- Import of materials, cross-sections, and internal forces from RFEM/RSTAB
- Steel design of thin‑walled cross‑sections according to EN 1993‑1‑1:2005 and EN 1993‑1‑5:2006
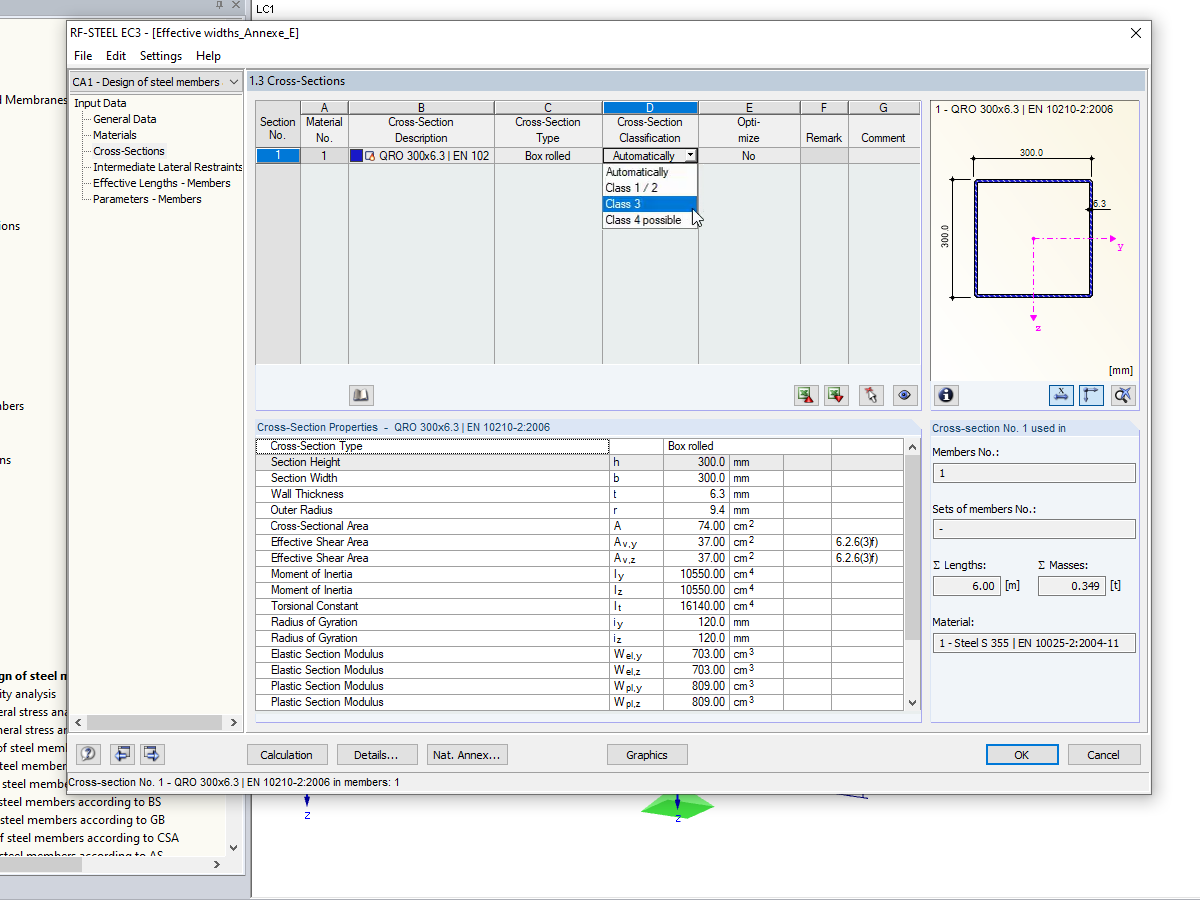
- Automatic classification of cross-sections according to EN 1993-1-1:2005 + AC:2009, Cl. 5.5.2, and EN 1993-1-5:2006, Cl. 4.4 (cross-section class 4), with optional determination of effective widths according to Annex E for stresses under fy
- Integration of parameters for the following National Annexes:
-
DIN EN 1993-1-1/NA:2015-08 (Germany)
-
ÖNORM B 1993-1-1:2007-02 (Austria)
-
NBN EN 1993-1-1/ANB:2010-12 (Belgium)
-
BDS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2008 (Bulgaria)
-
DS/EN 1993-1-1 DK NA:2015 (Denmark)
-
SFS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2005 (Finland)
-
NF EN 1993-1-1/NA:2007-05 (France)
-
ELOT EN 1993-1-1 (Greece)
-
UNI EN 1993-1-1/NA:2008 (Italy)
-
LST EN 1993-1-1/NA:2009-04 (Lithuania)
-
UNI EN 1993-1-1/NA:2011-02 (Italy)
-
MS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2010 (Malaysia)
-
NEN EN 1993-1-1/NA:2011-12 (Netherlands)
- NS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2008-02 (Norway)
-
PN EN 1993-1-1/NA:2006-06 (Poland)
-
NP EN 1993-1-1/NA:2010-03 (Portugal)
-
SR EN 1993-1-1/NB:2008-04 (Romania)
-
SS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2011-04 (Sweden)
-
SS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2010 (Singapore)
-
STN EN 1993-1-1/NA:2007-12 (Slovakia)
-
SIST EN 1993-1-1/A101:2006-03 (Slovenia)
-
UNE EN 1993-1-1/NA:2013-02 (Spain)
-
CSN EN 1993-1-1/NA:2007-05 (Czech Republic)
-
BS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2008-12 (the United Kingdom)
-
CYS EN 1993-1-1/NA:2009-03 (Cyprus)
- In addition to the National Annexes (NA) listed above, you can also define a specific NA, applying user‑defined limit values and parameters.
- Automatic calculation of all required factors for the design value of flexural buckling resistance Nb,Rd
- Automatic determination of the ideal elastic critical moment Mcr for each member or set of members on every x-location according to the Eigenvalue Method or by comparing moment diagrams. You only have to define the lateral intermediate supports.
- Design of tapered members, unsymmetric sections or sets of members according to the General Method as described in EN 1993-1-1, Cl. 6.3.4
- In the case of the General Method according to Cl. 6.3.4, optional application of "European lateral-torsional buckling curve" according to Naumes, Strohmann, Ungermann, Sedlacek (Stahlbau 77 [2008], pp. 748‑761)
- Rotational restraints can be taken into account (trapezoidal sheeting and purlins)
- Optional consideration of shear panels (for example, trapezoidal sheeting and bracing)
- RF-/STEEL Warping Torsion module extension (license required) for stability analysis according to the second-order analysis as stress analysis including consideration of the 7th degree of freedom (warping)
- Module extension RF-/STEEL Plasticity (license required) for plastic analysis of cross‑sections according to Partial Internal Forces Method (PIFM) and Simplex Method for general cross‑sections (in connection with the RF‑/STEEL Warping Torsion module extension, it is possible to perform the plastic design according to the second‑order analysis)
- Module extension RF-/STEEL Cold-Formed Sections (license required) for ultimate and serviceability limit state designs for cold-formed steel members according to the EN 1993-1-3 and EN 1993-1-5 standards
- ULS design: Selection of fundamental or accidental design situations for each load case, load combination, or result combination
- SLS design: Selection of characteristic, frequent, or quasi-permanent design situations for each load case, load combination, or result combination
- Tension analysis with definable net cross-section areas for member start and end
- Weld designs of welded cross-sections
- Optional calculation of warp spring for nodal support on sets of members
- Graphic of design ratios on cross-section and in RFEM/RSTAB model
- Determination of governing internal forces
- Filter options for graphical results in RFEM/RSTAB
- Representation of design ratios and cross‑section classes in the rendered view
- Color scales in result windows
- Automatic cross-section optimization
- Transfer of optimized cross-sections to RFEM/RSTAB
- Parts lists and quantity surveying
- Direct data export to MS Excel
- Verifiable printout report
- Possibility to include the temperature curve in the report
RF-/STEEL EC3 | Features




