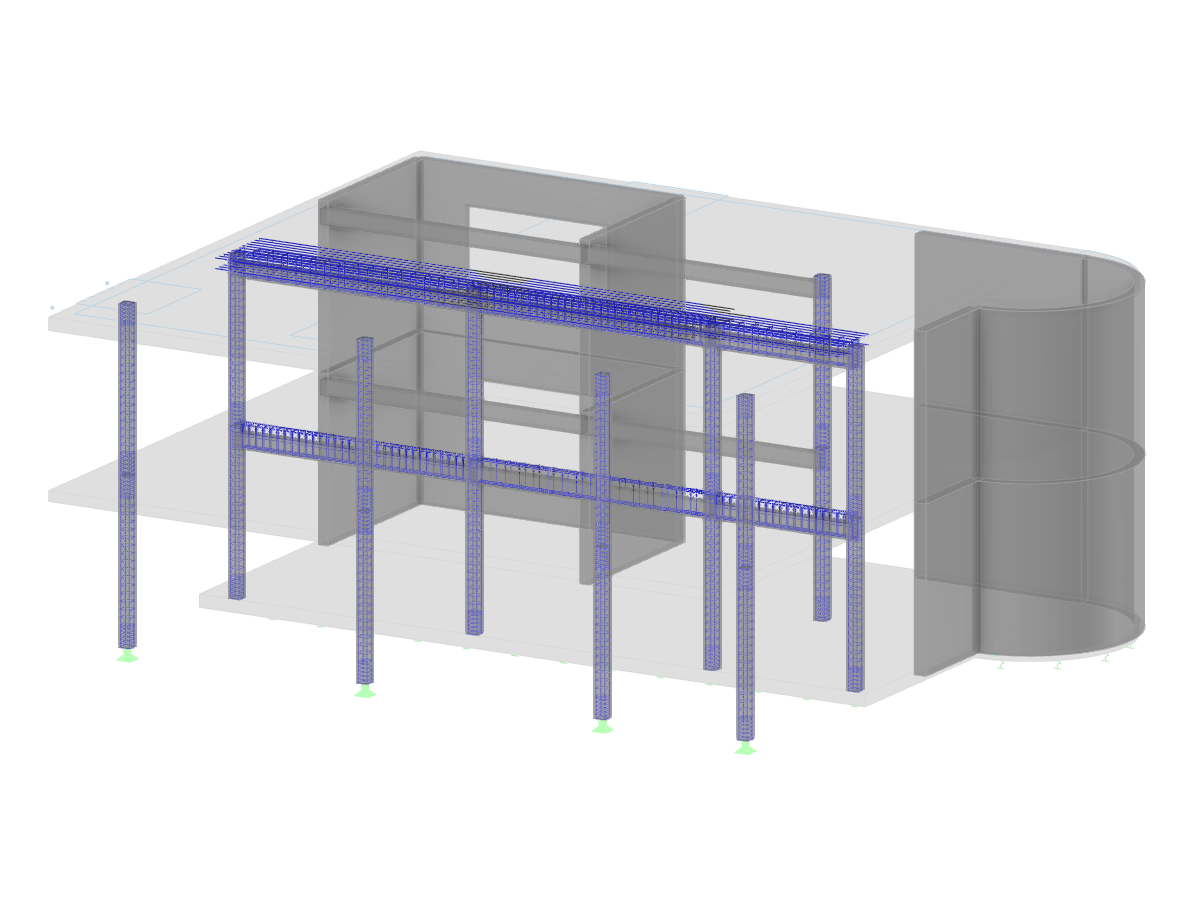
The model shows a spiral staircase as an innovative timber-concrete composite structure in the KF Aerospace Centre for Excellence in Canada. The structure combines high-quality cross-laminated timber with concrete for efficient use of materials. The details of the staircase are shown in precise detail to illustrate state-of-the-art construction techniques. Structural designers and construction experts gain valuable insights into the complex connection between timber and concrete, as realized by StructureCraft. The demands on stability and aesthetics are harmoniously combined.
| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Spiral Staircase in KF Aerospace Centre
| Number of Nodes | 2446 |
| Number of Lines | 1104 |
| Number of Members | 954 |
| Number of Surfaces | 10 |
| Number of Load Cases | 12 |
| Number of Load Combinations | 8 |
| Number of Result Combinations | 3 |
| Total Weight | 13,139 t |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 20.803 x 13.151 x 14.244 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 68.25 x 43.15 x 46.73 feet |
| Program Version | 5.26.02 |
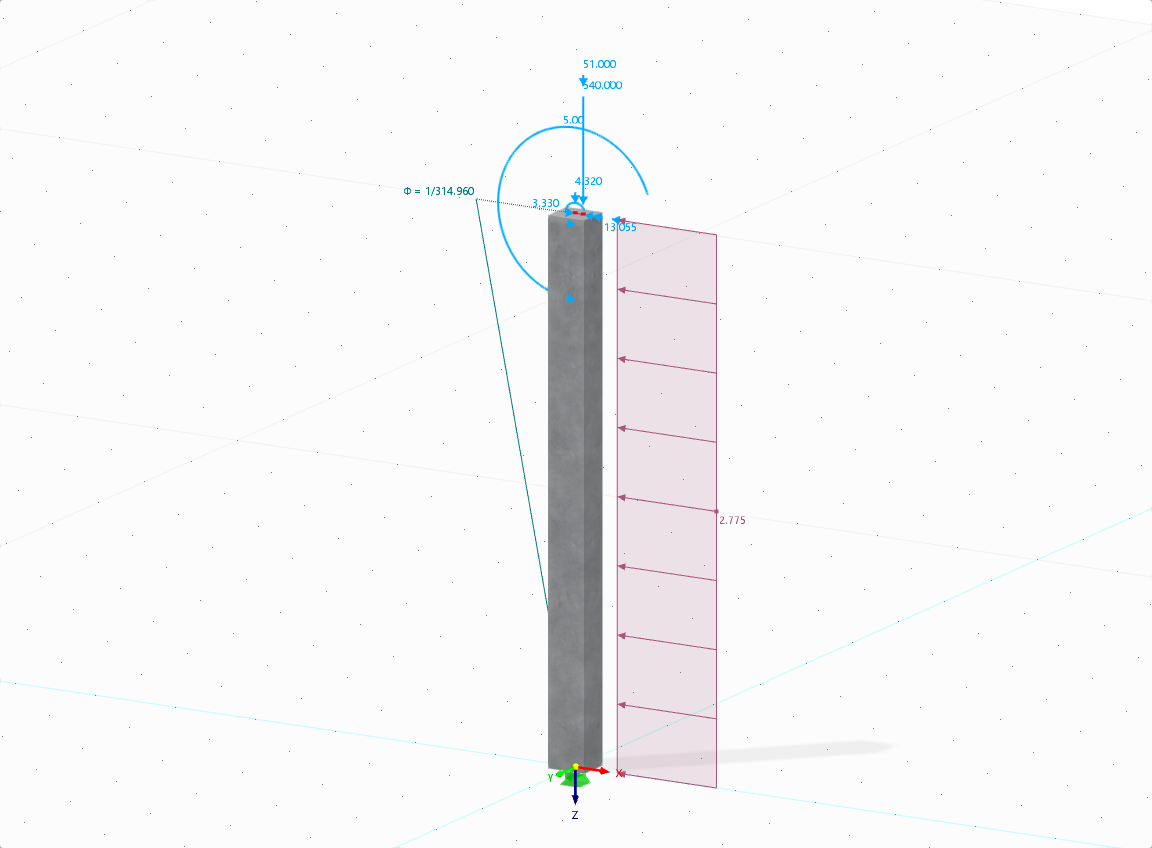
The aim of this technical article is to perform a design according to the general design method of Eurocode 2, using the example of a slender reinforced concrete column.

