A combination wizard supports you when superimposing load cases in combinations conforming to standards. It controls the rules according to which the actions are combined in a Design Situation .
The combination wizard is activated automatically when creating a model (see image 'Add-ons' Tab ). It is also possible to activate or deactivate the combination wizard in the Load Cases and Combinations dialog box.
A combination wizard manages the specifications according to which the combinations are created. You can define several combination wizards and assign them to the design situations.
The 'Name' is a short description. It is based on the generation type and the analysis type.
Main
The Main tab manages the general specifications of the wizard selected in the 'List' to the left.
Settings
The 'Generate' options control whether Load Combinations or Result Combinations are generated. The generation of load combinations is preset because nonlinear effects and results according to second-order analysis are only correctly determined using load combinations.
In the 'Static analysis settings' list, you can select the calculation theory according to which the combinations are to be analyzed (see Static Analysis Settings chapter).
Options I
If the Structure Stability add-on is selected in the Base Data of the model (license required), you can consider the specifications for the 'Stability Analysis' when creating the combinations.
The 'Consider imperfection cases' check box controls whether the combinations are created with or without imperfections (see Imperfection Cases chapter). The 'Generate same load combinations without imperfection case' option allows you to create combinations once with and once without imperfections.
If you activate the 'Consider initial state from' check box, you can select a load case in the Initial State tab whose deformations represent the initial state for the generated load combinations. The option to generate combinations both with and without taking an initial state into account is also available here.
The 'Consider structure modification' check box allows you to consider a stiffness adjustment or a special treatment of nonlinearities in the load combinations (see Structure Modifications chapter).
Options II
If you activate the 'User-defined action combinations' check box, no action combinations are created (see Action Combinations chapter). You then have to combine the actions manually.
With the 'Favorable permanent actions' option, a distinction is made between favorably and unfavorably acting permanent actions during the generation. They are included in the superposition with specific partial safety factors. Additional load combinations are created.
With the 'Reduce number of generated combinations' check box, you can generally limit the number of load cases occurring in the load combinations. RFEM finds out which load cases provide positive or negative internal forces and deformations. Then, all positively acting and all negatively acting load cases are combined. Thus, combinations take into account only the load cases that are relevant for the maximum or minimum values.
For 'Result combinations' it is possible to create sub-combinations of the 'Superposition' combination type including contained components (see Result Combinations chapter).
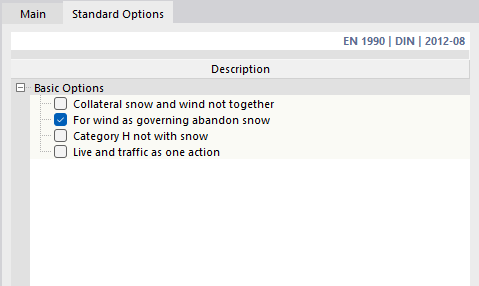
Standard Options
The Standard Options tab manages the basic settings for superimposing certain action categories.
The options are adapted to the standard. For EN 1990, for example, it is possible to neglect certain constellations if they have a low probability of occurrence. This way, snow load, for example, can be ignored for the leading action of wind for certain model properties. If you activate one of the options, the number of generated combinations will be reduced accordingly.
Initial State
In the Initial State tab, you can select a load case whose deformations represent the initial position for the created combinations. This allows, for example, the influence of prestressing to be taken into account.
The list in the 'Assigned for' dialog section allows you to adjust the initial state type for the selected load case. The individual options are described in the Load Cases chapter.