- Pure torsional shear stress (Equation 4.1)
- Shear stress due to warping (Equation 4.2a)
- Normal stress due to warping (Equation 4.3a)
In addition to torsional stresses, bending and shear stresses (Equations 4.5 and 4.6) due to plane bending and axial load (Equation 4.7) must also be considered.
With the Torsional Warping (7 DOF) add-on, these stresses can be calculated in the Steel Design add-on.
This allows for a more accurate determination of the total shear and normal stresses compared to results without the 7 DOF add-on, which generally produce a lower design check ratio. However, design checks for buckling limit states are not included.
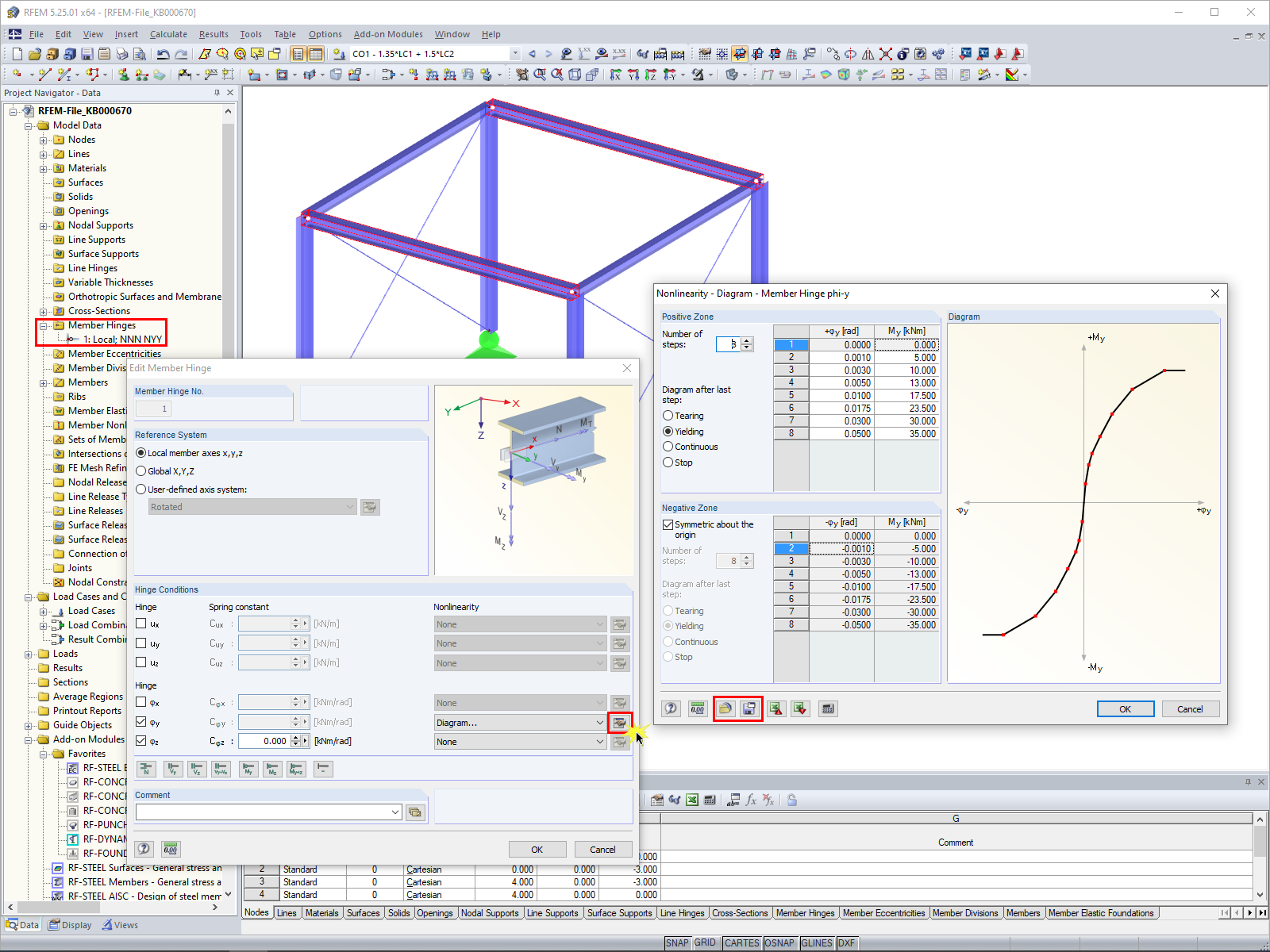
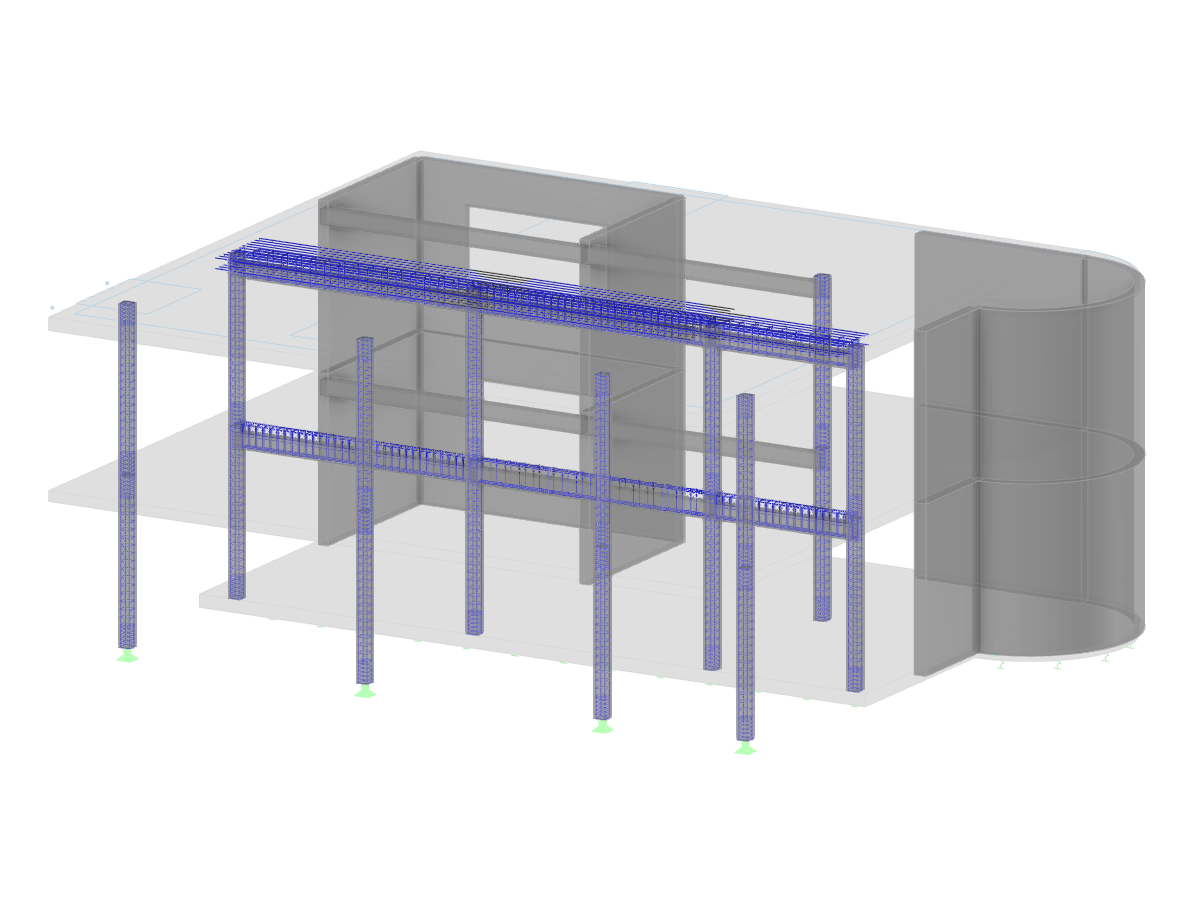
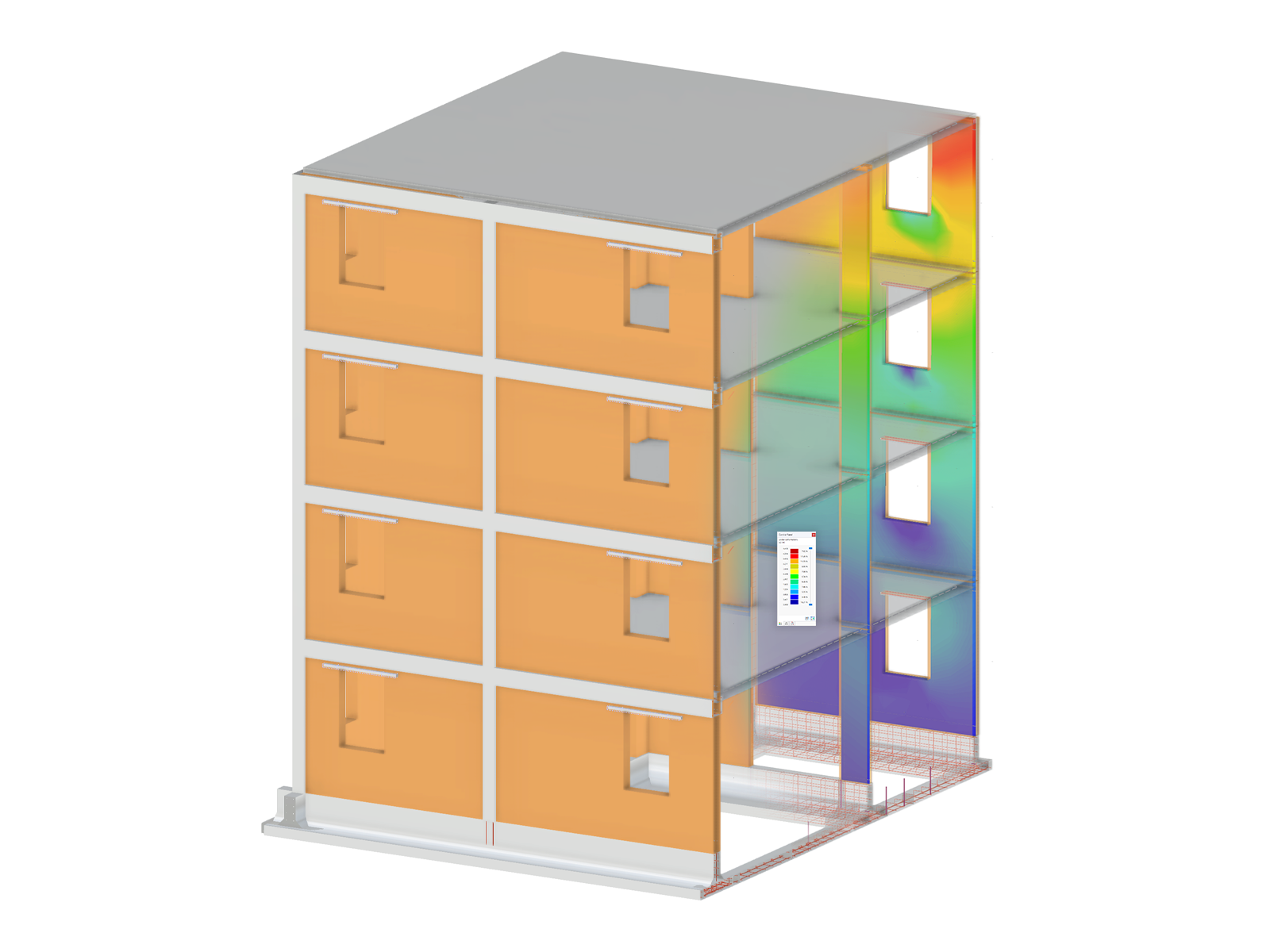
Torsional restraint must be defined using "actual" nodal supports in RFEM (Image 01).