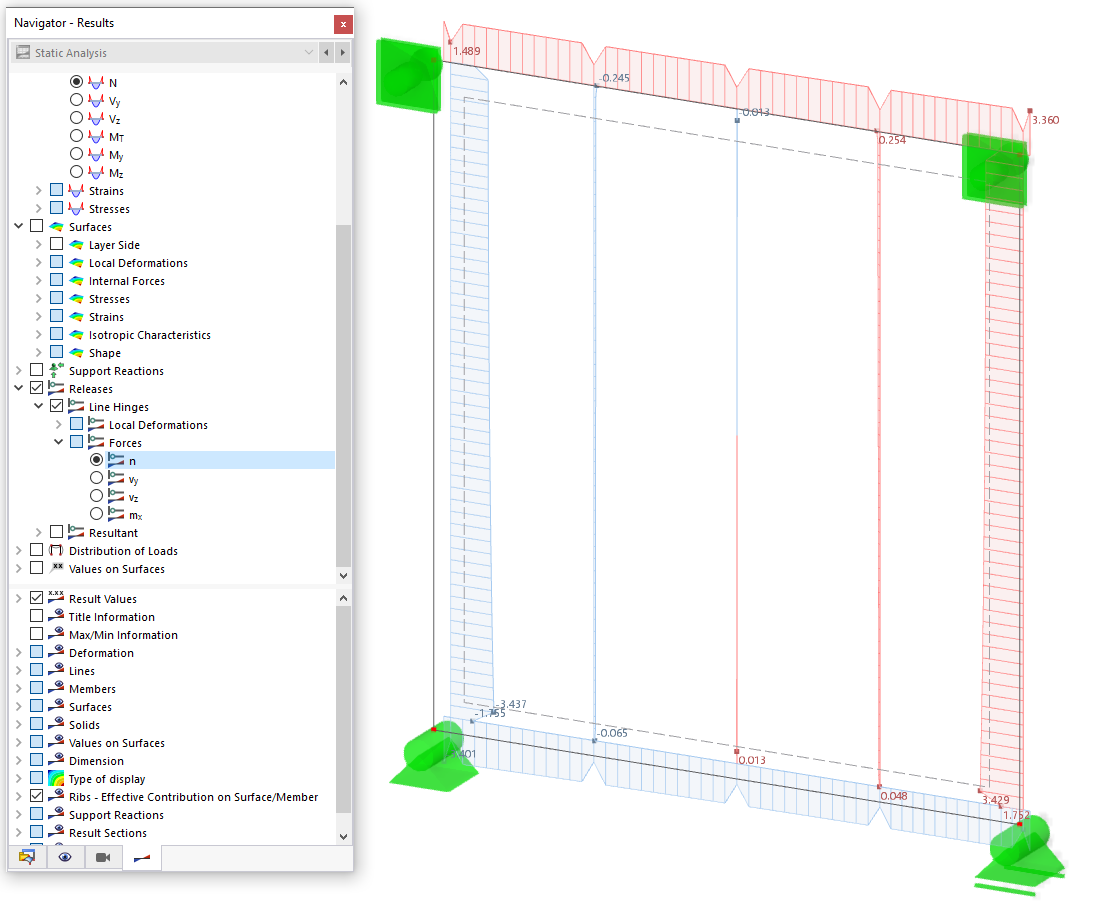
.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)
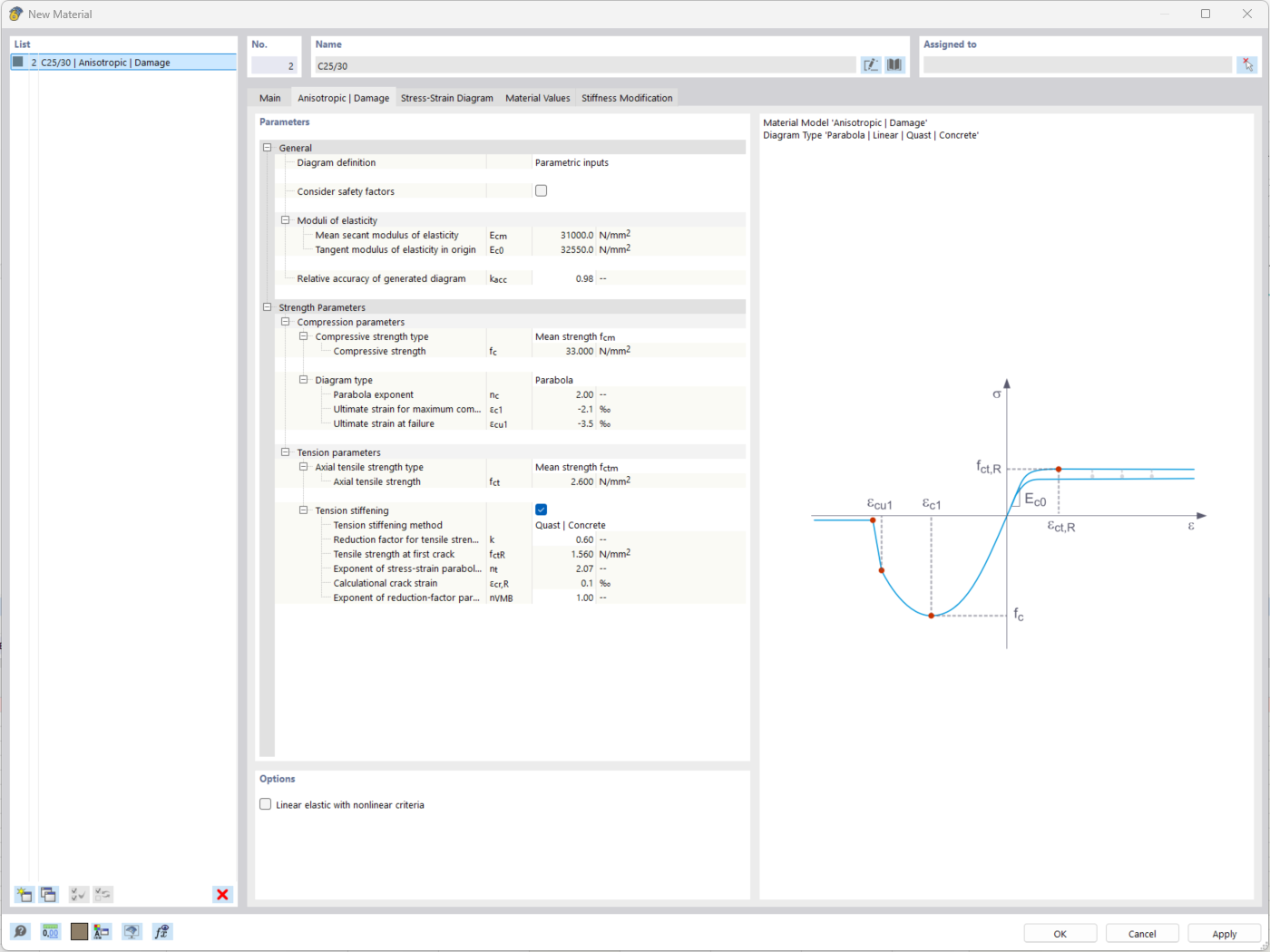
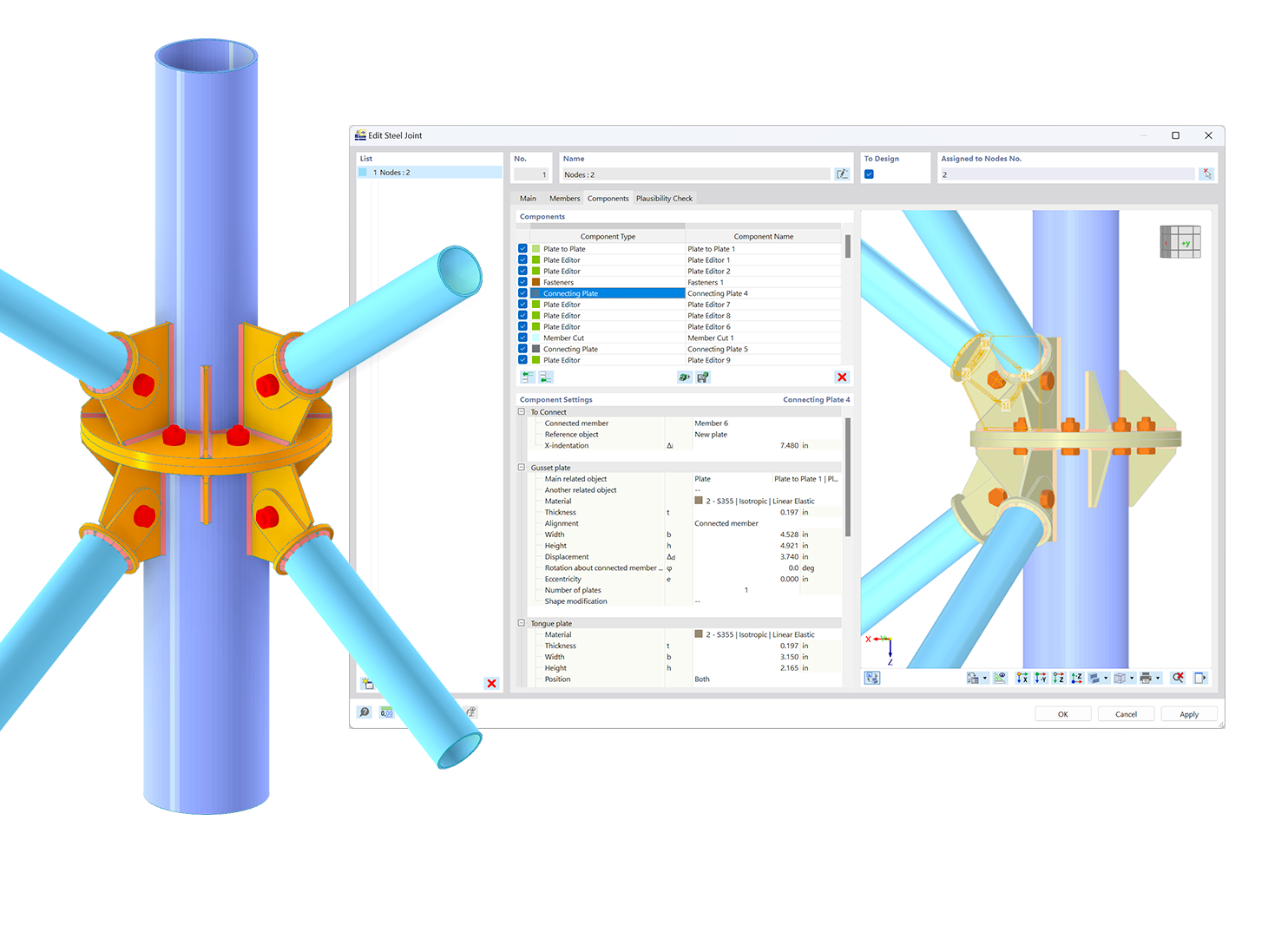
The "Nonlinear Material Behavior" add-on includes the Anistropic | Damage material model for concrete structural components. This material model allows you to consider concrete damage for members, surfaces, and solids.
You can define an individual stress-strain diagram via a table, use the parametric input to generate the stress-strain diagram, or use the predefined parameters from the standards. Furthermore, it is possible to consider the tension stiffening effect.
