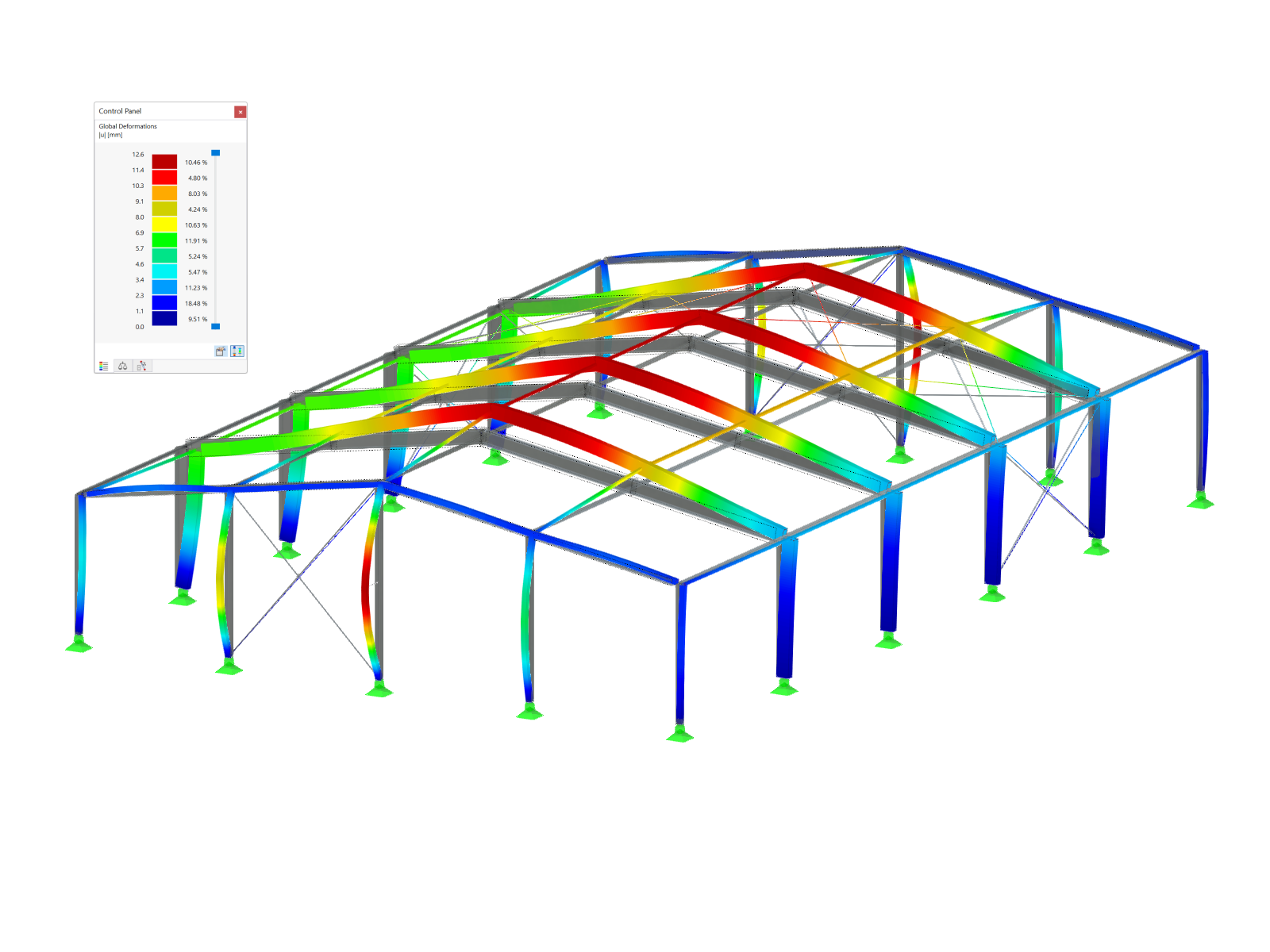
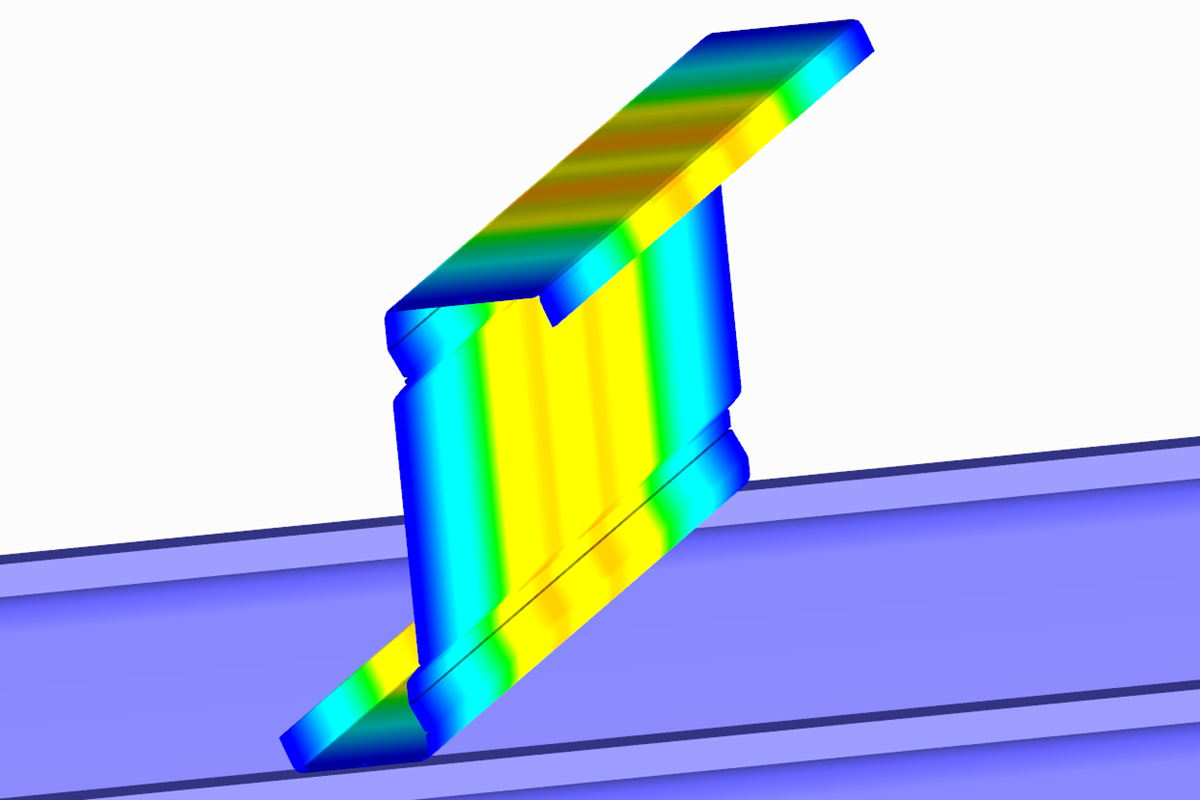
The RWIND Simulation program provides an optional consideration of the k‑ε and k‑ω turbulence models for a numerical flow simulation that is variable over the height. The necessary turbulence parameters can be specified manually or determined automatically from a user-defined turbulence intensity value. In the standard, the turbulence intensity of 1% is specified as a constant over the wind tunnel height. This value is based on the recommendation by the CFD Support company, which has many years of experience in the field of numerical flow simulation.
CFD Support
The standard k-epsilon model is used for the k-ε turbulence model.
Standard k-epsilon Model
The SST k-omega model is used for the k-ω turbulence model.
SST k-omega Model
In RWIND Simulation, the turbulence model is organized in the "Parameters of Simulation" menu under the "Turbulence" tab.
The RFEM or RSTAB interface menu organizes the turbulence model for the automatic calculation of wind loads in the background in the "Simulate and Generate Wind Loads" dialog box under the "Wind Load" tab. In this case, the "Use uniform turbulence at the inlet" function in the Turbulence Properties section creates a constant turbulence specification over the height of the wind tunnel. By deactivating this function, you can specify the turbulence variable over the height. In addition to the location-specific parameter of the wind speed profile, the turbulence property dependent on the terrain roughness over the height is also defined automatically. As an alternative, you can define the turbulence property manually in the form of a table entry using the "User-Defined Turbulence" function.























.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)















.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)












_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)






.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)