When working with the parameterized models and blocks, the optimization based on minimum cost is also possible. In this chapter, you will learn how to carry out such an optimization.
The model shown in the image Truss is used as an example. The following values are to be optimized:
- Number of cells
- Truss height
- Cross-sections
In the list of global parameters, the number of cells and the truss height are set as global parameters.
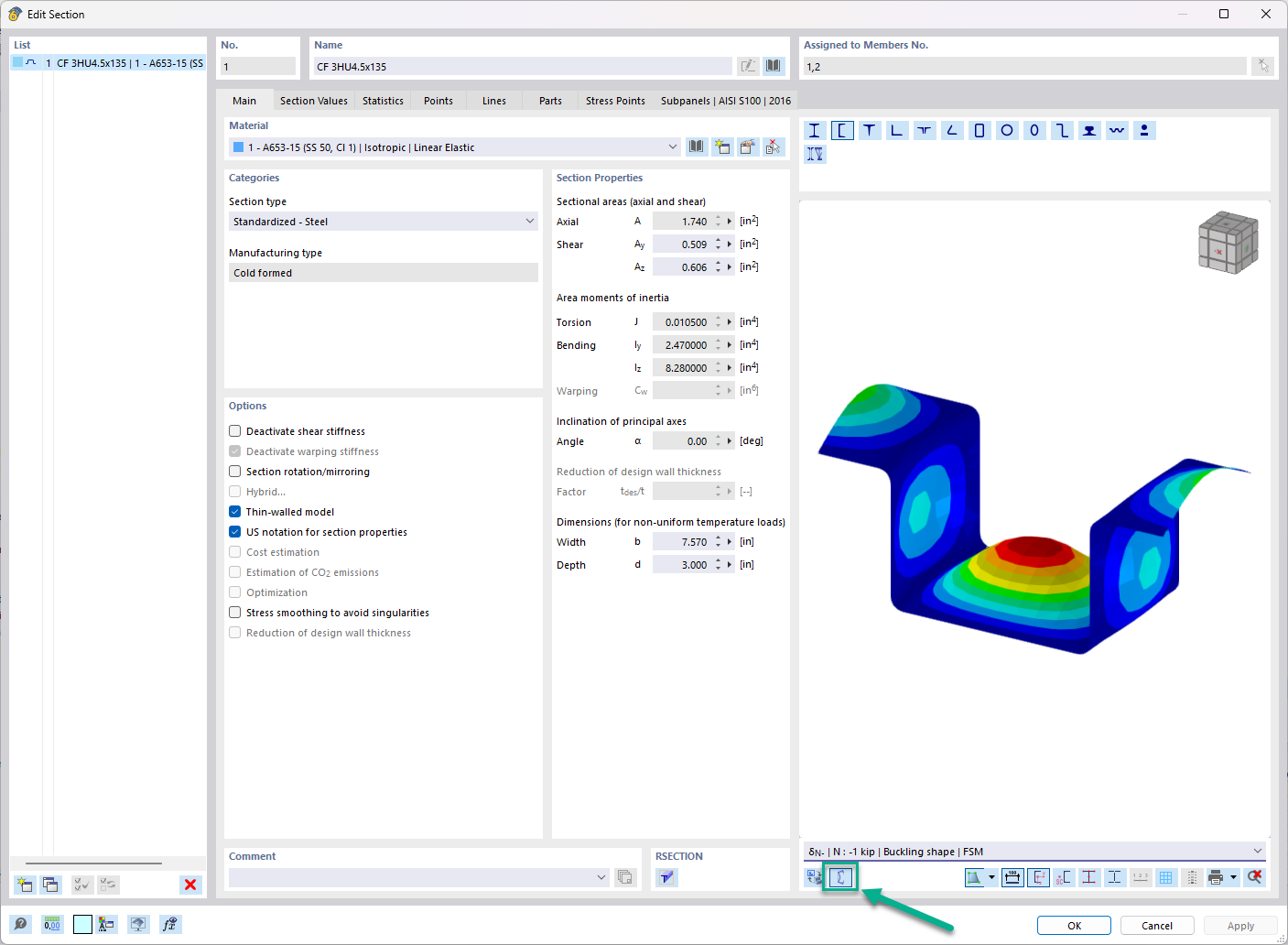
To optimize the cross-sections as well, open the "Edit Section" dialog box and select the "Optimization" check box in the "Options" section.
Since the optimization is cost-based, it is necessary to estimate the cost before performing the optimization. This is done according to the procedure described in Chapter Cost Estimation.
You can access the optimization settings in the program using the "Calculate" menu. As shown in the image Optimization Settings, it is necessary to optimize the number of cells, the truss height, and the cross-sections. Since the optimization should determine the most cost-efficient variant, the "Min. cost" is selected. In our example, the particle swarm optimization (PSO) is used and the number of random mutations is set to 40% of the total number.
After optimizing the cross-sections, the number of cells, and the truss height, the program displays a list of the model mutations (variants). You will also find the decisive optimization results there, including the associated value assignment of the optimization parameters. This list is sorted in descending order: At the top, it shows the assumed best solution; that is, the solution closest to the optimization criterion. Thus, you can see the costs obtained by changing the individual parameters, and you can determine the optimal values for the respective parameters.









.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)















.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)












_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)