For the reinforcement, both nonlinear material models "Isotropic | Plastic (Members)" and "Isotropic | Nonlinear Elastic (Members)" are available.
It is possible to consider the long-term effects due to creep and shrinkage using the "Static Analysis | Creep & Shrinkage (Linear)" analysis type that has been recently released. Creep is taken into account by stretching the stress-strain diagram of the concrete using the factor (1+phi), and shrinkage is taken into account as the pre-strain of the concrete. More detailed time step analyses are possible using the "Time-Dependent Analysis (TDA)" add-on.
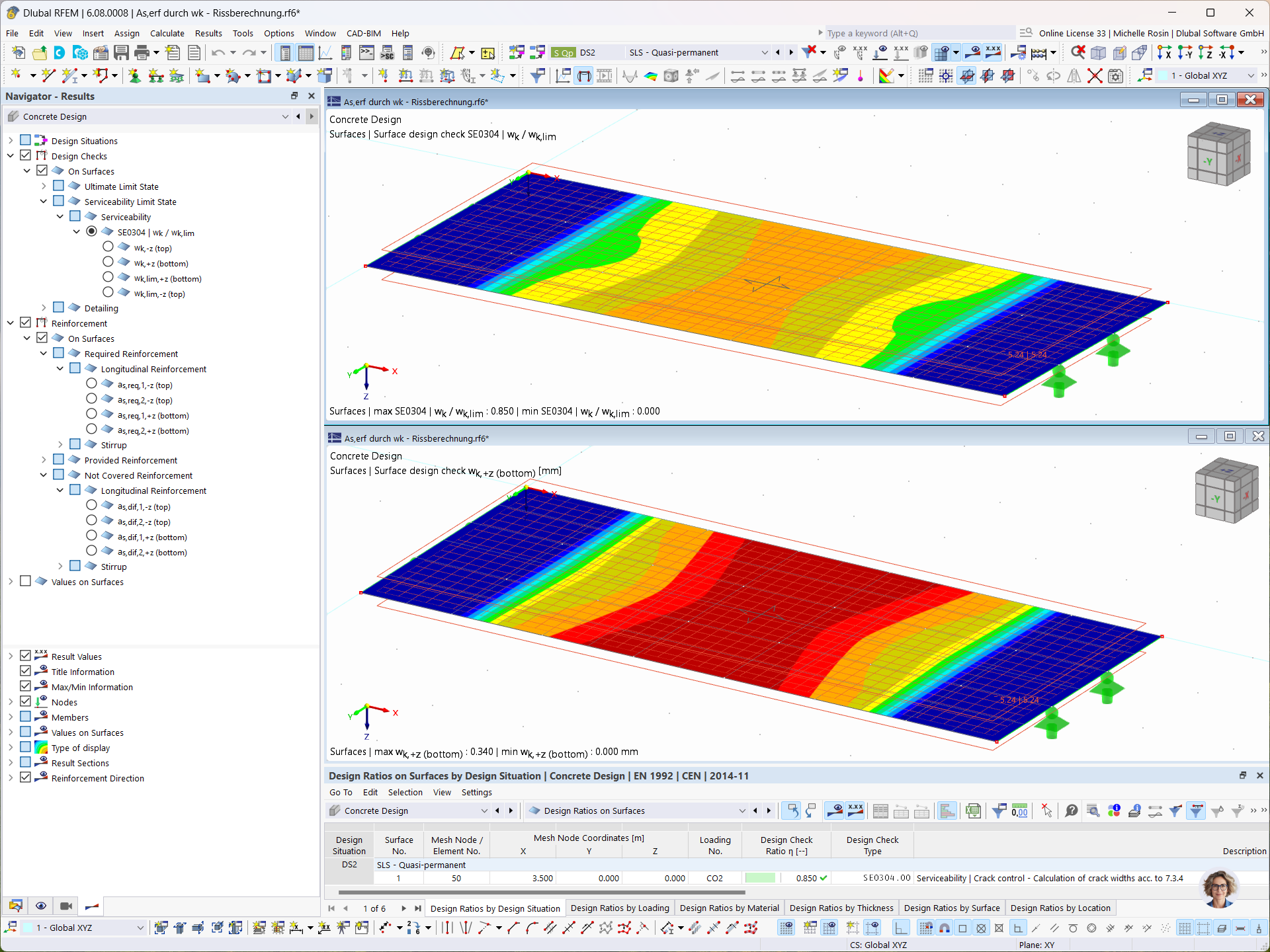
In the Concrete Design add-on, you can determine the required longitudinal reinforcement for the direct crack width analysis (w k).
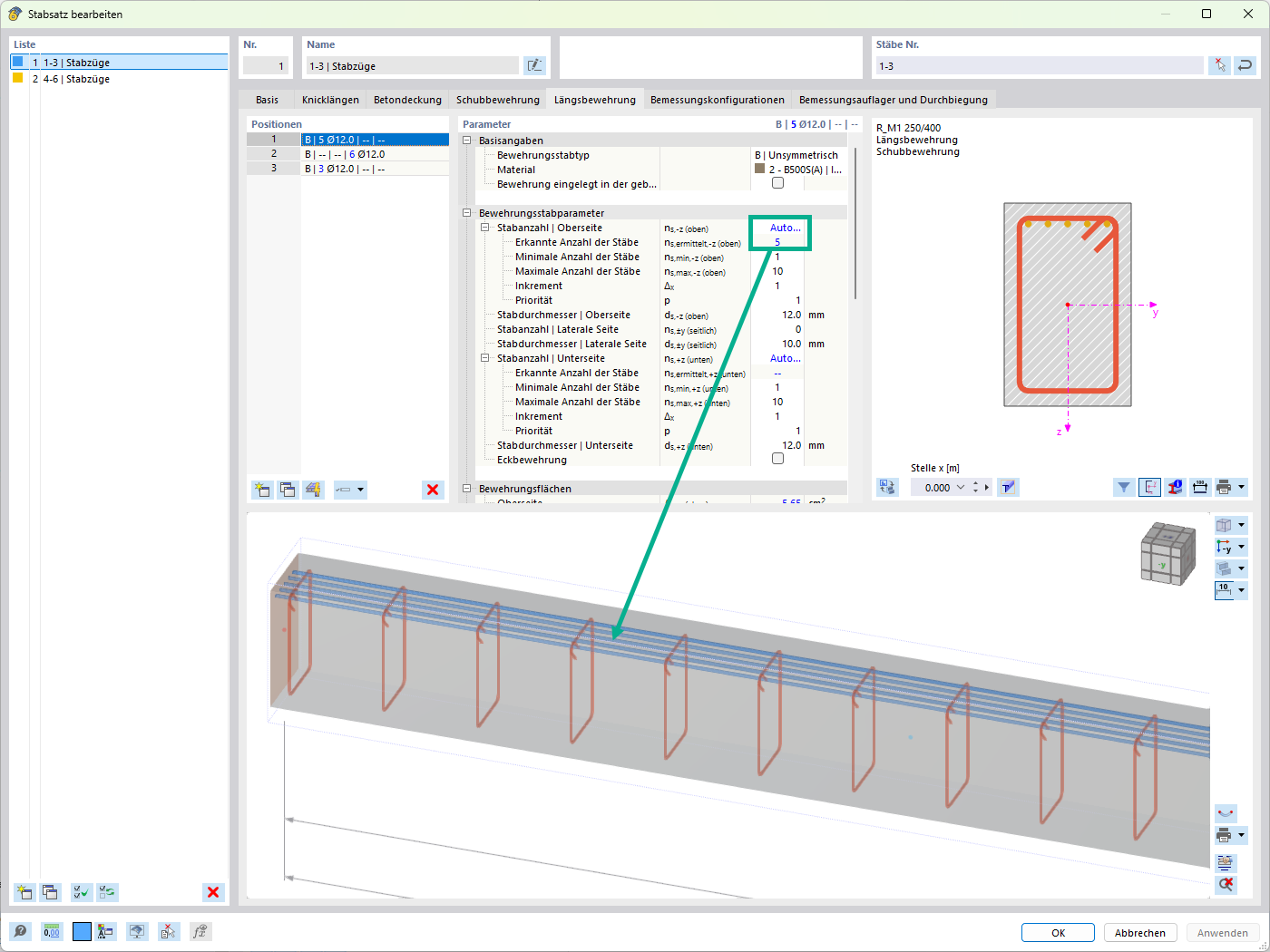
For the design of reinforced concrete members, there is the option to automatically determine the number or diameter of rebars.
