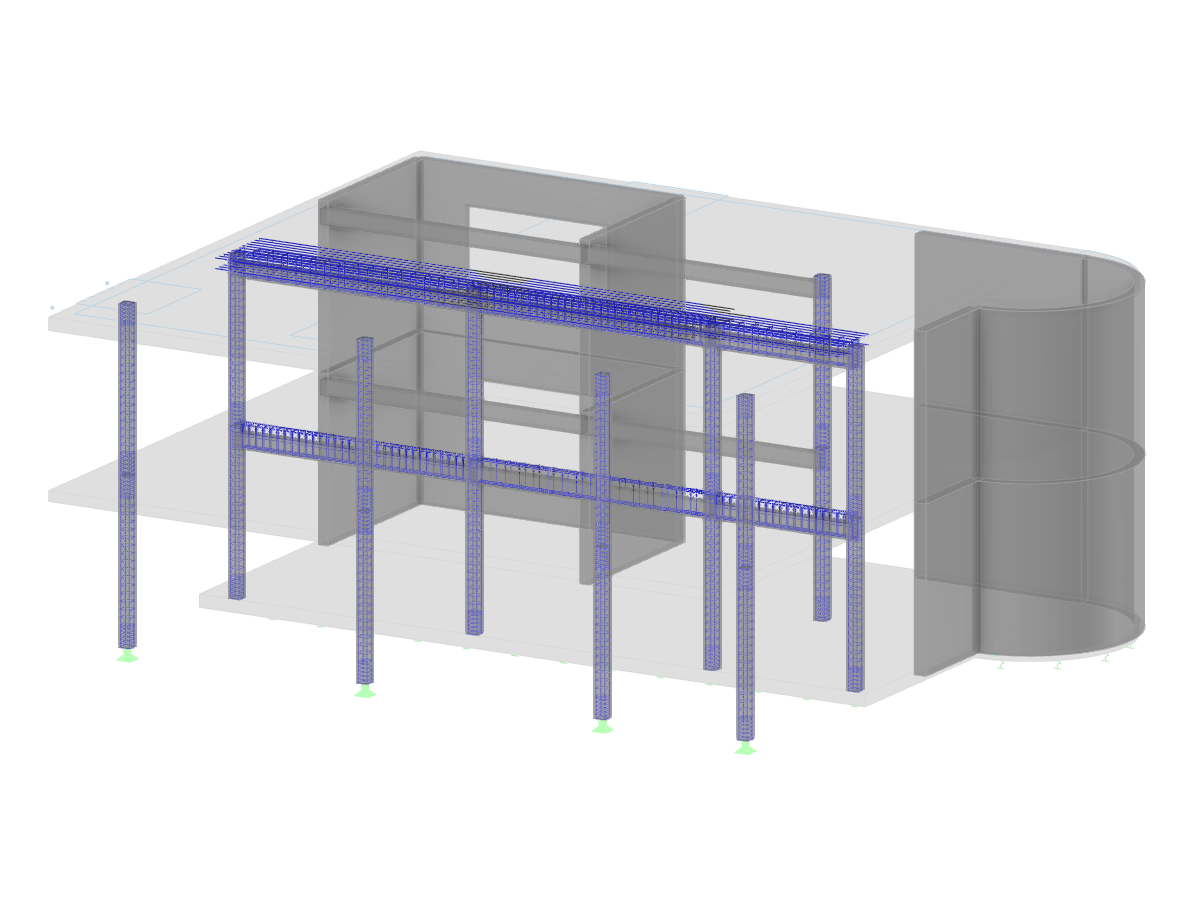
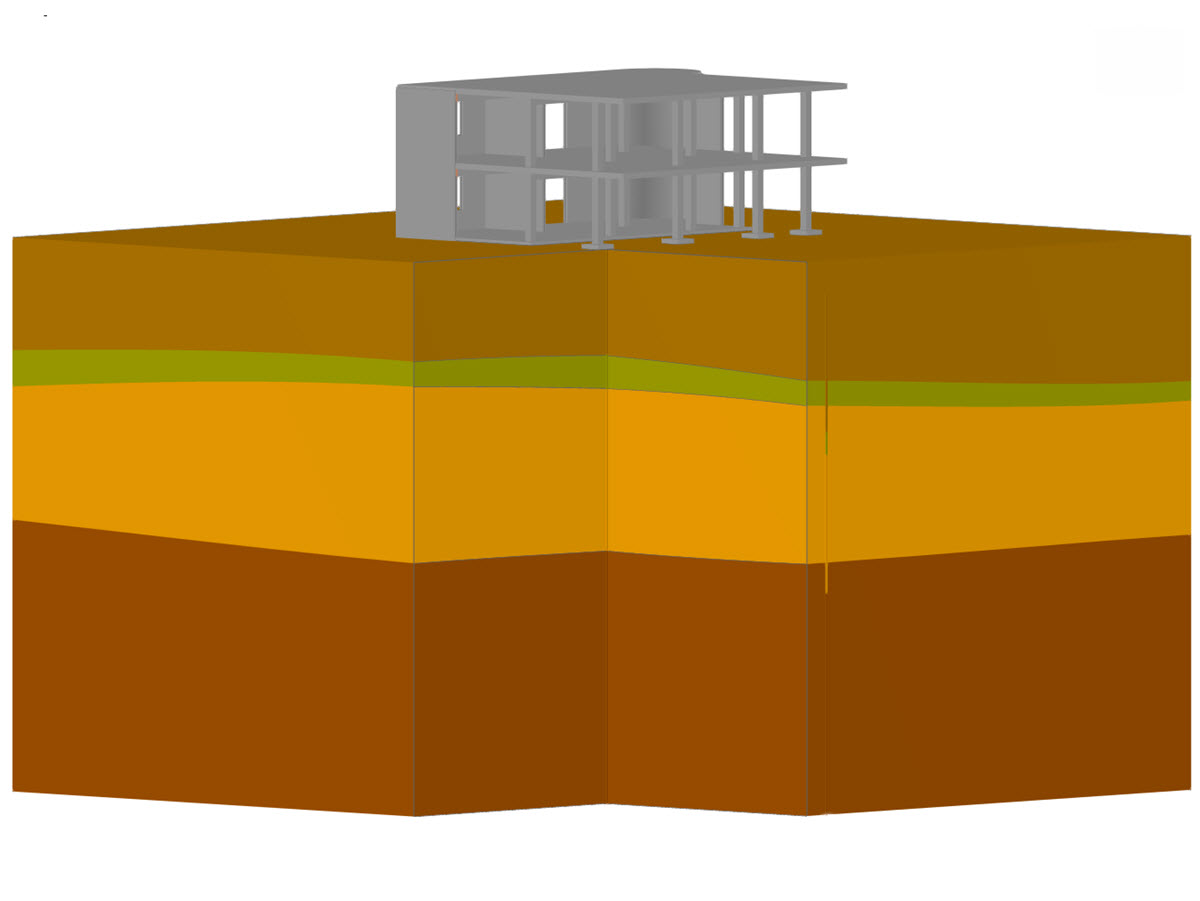
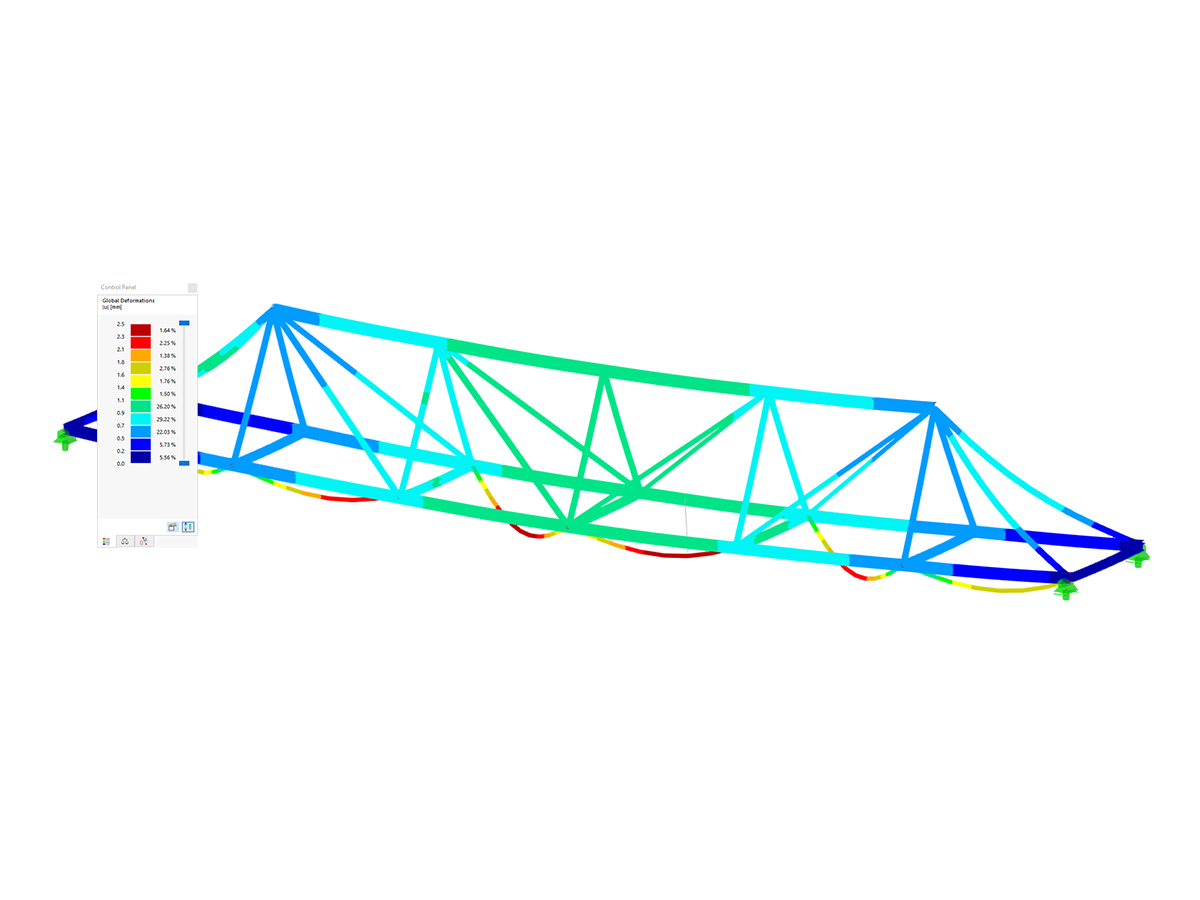
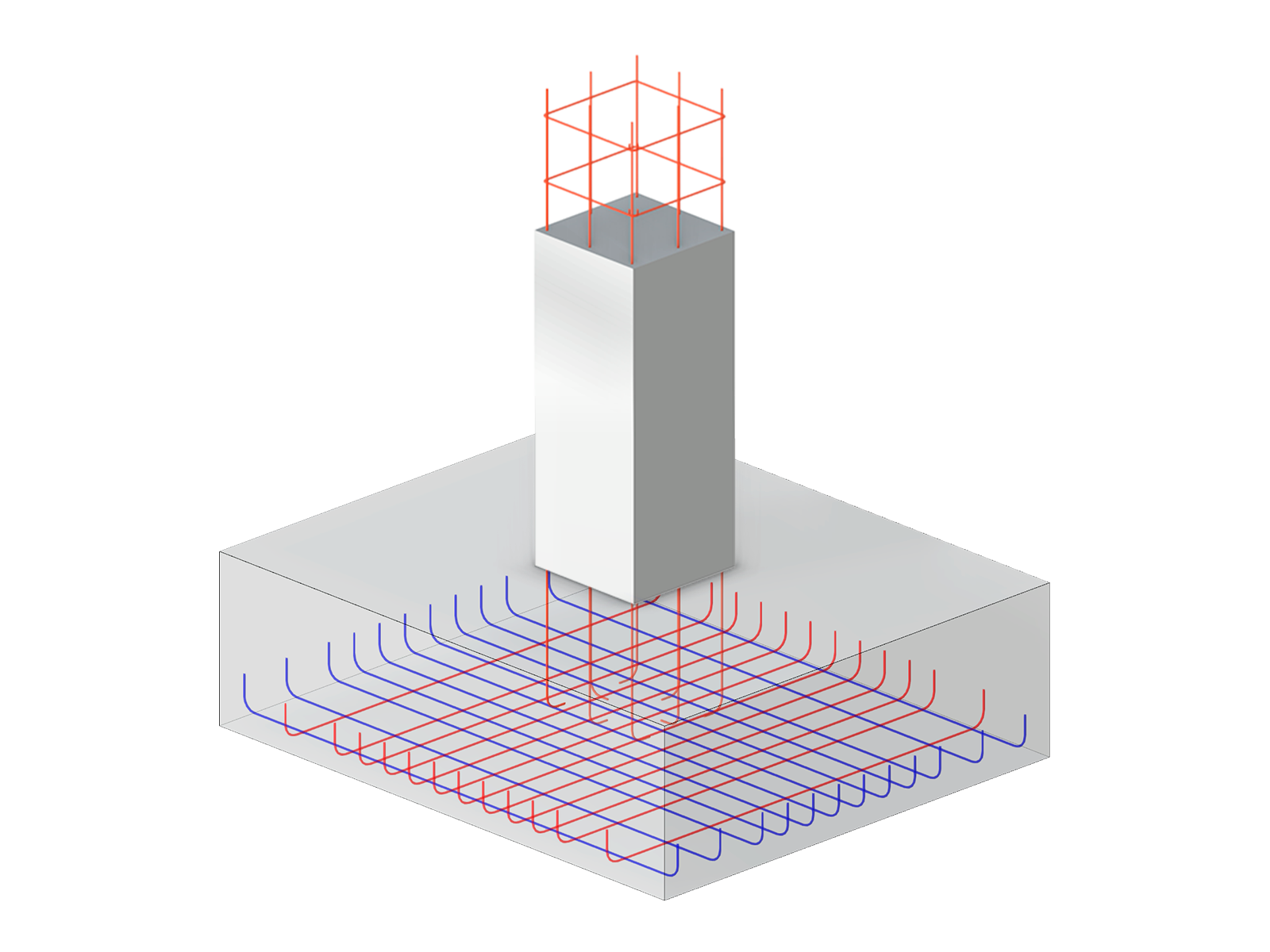
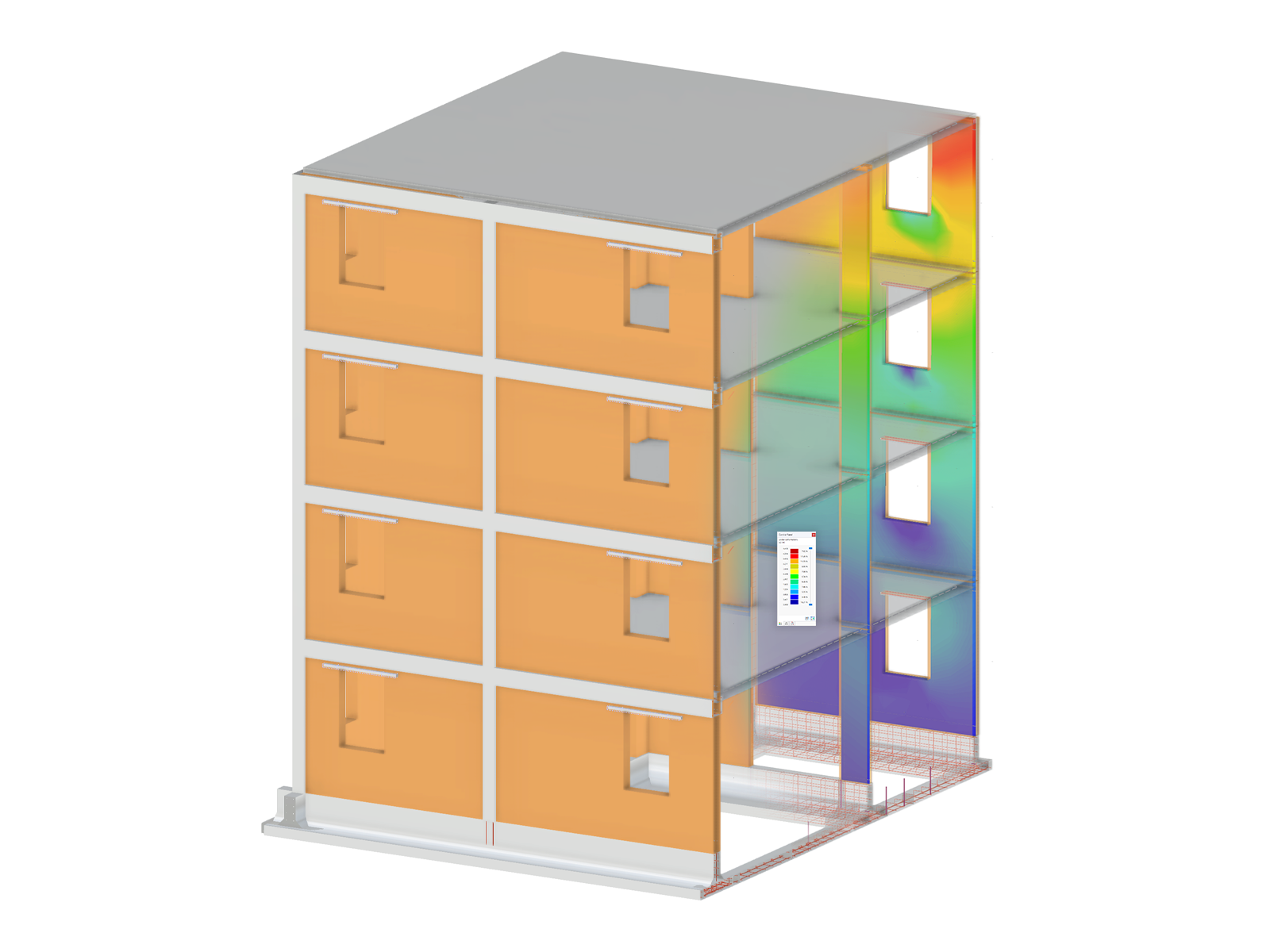
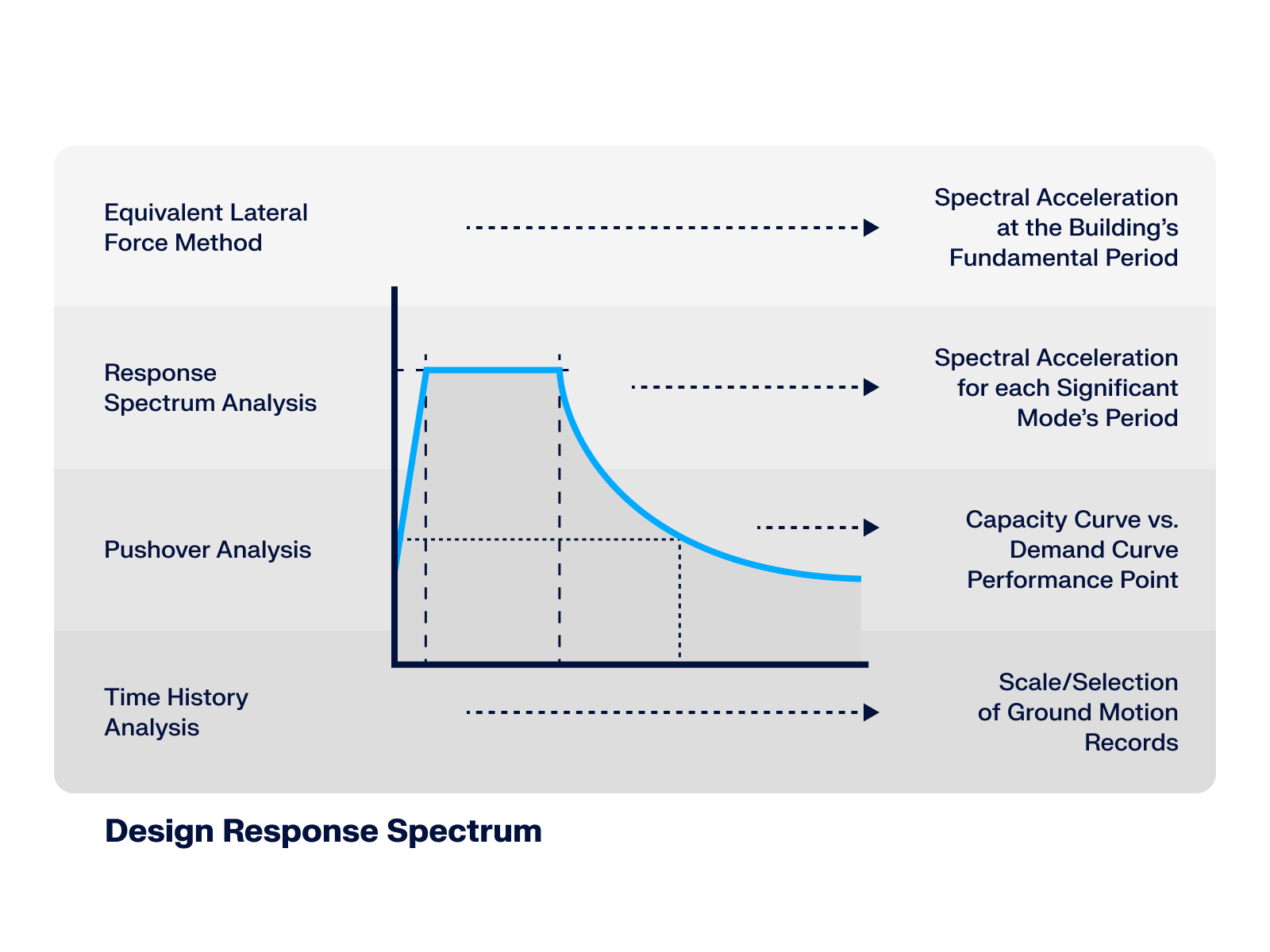
- Response spectra of the following standards are implemented:
-
EN 1998-1:2010 + A1:2013 (European Union)
-
DIN 4149:2005-04 (Germany)
-
SIA 261:2020-08 (Switzerland)
-
SIA 261:2014-07 (Switzerland)
-
ASCE 7 | 2022 - IBC | 2024 (USA)
