The steel launching nose is designed for a specific construction site, taking into account the possible subsequent use on similar structures. The structure has been designed in such a way that dimensional variations are possible in the future (for example, shortening the launching nose by omitting the middle component). The launching nose is adapted for attachment to the concrete section using prestressing bars.
Structural Engineering Solution of Launching Nose
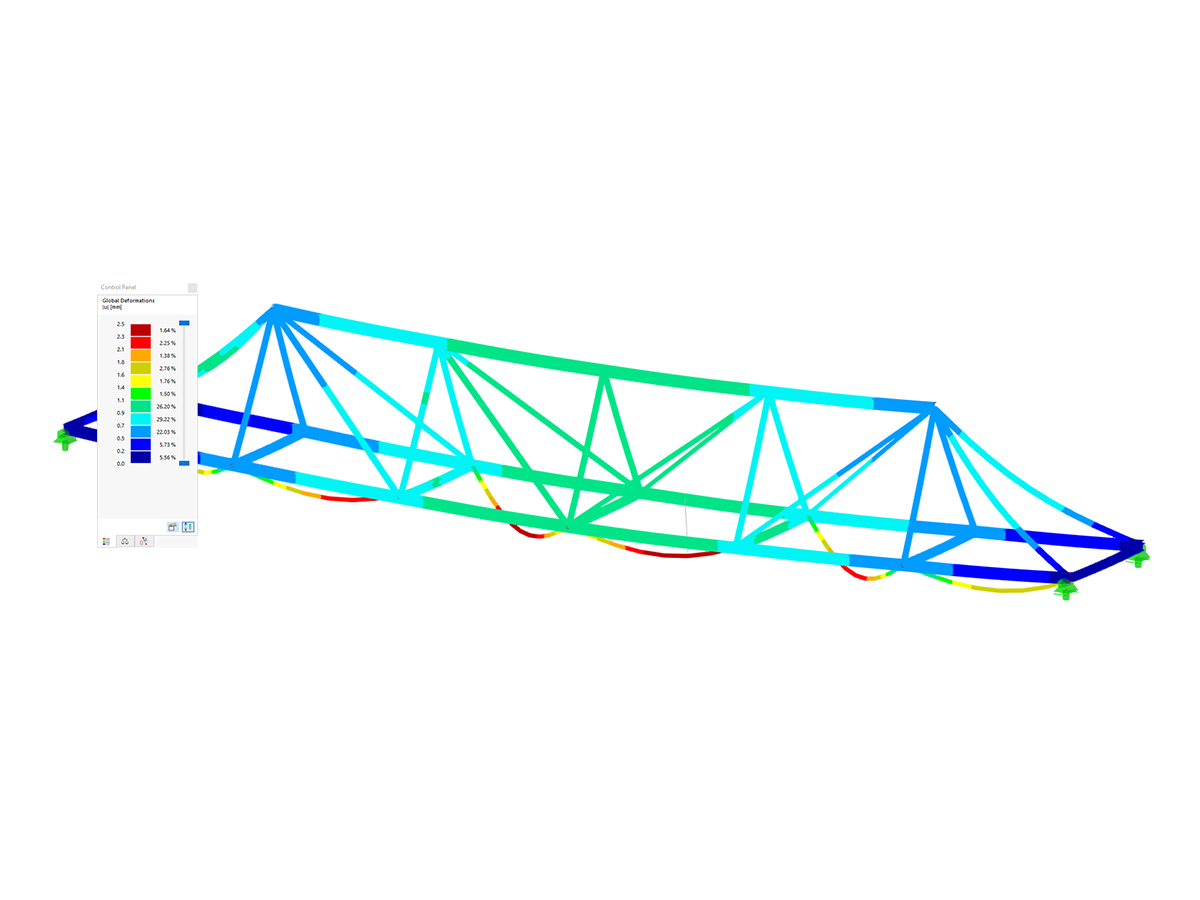
The bridge superstructure spans the I/35 road and the Mikuleč brook, with a span of up to 62 m (203.4 ft). In order to ensure an efficient construction process, it was necessary to design a launching nose that would allow for a safe and controlled movement of the concrete structure. The launching nose was designed as a demountable element, the length of which can be adapted to the specific construction conditions and reused on further projects.
