Each model is defined by structural objects. These objects fulfill a certain function in the structural system. For example, a line support or a surface represents objects of the Structure type, but not a dimension line or a section. The geometric and stiffness-related properties of a structural object are taken into account in the structural analysis of the model. This way, the length, material, member type, and cross-section of a member have an effect on the stiffness, and thus on the distribution of internal forces and moments in the system.
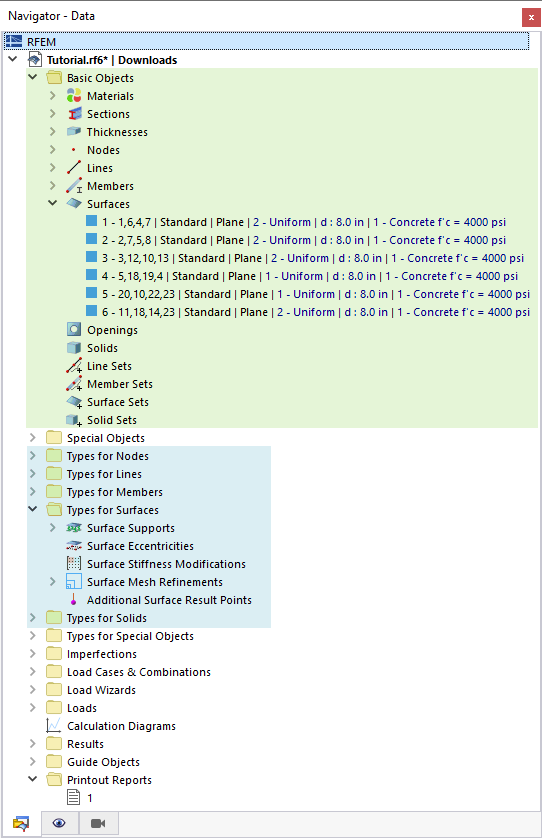
The structural data are organized in the navigator and in the table as follows: The Basic Objects category manages elementary structural objects such as nodes or lines. The Types categories describe specific properties of the basic objects, such as supports of nodes or lines.
The table manages the basic objects and the corresponding types in the Structure category.
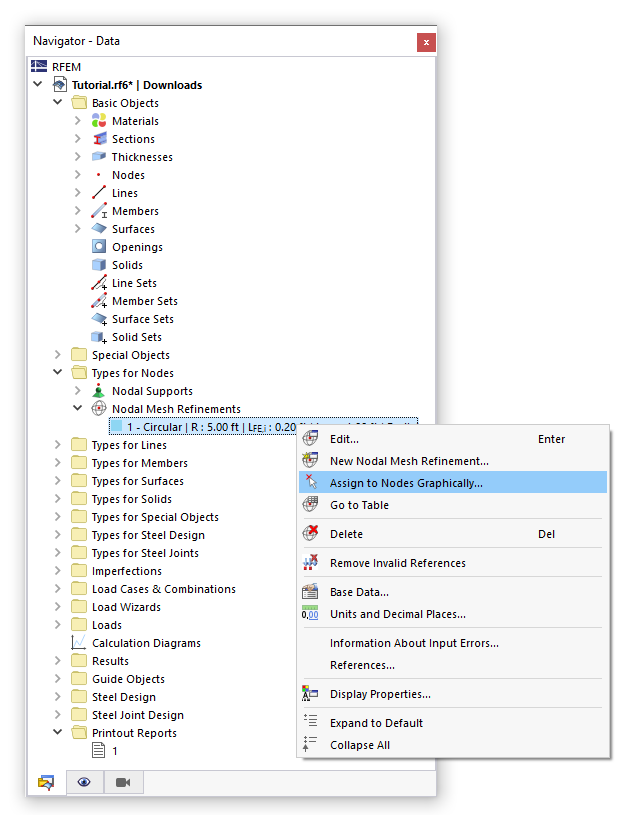
In the input dialog boxes, the basic objects are interactively linked to the types. This way, types can be redefined without leaving the dialog box, or properties can be graphically assigned as types to a basic object (see the image Edit Line Support ).
Example
A node represents a basic object. You want to provide this node with a support and a mesh refinement. You can activate these additional properties in the "Main" tab. Two new tabs are now available in the dialog box. You can select the "Nodal support" and "Nodal mesh refinement" properties from the lists or redefine them to assign them to the node.