-
ASCE 7 | 2016 - IBC | 2018/21 (USA)
-
ASCE 7 | 2010 - IBC | 2012/15 (USA)
-
ASCE 7 | 2005 - IBC | 2009 (USA)
-
IBC 2000 (USA)
-
CFE Sismo:2015-07 (Mexico)
-
CIRSOC 103:2013-07 (Argentina)
-
GB 50011-2010-12 (China)
-
IS 1893:2016-12 (India)
-
NBC 2020 (Canada)
-
NBC 2015 (Canada)
-
NCSE 02:2009 (Spain)
-
NPR 9998:2020-12 (Netherlands)
-
NTC 2018-01 (Italy)
-
P 100-1:2013-08 (Romania)
-
SANS 10160-4:2017 (South Africa)
-
SBC 103:2018 (Saudi Arabia)
-
TBEC:2018 (Türkiye)
-
- The following National Annexes according to EN 1998‑1 are available:
-
DIN EN 1998-1/NA:2023-11 (Germany)
-
ÖNORM EN 1998-1/NA:2017-07 (Austria)
-
SN 1998-1/NA:2019-12 (Switzerland)
-
1998-1/NA:2013-05 (European Union)
-
BAS EN 1998-1/NA:2018 (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
-
BDS 1998-1/NA:2012-03 (Bulgaria)
-
BS EN 1998-1/NA:2008-08 (United Kingdom)
-
CSN EN 1998-1/NA:2016-09 (Czech Republic)
-
CYS EN 1998-1/NA:2009-03 (Cyprus)
-
