Loads from a specific action are stored in a load case (LC). Load cases are, for example, self-weight, snow, or imposed load.
List
The "List" manages all the load cases of the model. The Buttons for "List" of Object Types table describes the functions that you can use to create, copy, or delete objects of a list.
No. and Load Case Name
The number of the new load case is preset. Use the Table input in the RFEM workspace if you want to leave gaps in the numbering for later additions.
Enter a load case name, or select an entry from the list that briefly describes the load case.
To Solve
The check box controls whether the load case is analyzed in the calculation. This way, you can exclude load cases from the calculation that do not occur in isolation, such as wind, without considering the self-weight.
Main
The Main tab manages the general specifications of the load case selected in the "List" to the left.
Categories
If you have not activated any add-ons in the model's Base Data, only the "Static Analysis" is available in the "Analysis type" list.
In the "Static analysis settings" list, you can select the calculation theory according to which the load case is to be analyzed. The following analysis types are available:
- Geometrically linear
- Second-order (P-Δ)
- Large deformations
The analysis types are described in the Static Analysis Settings chapter. Use the
![]() button to add a new analysis type.
button to add a new analysis type.
Self-Weight
If you want to consider the self-weight of the model as a load in the load case, select the "Active self-weight" option. Use the "Factor in direction" fields to define the effective direction of the self-weight. The default setting is factor 1.00 in direction Z, or -1 if the global Z-axis is pointing upwards.
RSTAB determines the self-weight from the material and object properties. If you apply the automatic self-weight in several load cases, you should consider this when combining the load cases.
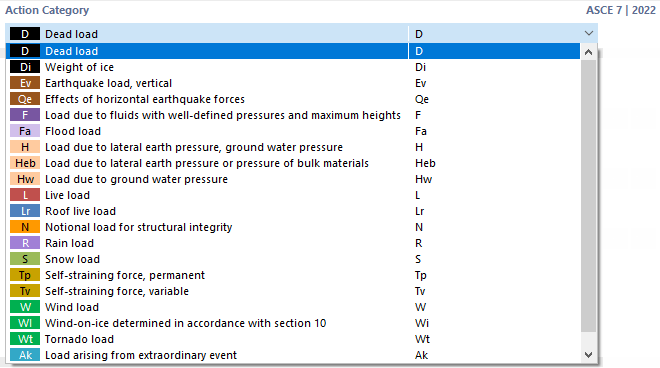
Action Category
The standards mention different action categories that control the superposition of load cases, as well as the partial safety factors and combination coefficients.
You have to assign a category to each load case. You can do this using the list. The categories are linked to the standard you defined in the "Base" tab.
The "None" action category represents a special case: It allows you to create a load case without assigning a category; for example, to apply imperfections by means of user-defined equivalent loads (stabilizing loads). Load cases of this type are not considered in the action combinations.
Options
If you activate the "Consider imperfection" check box, you can select an imperfection case (see the chapter Imperfection Cases) in the list, or use the
![]() button to create a new one. In this way, an imperfection is applied in the load case at the same time.
button to create a new one. In this way, an imperfection is applied in the load case at the same time.
Example: in the "Wind in X" load case, the imperfection case named "Imperfection in X" is considered. Thus, imperfections in X are applied for all load combinations with wind in the X-direction, but not imperfections acting in other directions.
The "Structure modification" check box allows you to consider a stiffness adjustment or a special treatment of nonlinearities in the load case. These functions are described in the Structure Modifications chapter. Select the structural modification in the list, or create a new modification type with the
![]() button.
button.
Special Options
If you activate the "Consider initial state from" check box, you can select a load case from the list whose deformations represent the initial position for the selected load case. This way, you can determine the effect of prestress, for example.
The
![]() button to the right of the list opens the "Initial State Settings" dialog box. Define the "Type of Initial State" that is available.
button to the right of the list opens the "Initial State Settings" dialog box. Define the "Type of Initial State" that is available.
The possibilities have the following meaning:
- Final State: The state of the model as it is after the calculation of the specified load case is imported and used as the initial state for the calculation of the current load case. This way, it is possible to take into account the effect of prestresses, for example.
- Strains: The member Strains , which are available in the specified load case, are adopted. Thus, the model is only deformed; no forces are generated. With the "Strains with user-defined factors" option, you can scale the strains in the "Individual Factors of Selected Objects" table for each member.