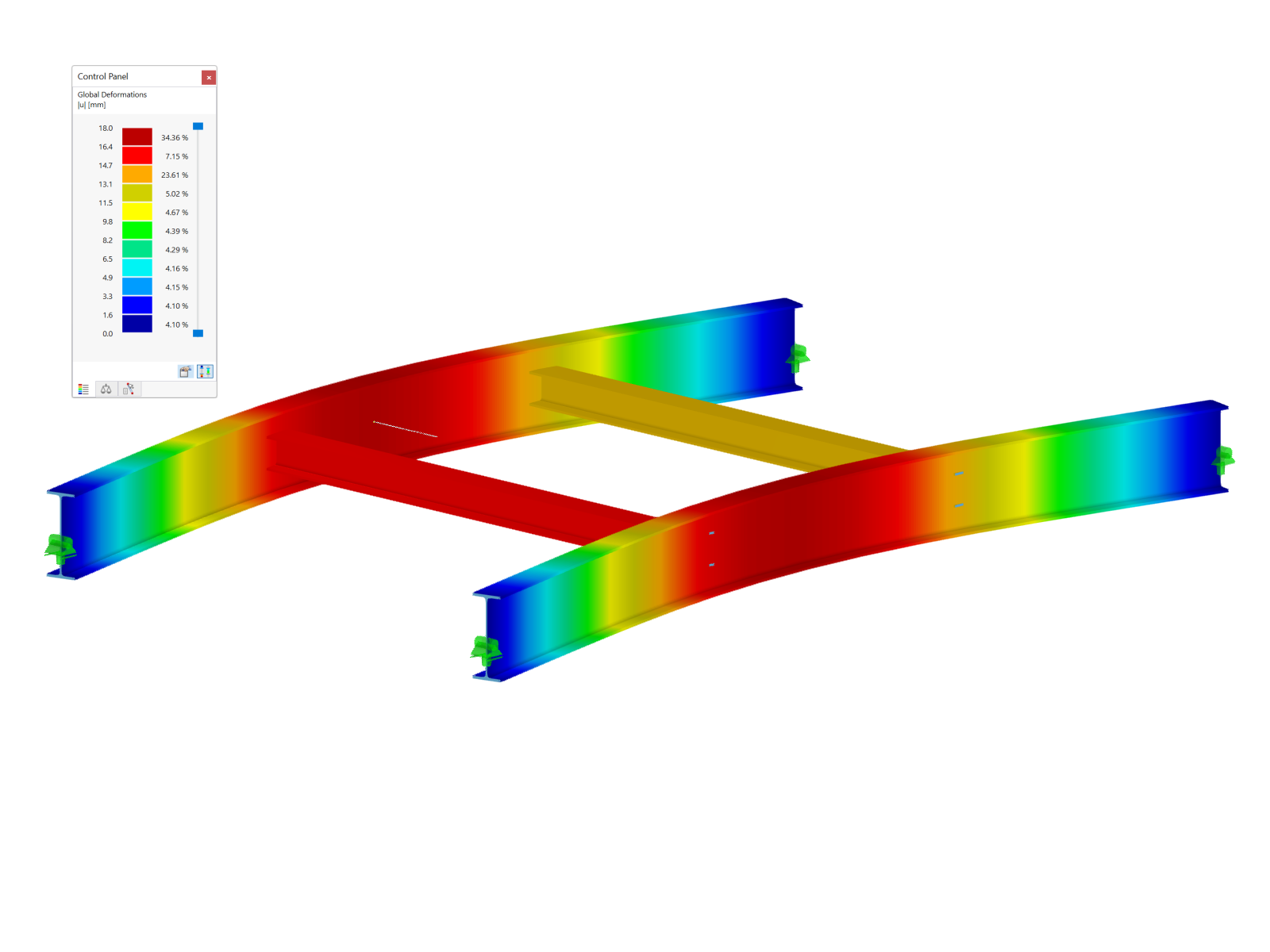
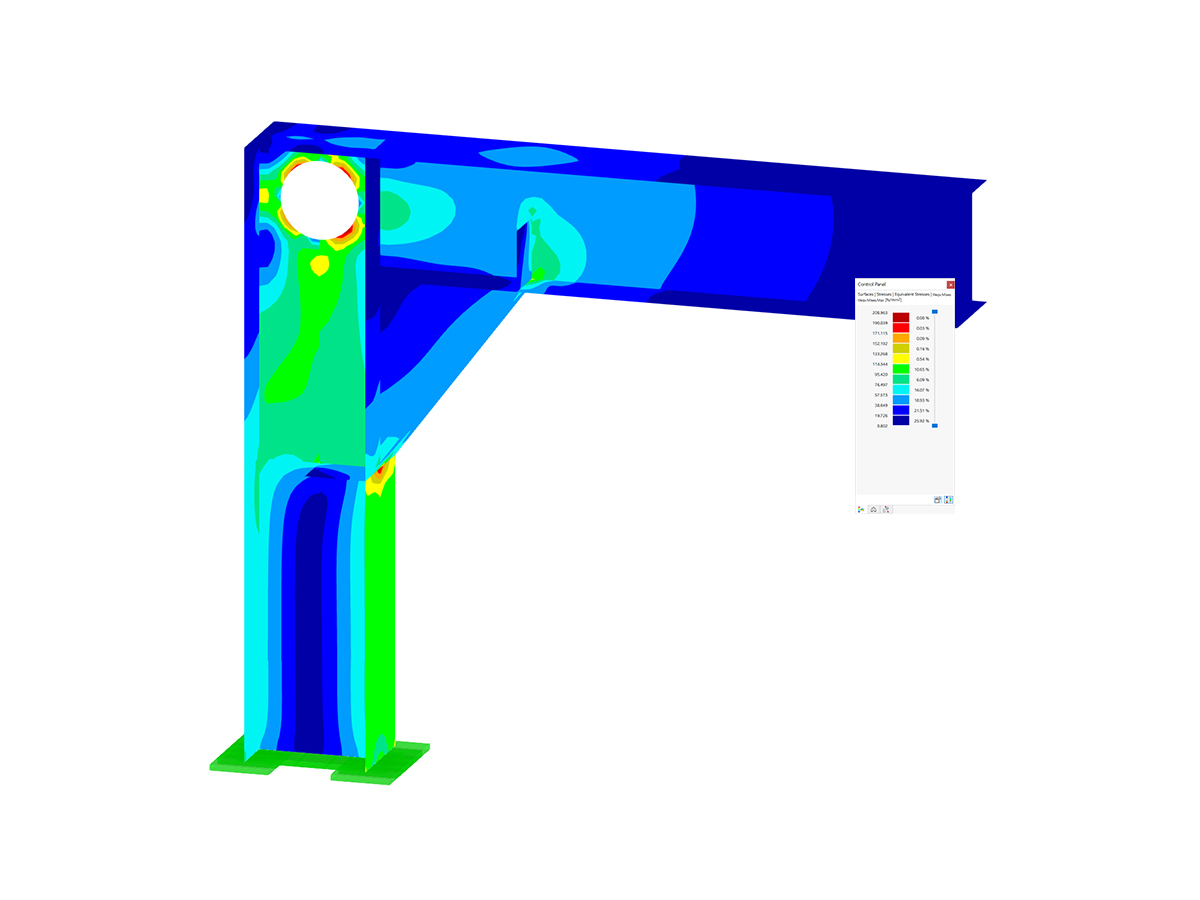
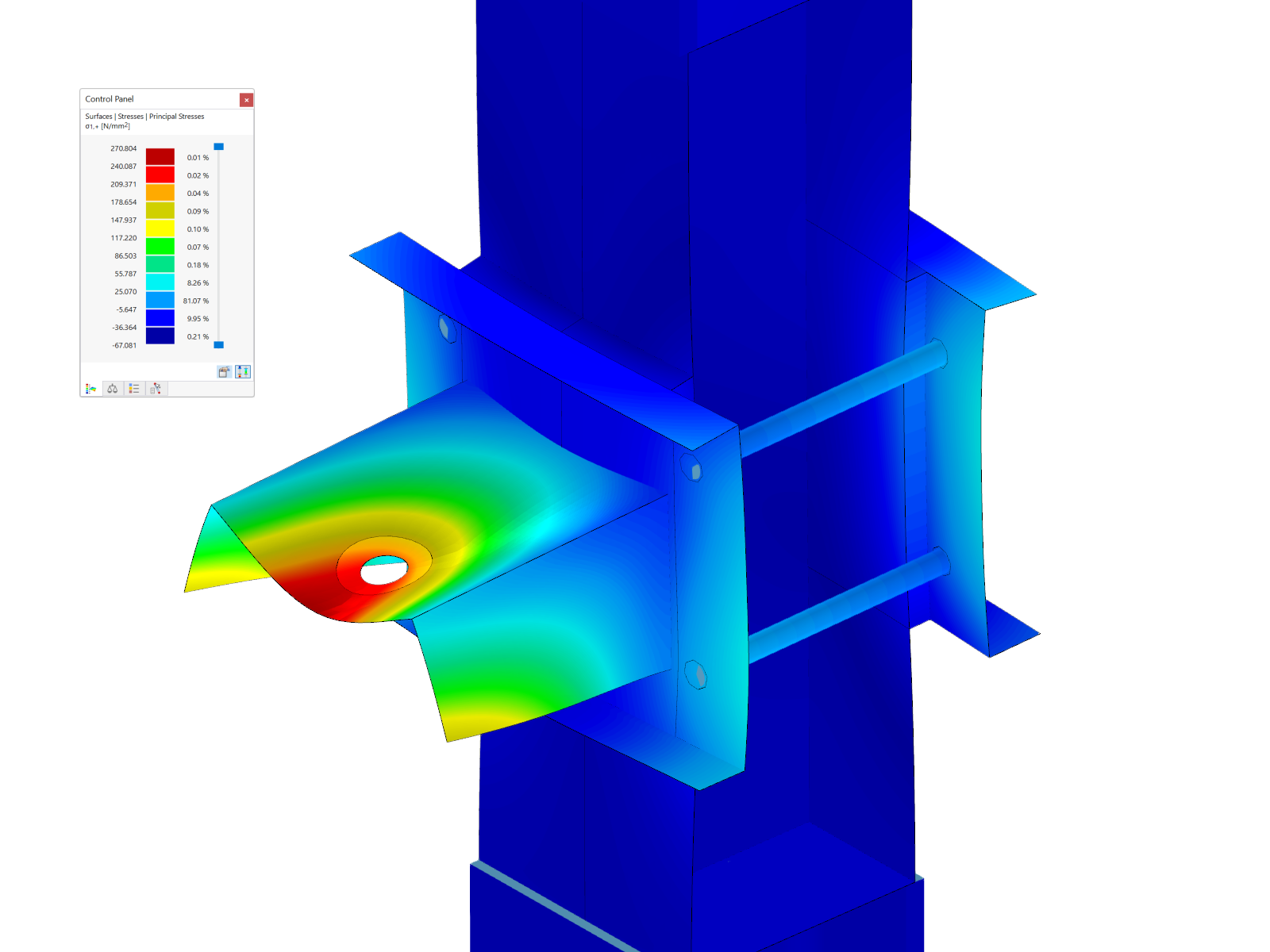
The supporting structure of the launching nose consists of two main girders connected by spatial bracing, which ensures sufficient rigidity of the entire system. The nose anchoring to the concrete box structure was solved by using prestressing bars, the dimensioning of which had to take into account not only structural loads, but also dynamic effects arising during the launch. The maximum load per anchor bar was 1567 kN, which required a careful analysis of the material behavior and the interaction between the steel and concrete elements.
Computational Models and Their Importance
For the structural analysis, several analysis models were created, all in the structural analysis program RFEM by Dlubal Software.
For the basic analysis of the structure, a spatial member model was created. All parts of the structure (the launching nose girder, transverse and longitudinal bracing) consist of members. The segmented cross-section of the launching nose was created in the stand-alone program SHAPE-THIN 8 and takes into