ELOT EN 1998-1/NA:2015-04 (Greece)
-
HRN EN 1998-1/NA:2011-06 (Croatia)
-
LST EN 1998-1/NA:2010-12 (Lithuania)
-
ILNAS EN 1998-1/NA:2011-09 (Luxembourg)
-
LVS EN 1998-1/NA:2015-01 (Latvia)
-
MS EN 1998-1/NA:2017-01 (Malaysia)
-
MSZ EN 1998-1/NA:2013-07 (Hungary)
-
NBN EN 1998-1/NA:2011-10 (Belgium)
-
NF EN 1998-1/NA:2013-12 (France)
-
NP EN 1998-1/NA:2010-03 (Portugal)
-
NS EN 1998-1/NA:2021-06 (Norway)
-
SIST EN 1998-1/NA:2009-01 (Slovenia)
-
SR EN 1998-1/NA:2008-11 (Romania)
-
SRPS EN 1998-1/NA:2018-12 (Serbia)
-
SS EN 1998-1/NA:2013-02 (Singapore)
-
STN EN 1998-1/NA:2009-04 (Slovakia)
-
UNE EN 1998-1/NA:2020-01 (Spain)
-
UNI EN 1998-1/NA:2013-03 (Italy)
-
- User-defined response spectra or those generated from accelerograms
- Direction-relative response spectrum approach
- Manual or automatic selection of the relevant mode shapes of response spectra (5% rule of EC 8 applicable)
- Result combinations by modal superimposition (SRSS or CQC rule) and by direction superimposition (SRSS or 100% / 30% rule)
- Accidental torsional actions can be taken into account automatically
- Signed results based on the dominant mode shape can be displayed
Response Spectrum Analysis | Features



In the Snow Load Wizard, you can optionally consider snow overhang and snow guard when generating snow loads according to Eurocode.

In the wind simulation, it is possible to consider member coatings (for example, from ice loads).