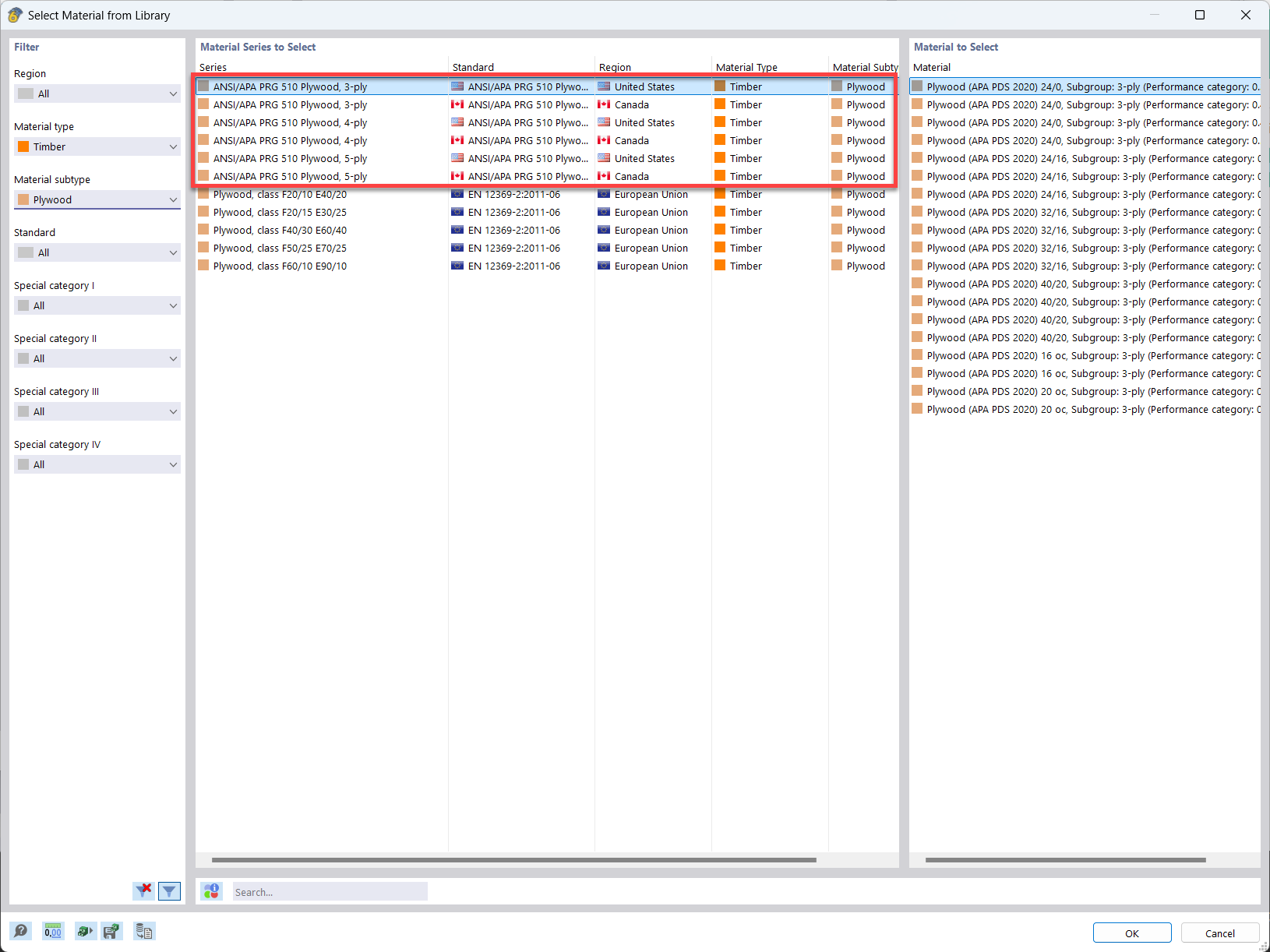
In the material library of RFEM, you can find plywood materials according to the US and Canadian standards ANSI/APA PRG 510 Plywood (USA/CAN).
Why is the effective depth different with the