account all longitudinal stiffeners and the variable height of the girder. The stiffeners are rigidly connected to the girder. Both girders are supported in points (restrained) at the start of the launching nose, at the connection to the box section of the bridge. The total internal forces of the girder are obtained from the model.
For a more detailed analysis of the structure, a spatial wall-beam model was created. The beam wall was modeled using a wall, all other parts of the structure (upper and lower flanges, transverse and longitudinal stiffeners of the beam, transverse and longitudinal stuffeners) were modeled using members.
The stiffeners are rigidly connected to the girder. Both girders are supported in points (restrained) at the start of the launching nose, at the connection to the box section of the bridge. All stability problems were solved on the model and more precise nonlinear calculations were performed.
Key Conclusions and Project Benefits
A detailed numerical analysis allowed for the optimization of the launching nose design and for the structure to be able to safely transfer all the loads when launching the superstructure. The stability analysis showed that the initial imperfections in the upper flange and beam walls can significantly affect the overall stability of the structure, which led to an optimization of the shape and dimensioning of the individual elements. Geometrically nonlinear calculations provided a more accurate view of the nose's behavior when launching it, and enabled the identification of critical points with the highest risk of local deformations.
Using advanced computational models, it was possible to design a structural solution that not only meets the requirements for safety and reliability, but also contributes to the efficiency and economy of the structure. This analysis also shows the important role that modern computational software plays in the design of complex engineering structures and their optimization for realistic building conditions.
| Location | Opatovec Svitavy district Czech Republic |
| Structural Engineering Solution | Ing. Petr Nečesal, Ing. David Marván, PIS PECHAL, s.r.o. |
| Construction | MI Roads a.s.| Metrostav Group |



















.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)