Torsional and/or warping restraint assignment in the Effective Lengths for the Steel Design add-on (Image 02) is not considered in the torsional analysis according to AISC Design Guide 9 (with or without the 7 DOF add-on). Torsional and warping restraint do affect the other design checks.
Example
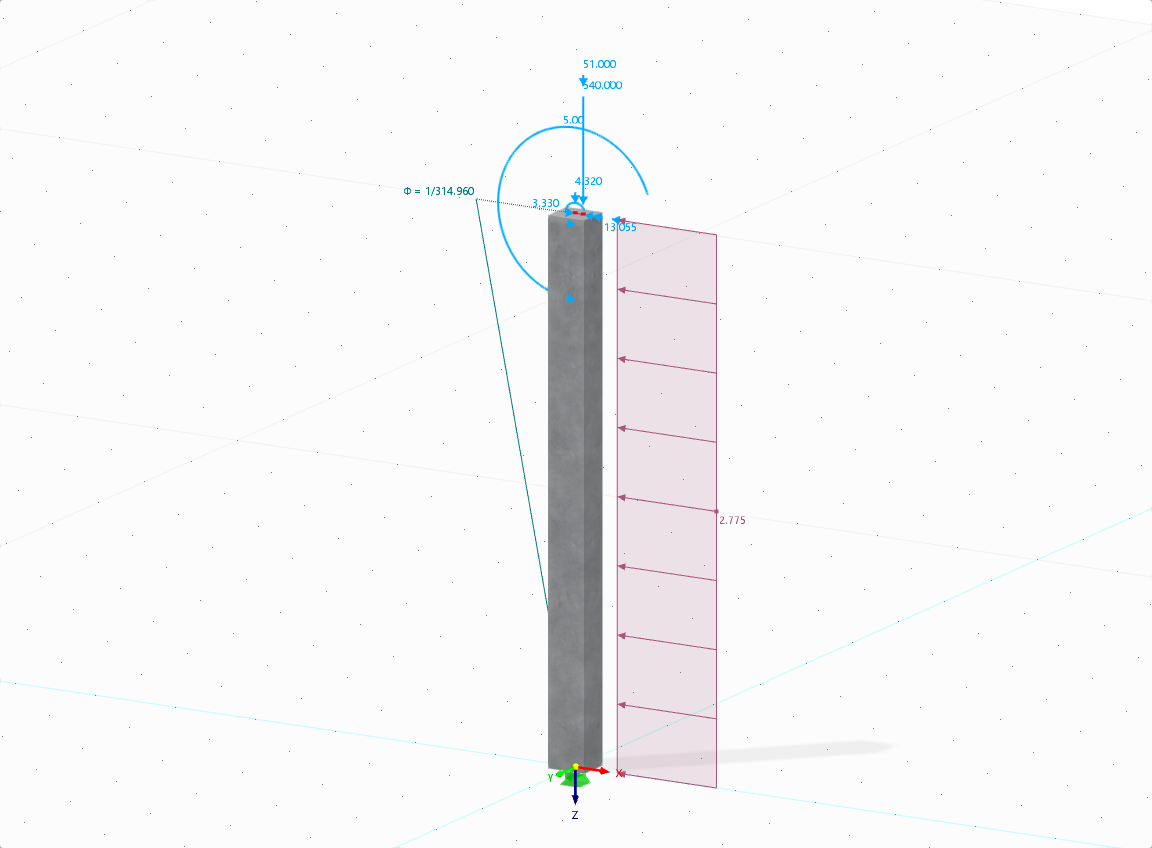
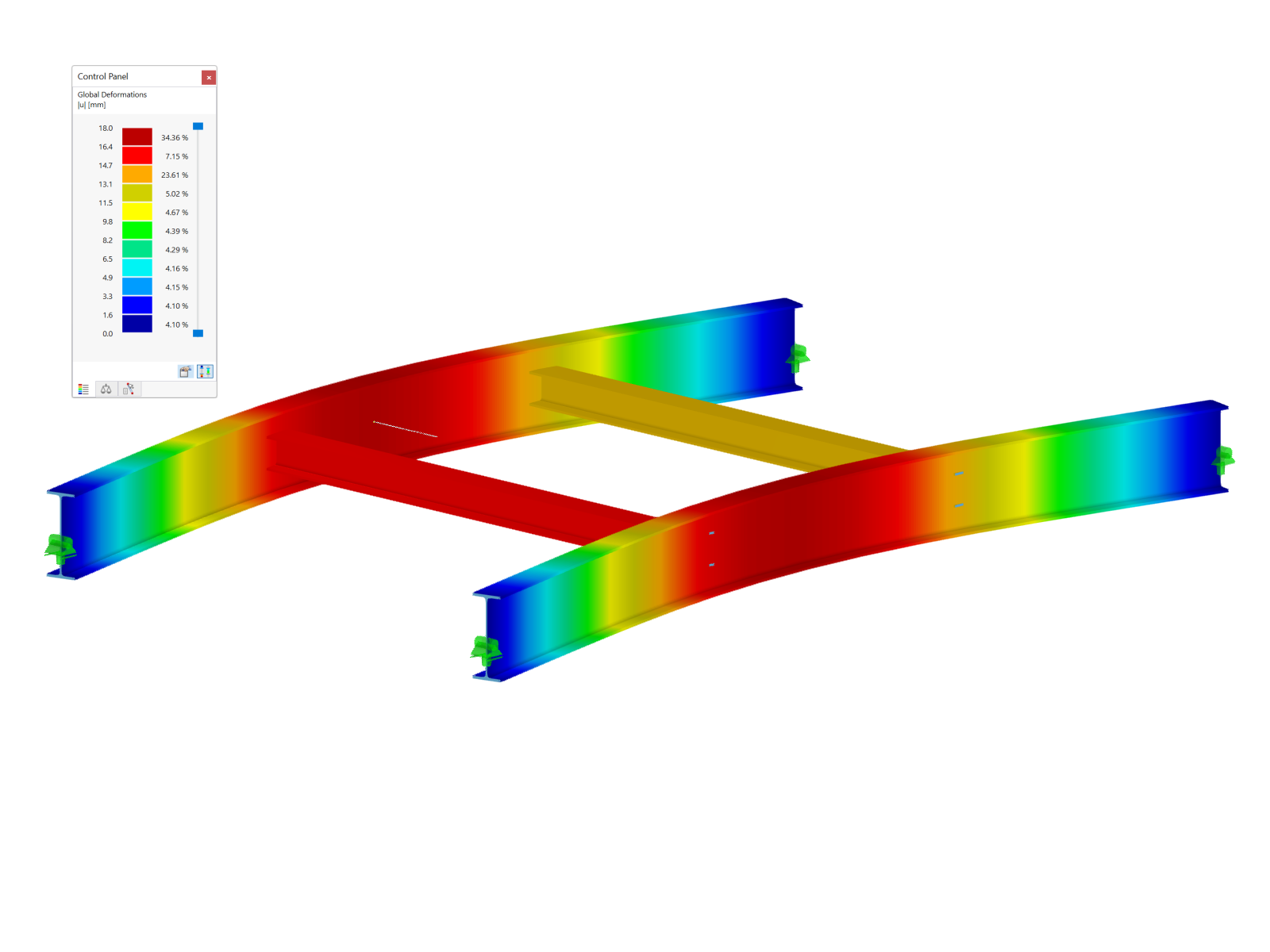