effective depth used in shear checks?
How can I check the determination of the required reinforcement?
Do I need to add a line hinge/line release for the CLT wall-to-floor connection in the Building Model add-on?
































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)


-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)



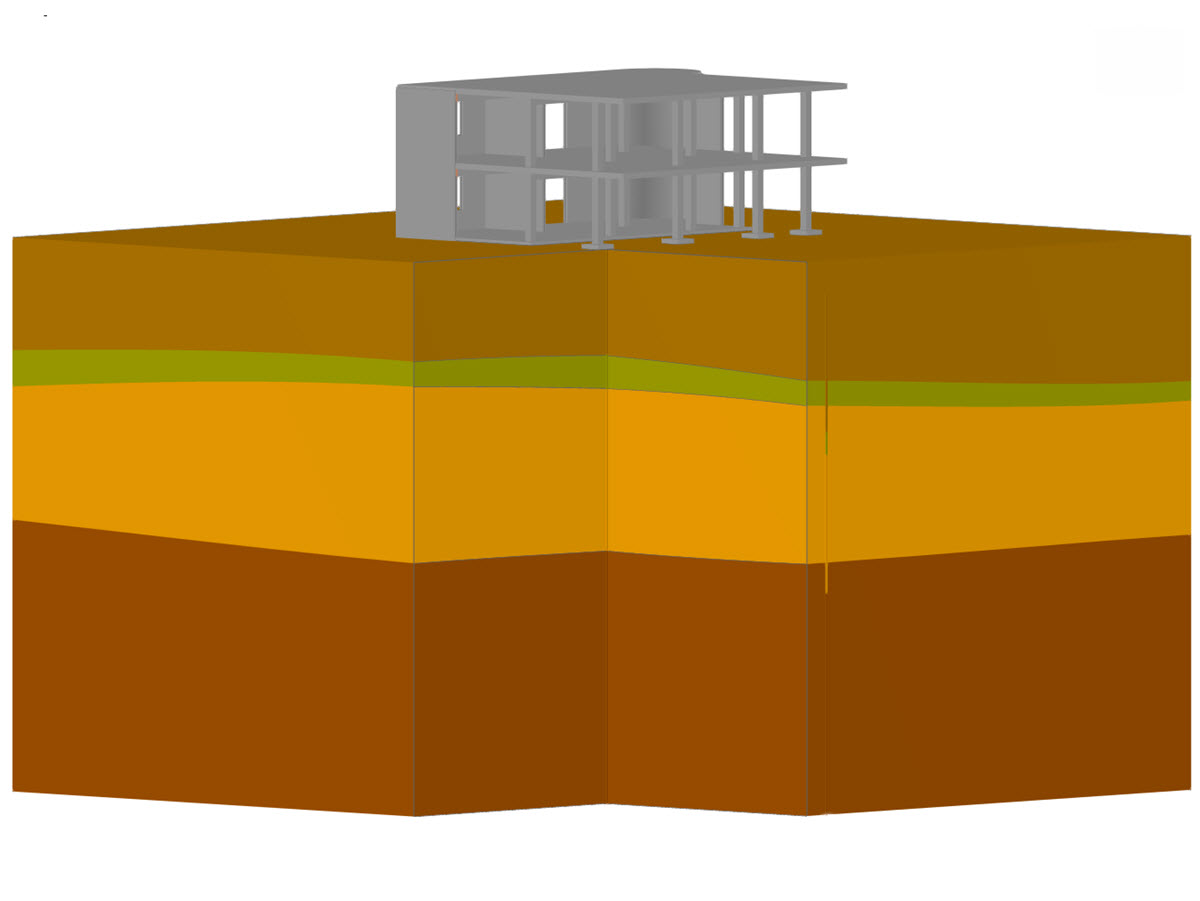

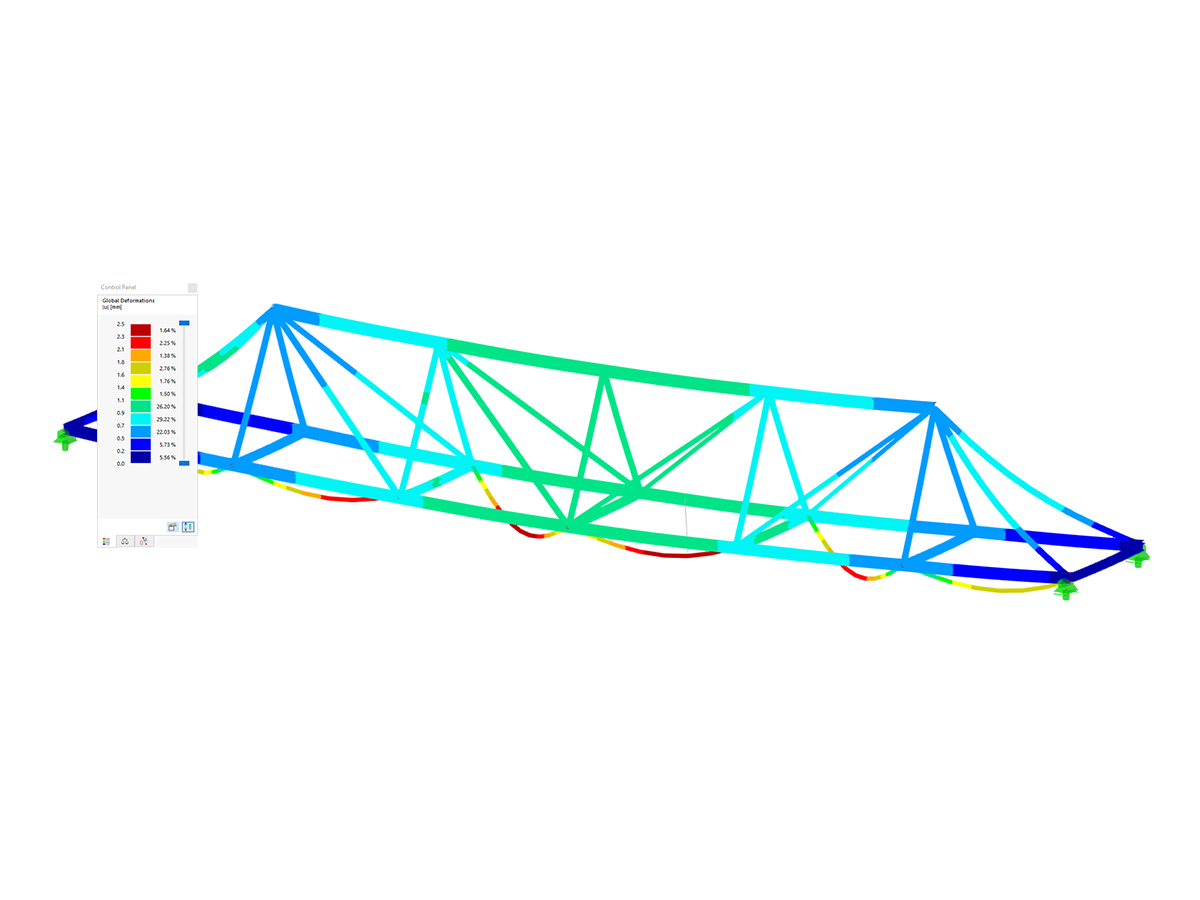


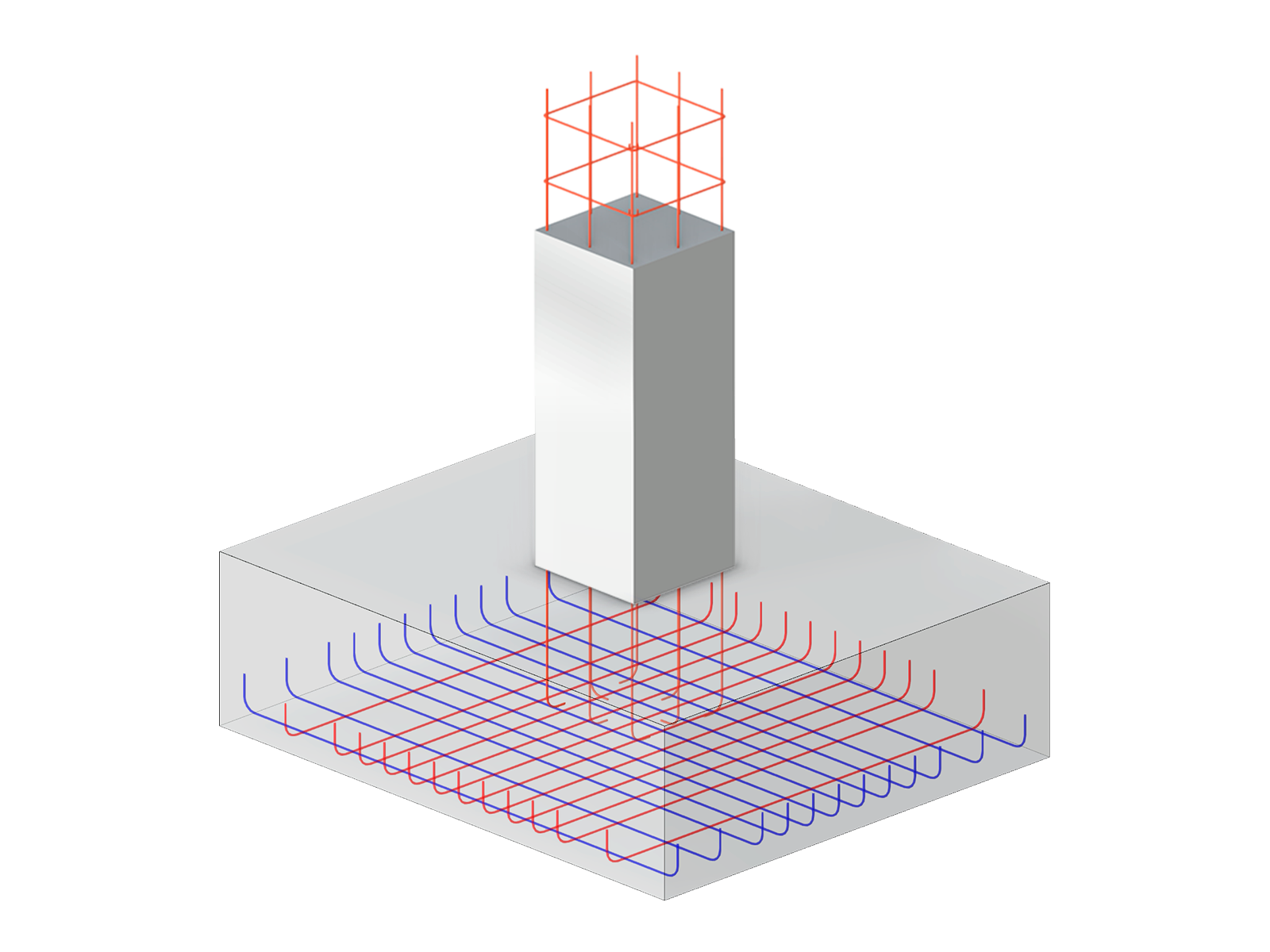