When performing the design of tension, compression, bending, and shear loading, the module compares the design values of the maximum load capacity to the design values of the actions.
If the components are subjected to both bending and compression, the program performs an interaction. In RF-/STEEL EC3, you can determine the factors according to Method 1 (Annex A) or Method 2 (Annex B).
The flexural buckling design requires neither the slenderness nor the elastic critical buckling load of the governing buckling case. The module automatically calculates all required factors for the bending stress design value. RF-/STEEL EC3 determines the elastic critical moment for lateral-torsional buckling for each member on every x-location of the cross-section. If required, you only need to specify lateral intermediate supports of the individual members/sets of members, definable in one of the input windows.
If members are selected for the fire resistance design in RF-/STEEL EC3, there is another input window available where you can enter additional parameters, such as: a coating or cladding type. Global settings cover the required time of fire resistance, temperature curve, and other coefficients. The printout report lists all intermediate results and the final result of the fire resistance design. Furthermore, it is possible to print the temperature curve in the report.

The results sorted by load case, cross-section, member, set of members, or x-location are displayed in clearly arranged result windows. By selecting the corresponding table row, detailed information about the performed design is displayed.
The results include a comprehensible list of all material and cross-section properties, design internal forces, and design factors. Furthermore, it is possible to display the distribution of internal forces of each x-location in a separate graphic window.
Parts lists by members/sets of members for the individual cross-section types complete the detailed and structured display of results. To print input data and results, you can use the global printout report in RFEM/RSTAB.
For further processing of various data, it is possible to export all tables to MS Excel.