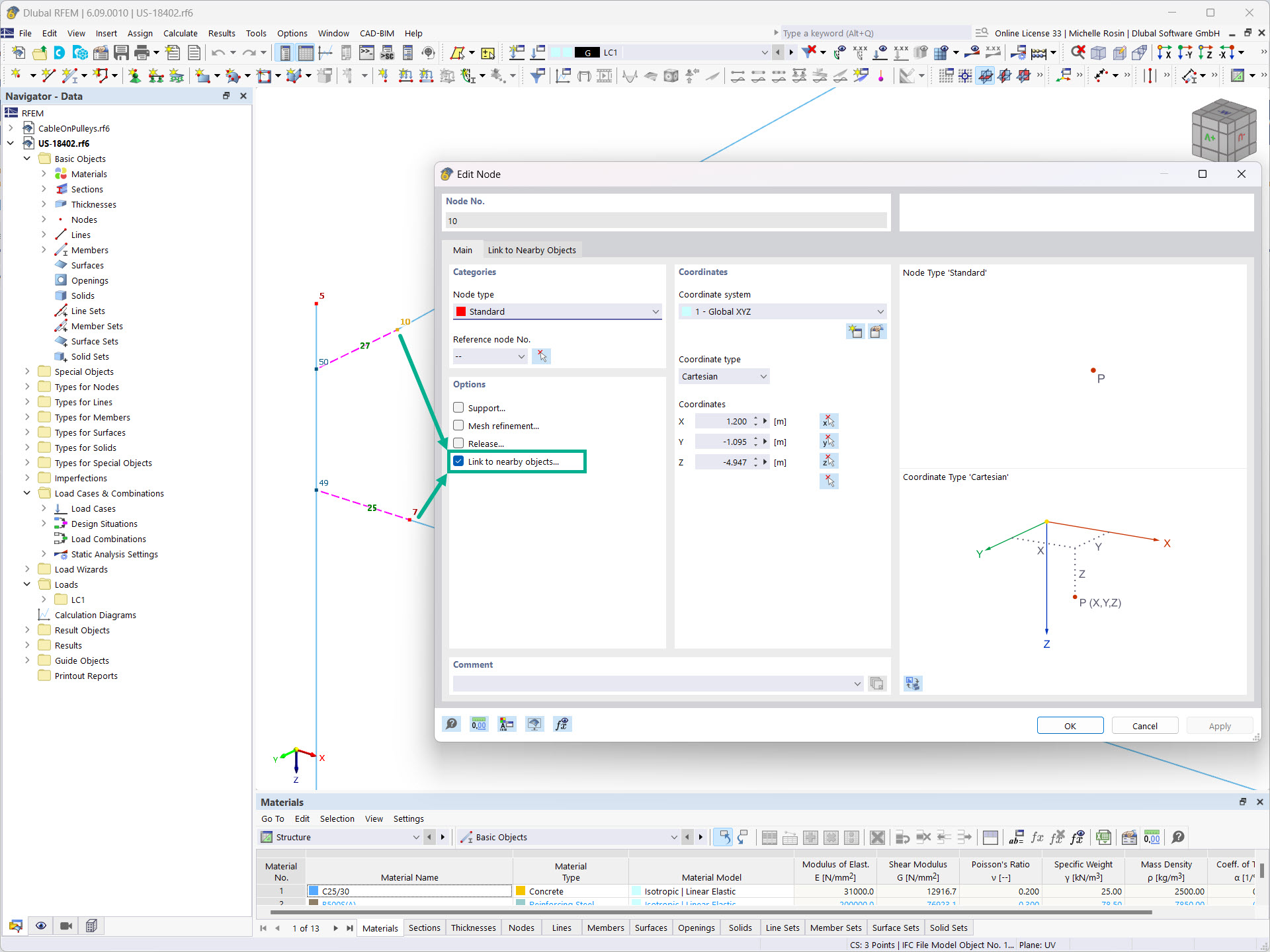
If you activate the "Link to Nearby Objects…" option for nodes, RFEM or RSTAB automatically searches for neighboring objects. A link in the form of a rigid member is then created for these members, nodes, or surfaces.
You can specify various settings for searching for nearby objects. Including search area, object types to be searched for, and objects to be excluded. Furthermore, you can specify member hinges for the created connecting member.