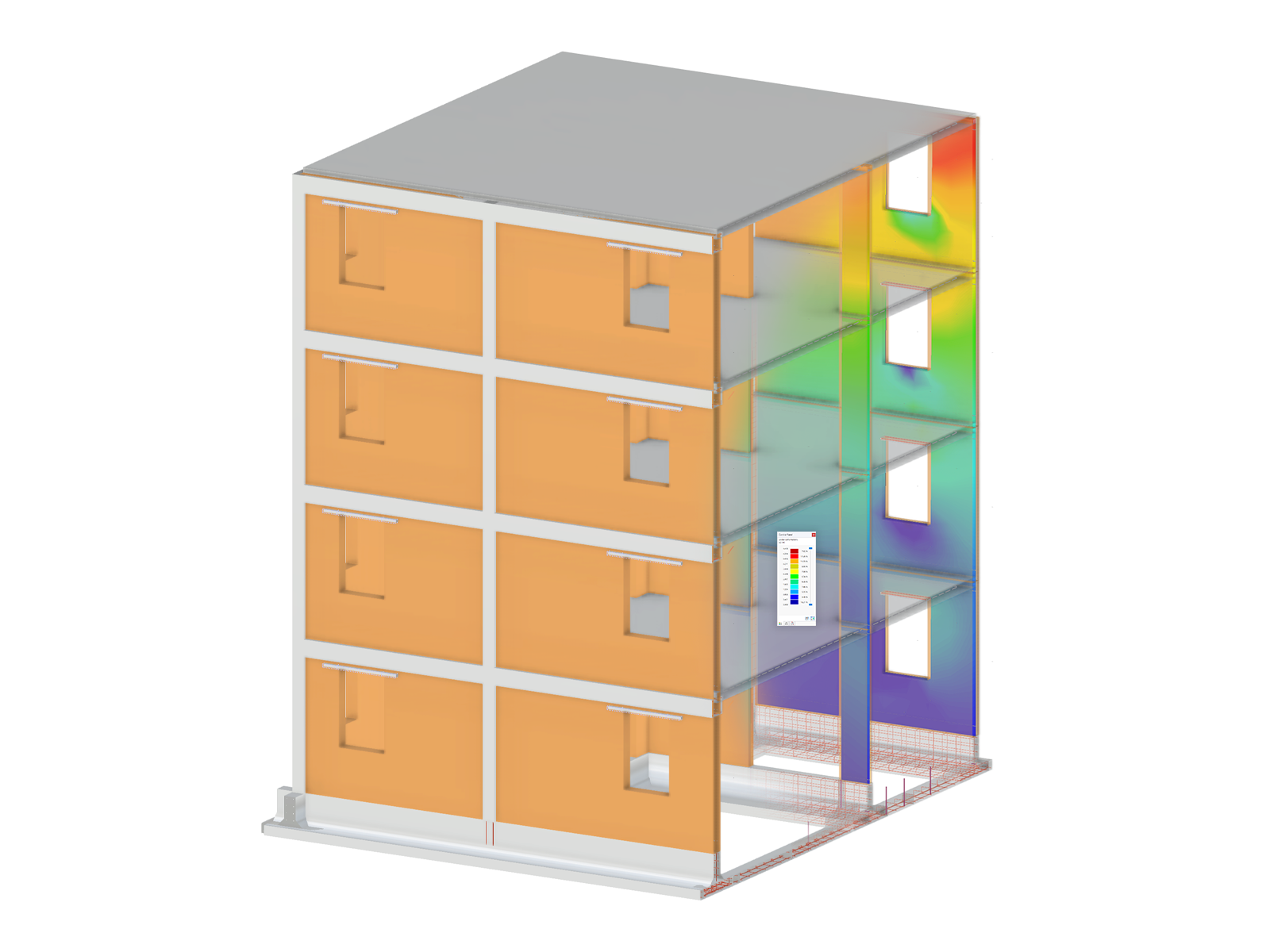
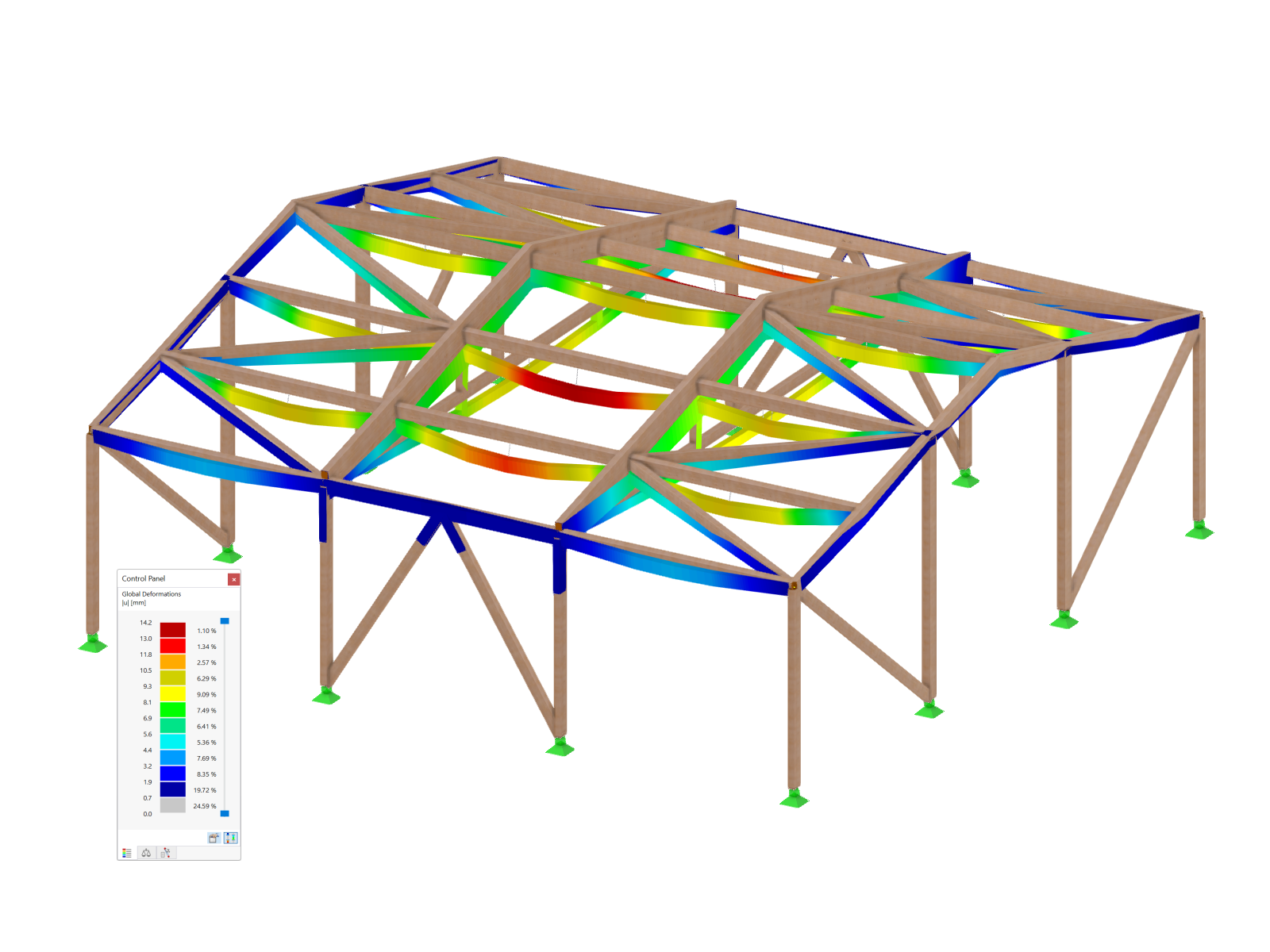
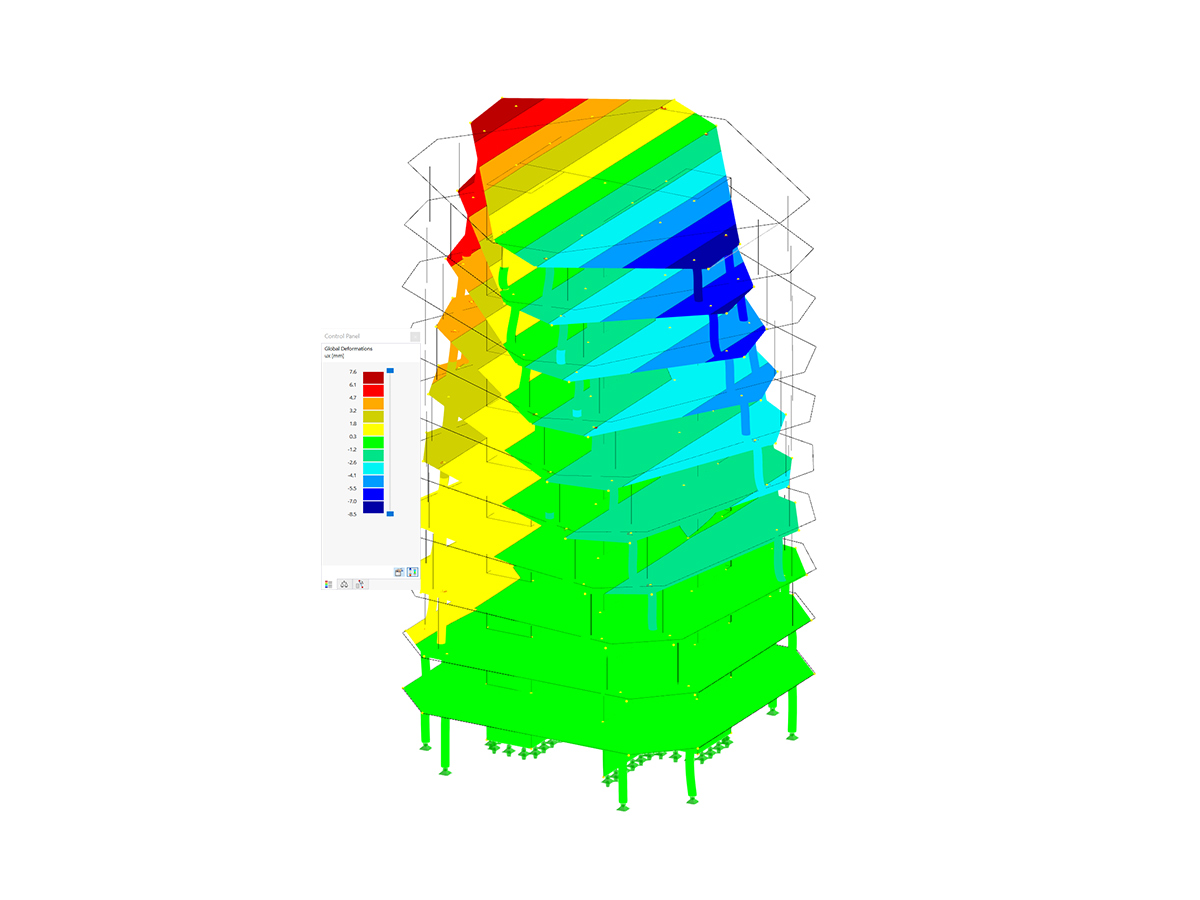
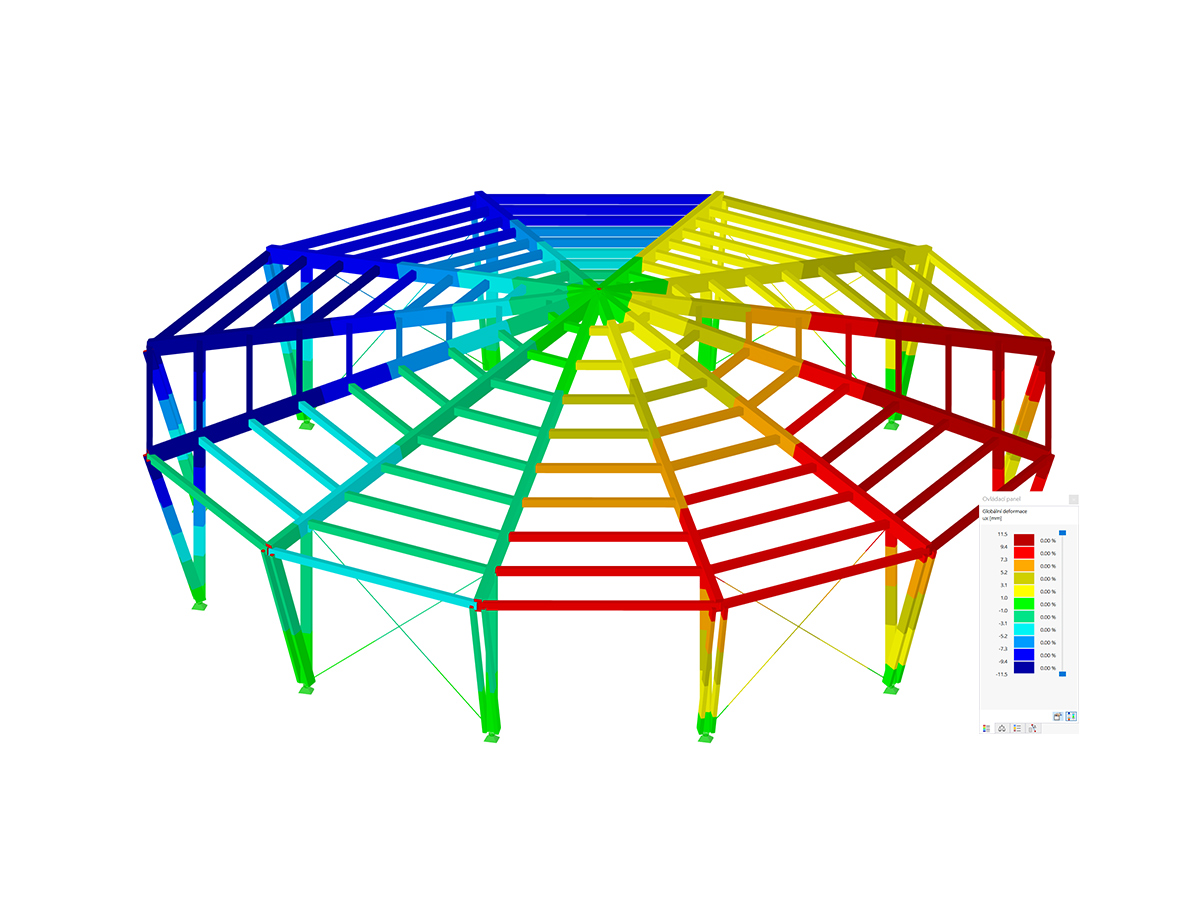







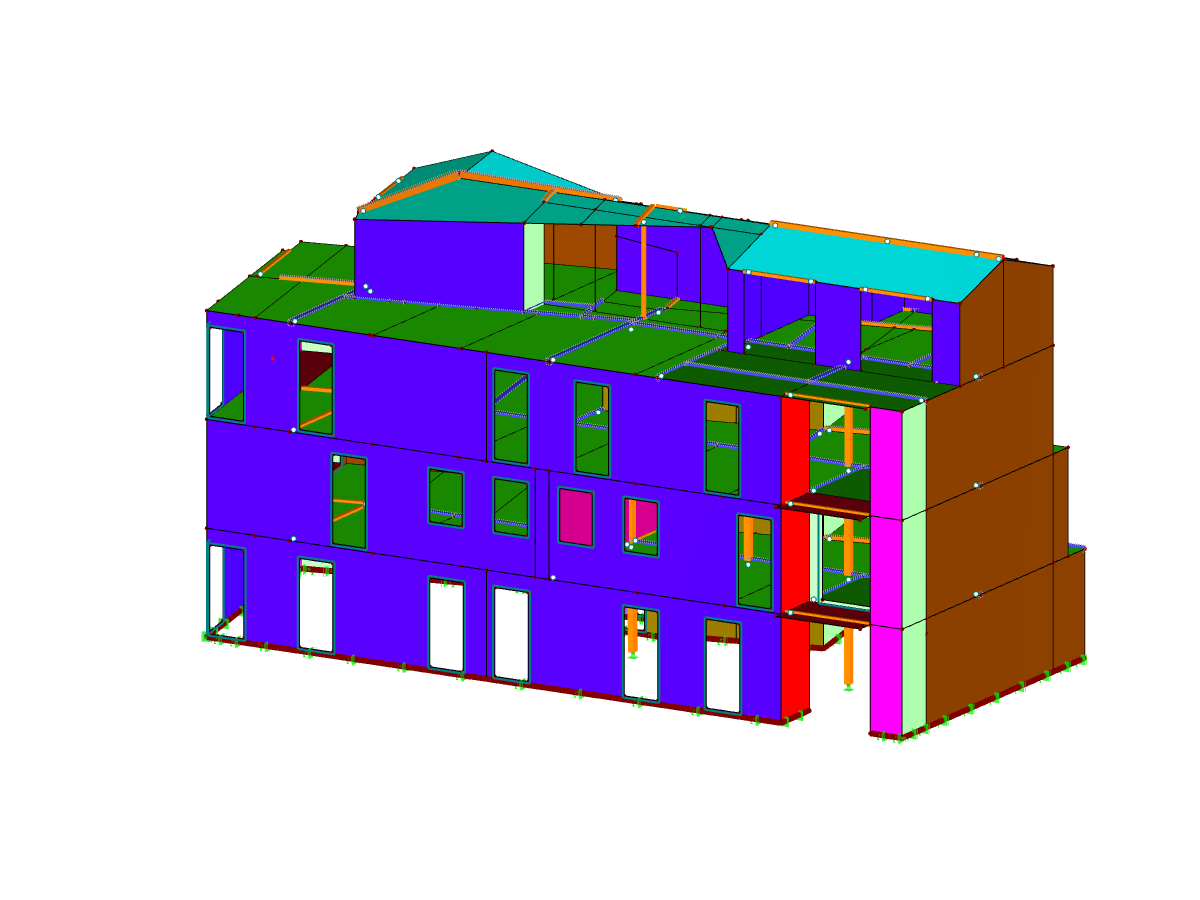