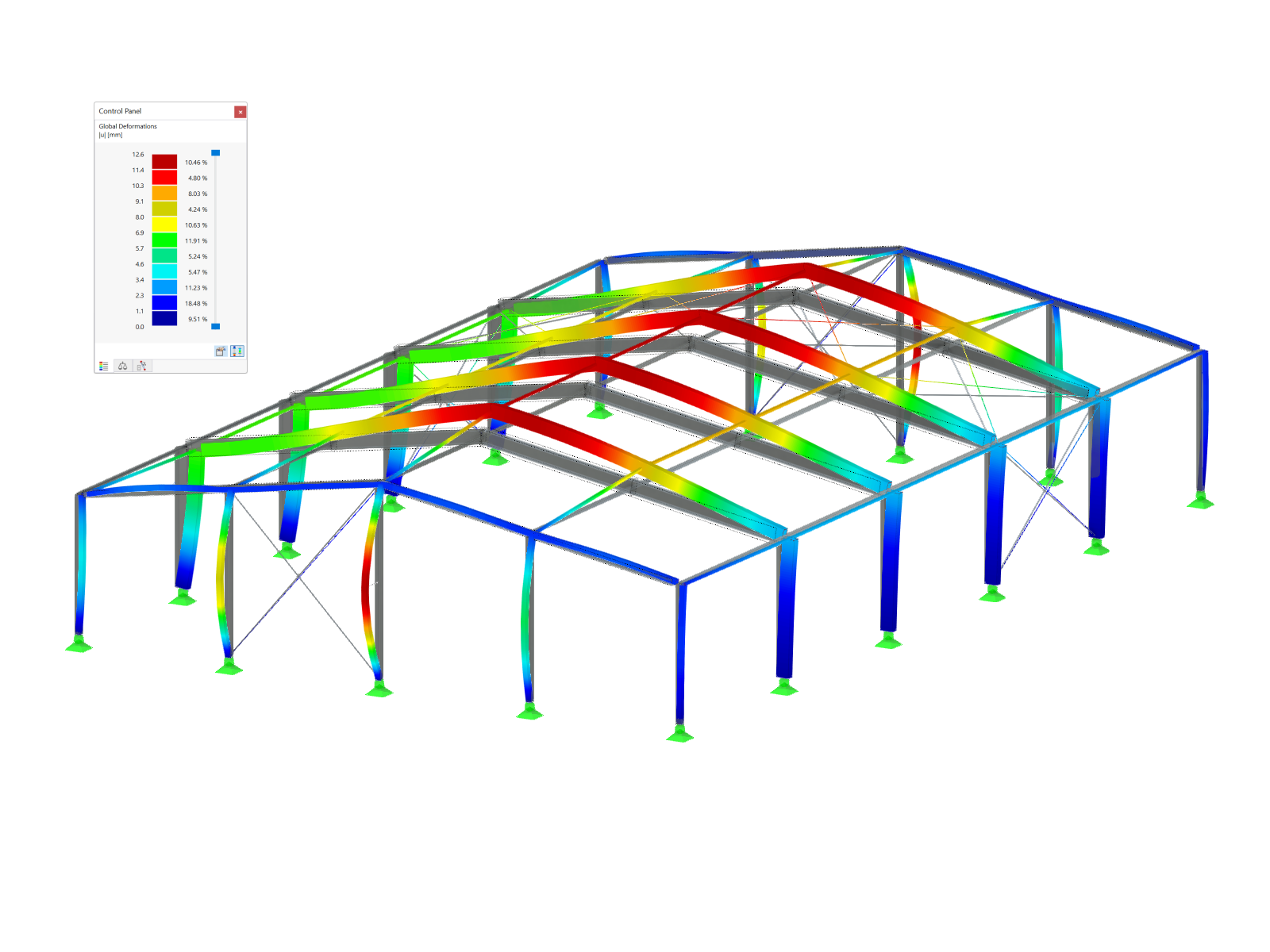
A W12x50 beam is subjected to various loads, including torsion. Rotational restraints around its longitudinal axis (X-axis) are provided at Nodes 5 and 7 (Image 03).
The results with and without the Torsional Warping (7 DOF) add-on are shown in Image 04. Without the add-on, the shear and normal stresses due to warping are not considered. In design check HH7370.00, the combined stresses are determined with highly conservative equations from AISC 360 Section H3.3 [2], “Non-HSS Members Subjected to Torsion and Combined Stress”.
With the add-on, design check HH7400.00 calculates the combined stresses according to AISC Design Guide 9 [1], which results in a much lower design check ratio compared to AISC 360 Section H3.3 [2].
