniform – Total: The support reactions of a line support are imported as a line load with a constant distribution, which represents the average value of the support reaction.
- Varying: The support reaction is applied with the actual distribution as a line load showing a variable load distribution.
The "Loading connection type" determines the way load cases are linked between both models. The list includes two entries:
- Manually: In the "Connected Loading" dialog section, you can define how the load cases of the connected model should be connected to those of the current model (see the image Selecting Connected Loading).
- Automatically: The program assigns the support reactions of the connected model by load case to the corresponding LC numbers of the current model.
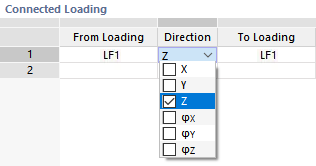
Connected Loading
If the "Manually" loading connection type is set, you can individually specify how the load cases of the connected model are to be linked with those of the current model: Select the relevant load case numbers in the lists of the "From Loading" and "To Loading" columns (see the image Selecting Connected Loading). These options are not available for the automatic assignment. RFEM assigns the support reactions by number to the corresponding load cases.
In the "Direction" list, you can specify which component(s) of the support reactions should be considered for the import. Both forces and moments are available for selection.