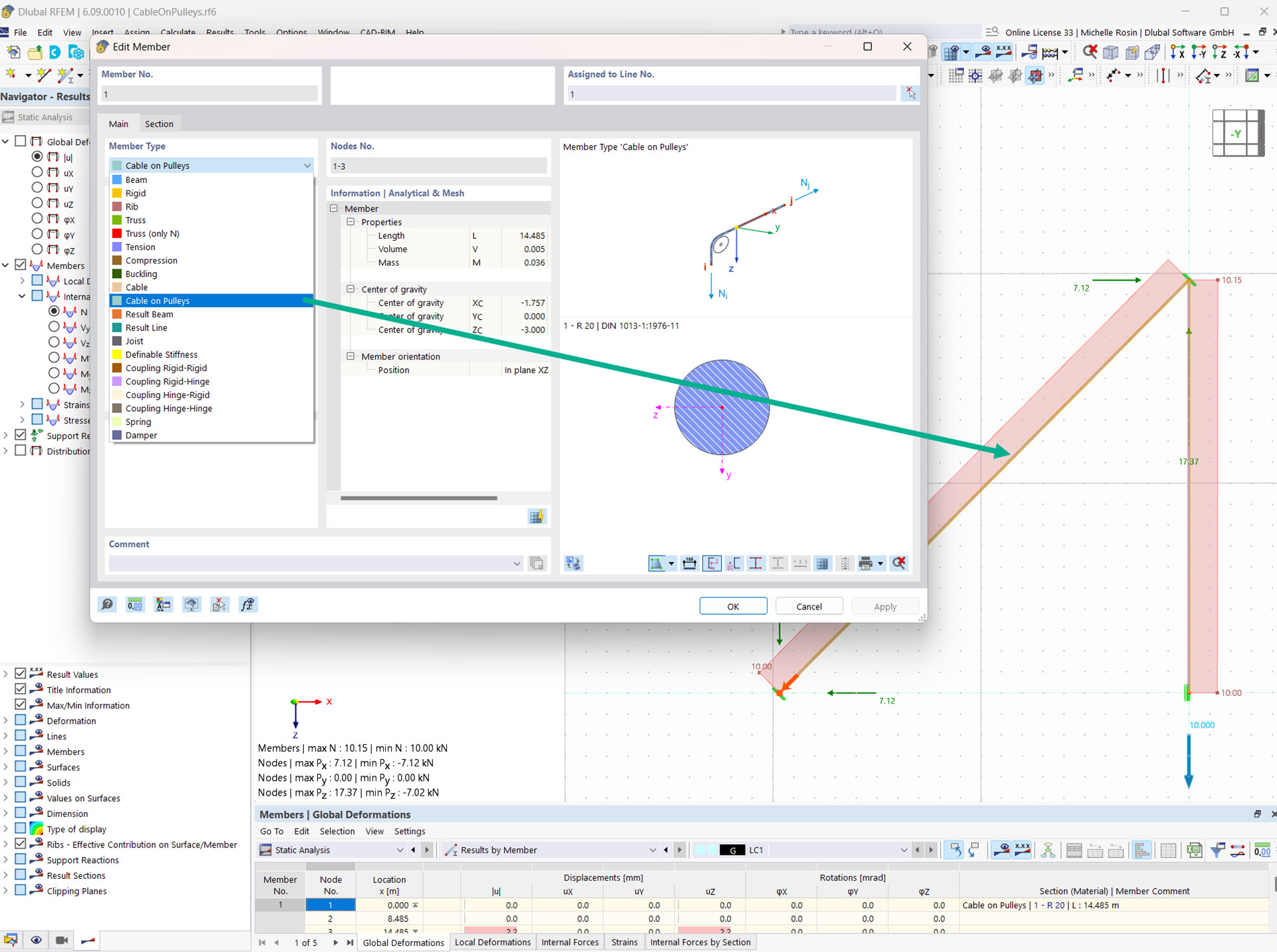
The Cable on Pulleys member type allows you to simulate a cable system deflected by pulleys.
This member type only absorbs tensile forces and can only be displaced in the longitudinal direction. It is suitable for flexible tension elements whose longitudinal forces are transferred through the model via deflection points (for example, a pulley).
How can I find out which graphics card is actually used by RFEM 6?
I'm experiencing problems with the graphics card. What can I do?
Can I use the Dlubal API in Rhino and Grasshopper?
Can I optimize parametric cross-sections?
How can I convert a member set or several members into a single member again?
How does single sign-on work with RFEM 6?















































-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)