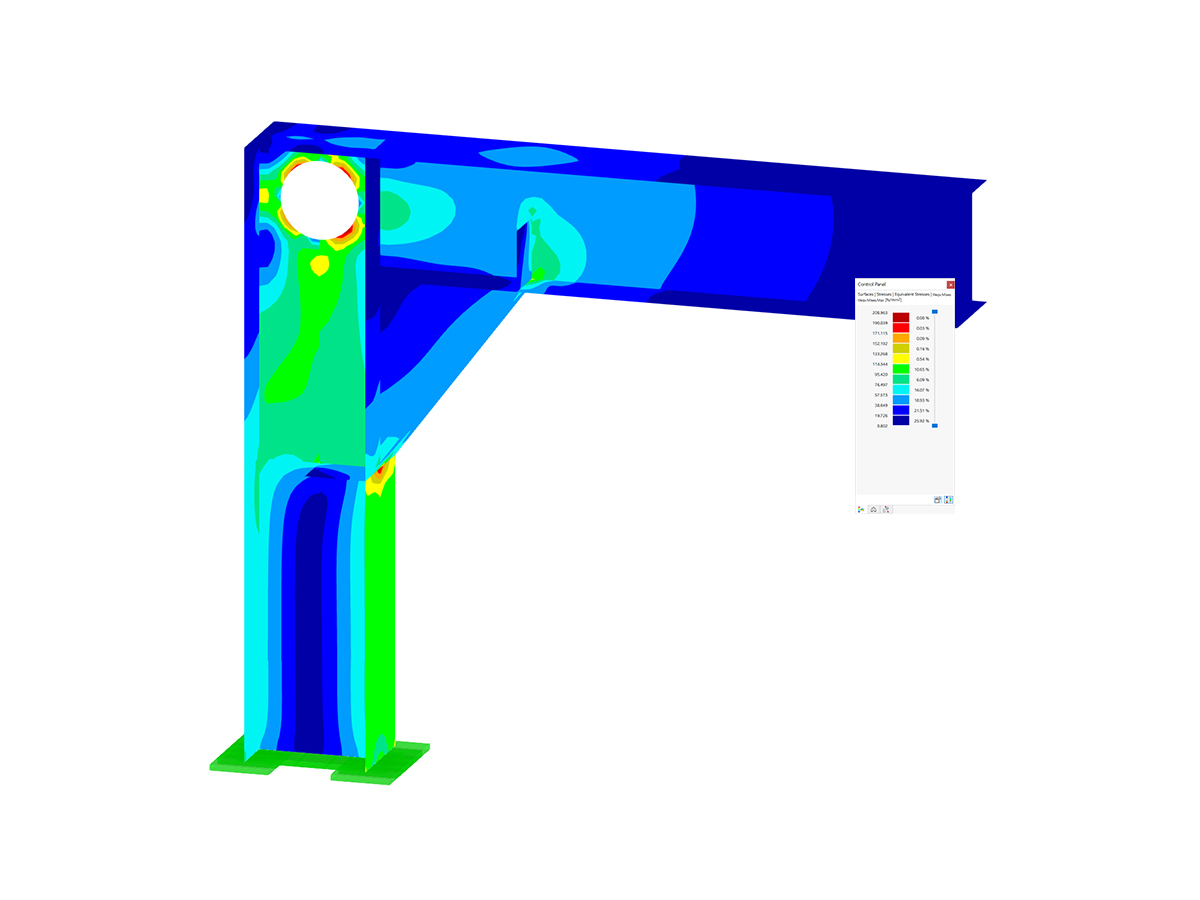
Viewing the design check details for GG6400.00 from both analyses, the pure torsional shear stress calculated without the add-on is significantly higher (Image 05).
Conclusion
The Torsional Warping (7 DOF) add-on introduces cross-section warping as an additional degree of freedom, enabling a more precise and comprehensive torsional analysis. When designing in accordance with AISC 360 within the Steel Design add-on, torsional stresses are calculated based on AISC Design Guide 9. Integrating the advanced 7 DOF add-on allows for a more accurate and economical design of steel members.

























































.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)