RF-/STEEL EC3 automatically imports the cross-sections defined in RFEM/RSTAB. It is possible to design all thin-walled cross-sections. The program automatically selects the most efficient method according to standards.
The ultimate limit state design takes into account several loads and you can select the interaction designs available in the standard.
The classification of designed cross-sections into Classes 1 to 4 is an essential part of the analysis according to Eurocode 3. This way, you can check the limitation of the design and rotational capacity by means of the local buckling of cross-section parts. RF-/STEEL EC3 determines the c/t-ratios of the cross-section parts subjected to compression stress and performs the classification automatically.
For the stability analysis, you can specify for each member or set of members whether flexural buckling occurs in the y- and/or the z-direction. You can also define additional lateral restraints in order to represent the model close to reality. The slenderness ratio and elastic critical load are determined automatically on the basis of the boundary conditions of RF-/STEEL EC3. The elastic critical moment for lateral-torsional buckling required for the lateral-torsional buckling analysis can be determined automatically or specified manually. The load application point of transverse loads, which has an influence on the torsional resistance, can also be taken into account via the setting in the details. In addition, you can take into account rotational restraints (for example trapezoidal sheeting and purlins) and shear panels (for example trapeziodal sheeting and bracing).
In modern construction, where cross-sections are increasingly slender, the serviceability limit state is an important factor in structural analysis. RF-/STEEL EC3 assigns load cases, load combinations, and result combinations to different design situations. The respective limit deformations are preset in the National Annex and can be adjusted, if necessary. In addition, it is possible to define reference lengths and precambers for the design.
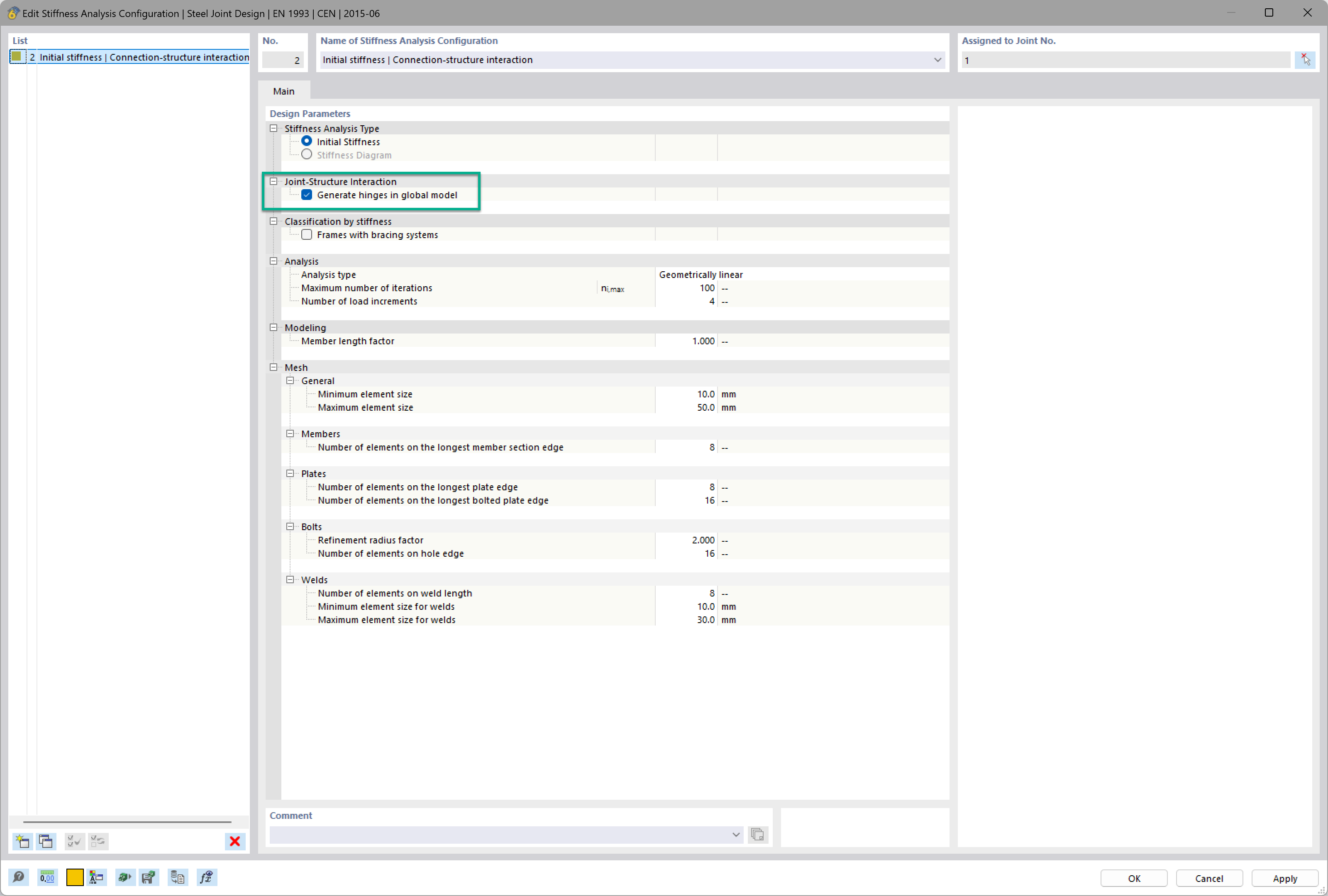
Want to automatically consider steel joint stiffness in your global RFEM model? Utilize the Steel Joints add-on!
Activate joint-structure interaction in the stiffness analysis of your steel joints. Hinges with springs are then automatically generated in the global model and included in subsequent calculations.
What could be the reason?






































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)



.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)