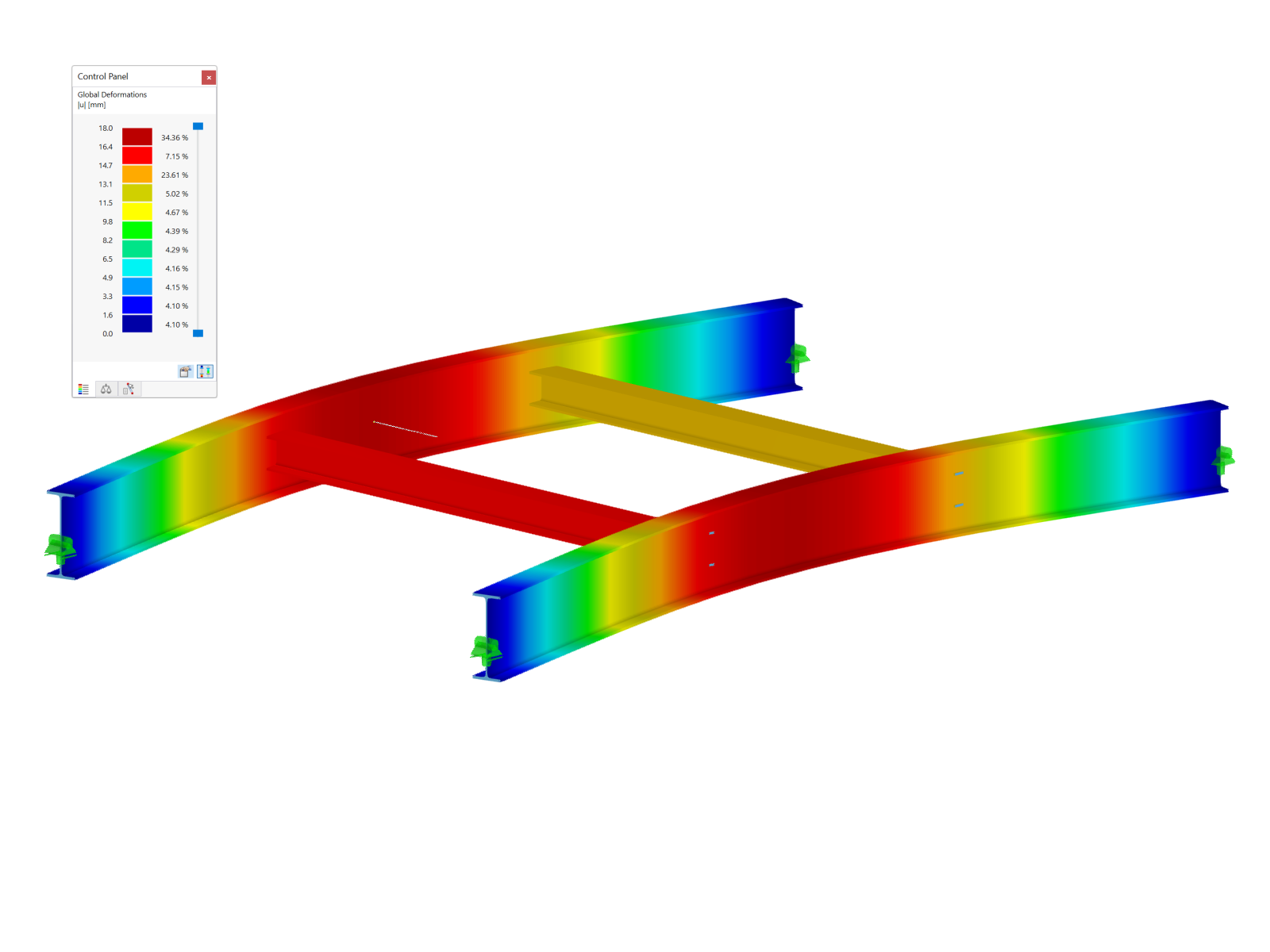
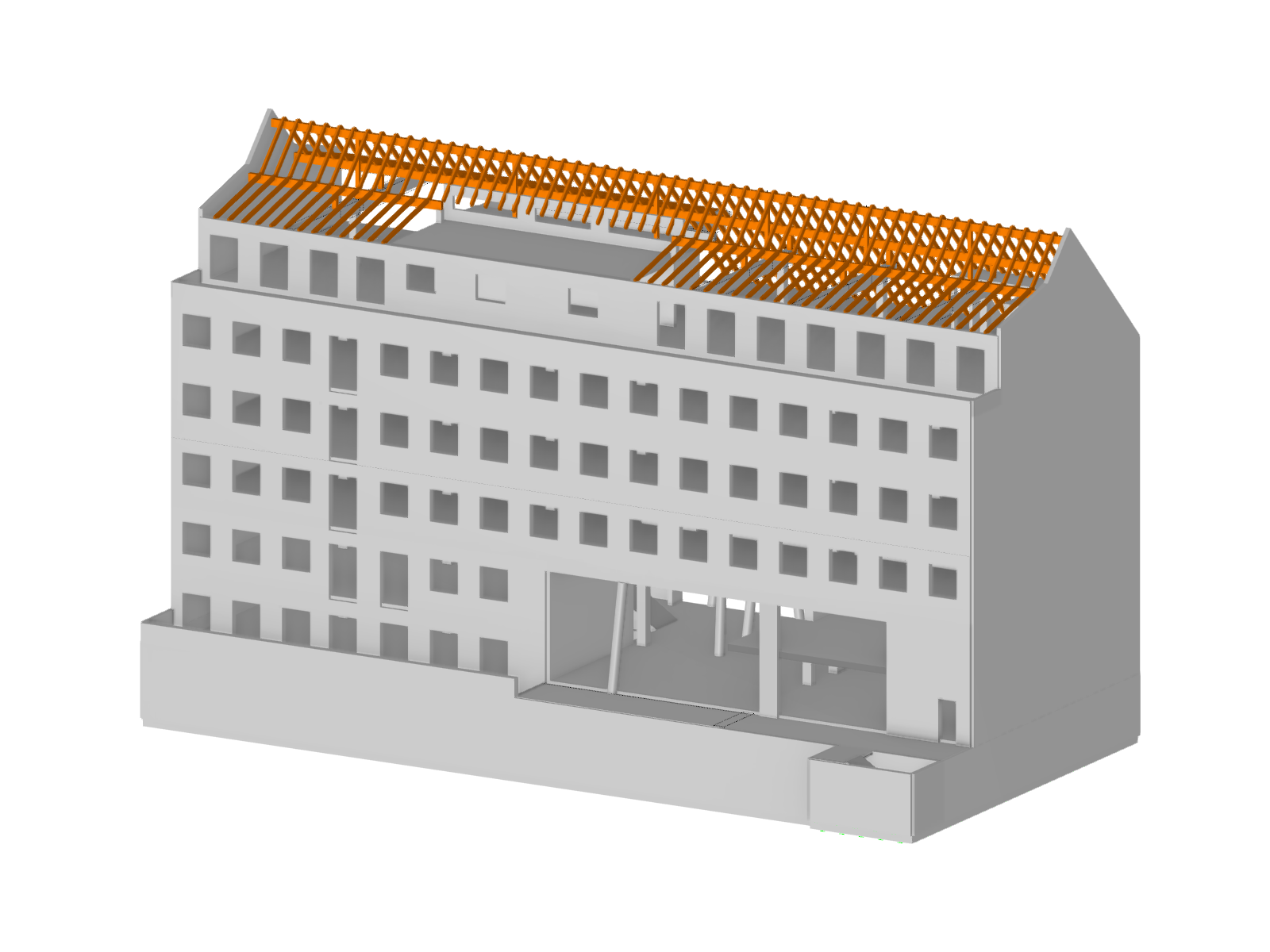
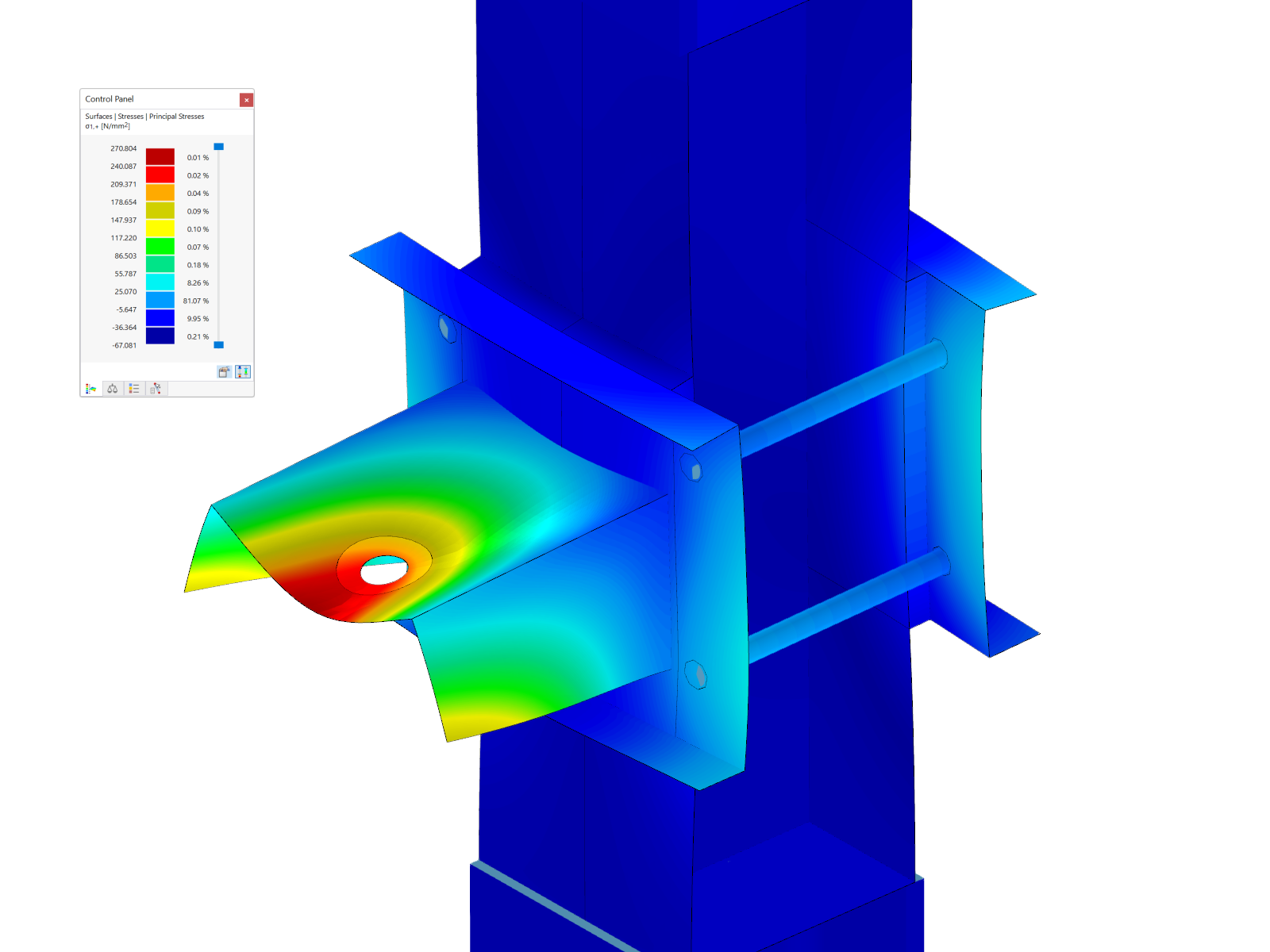

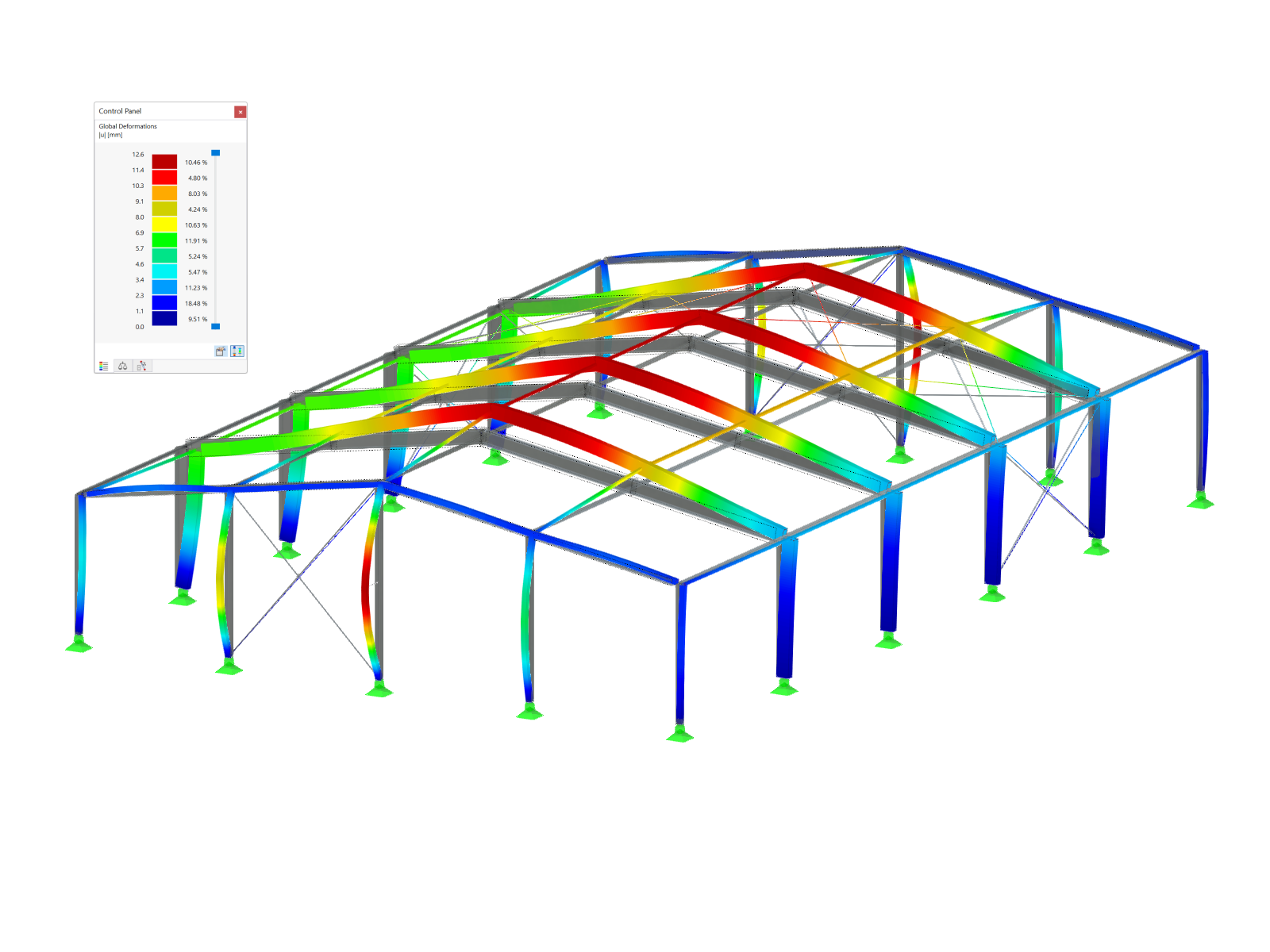
.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)