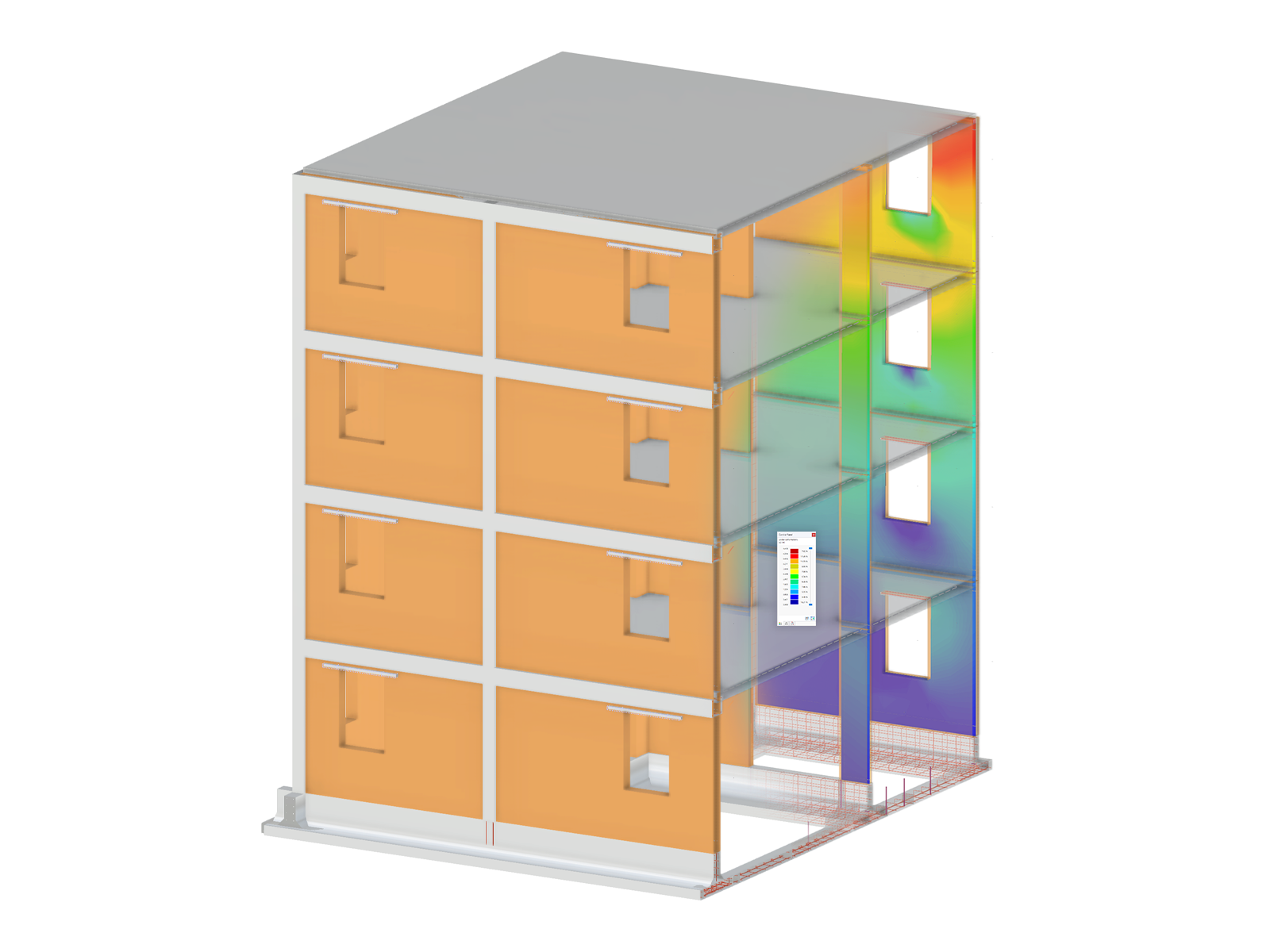
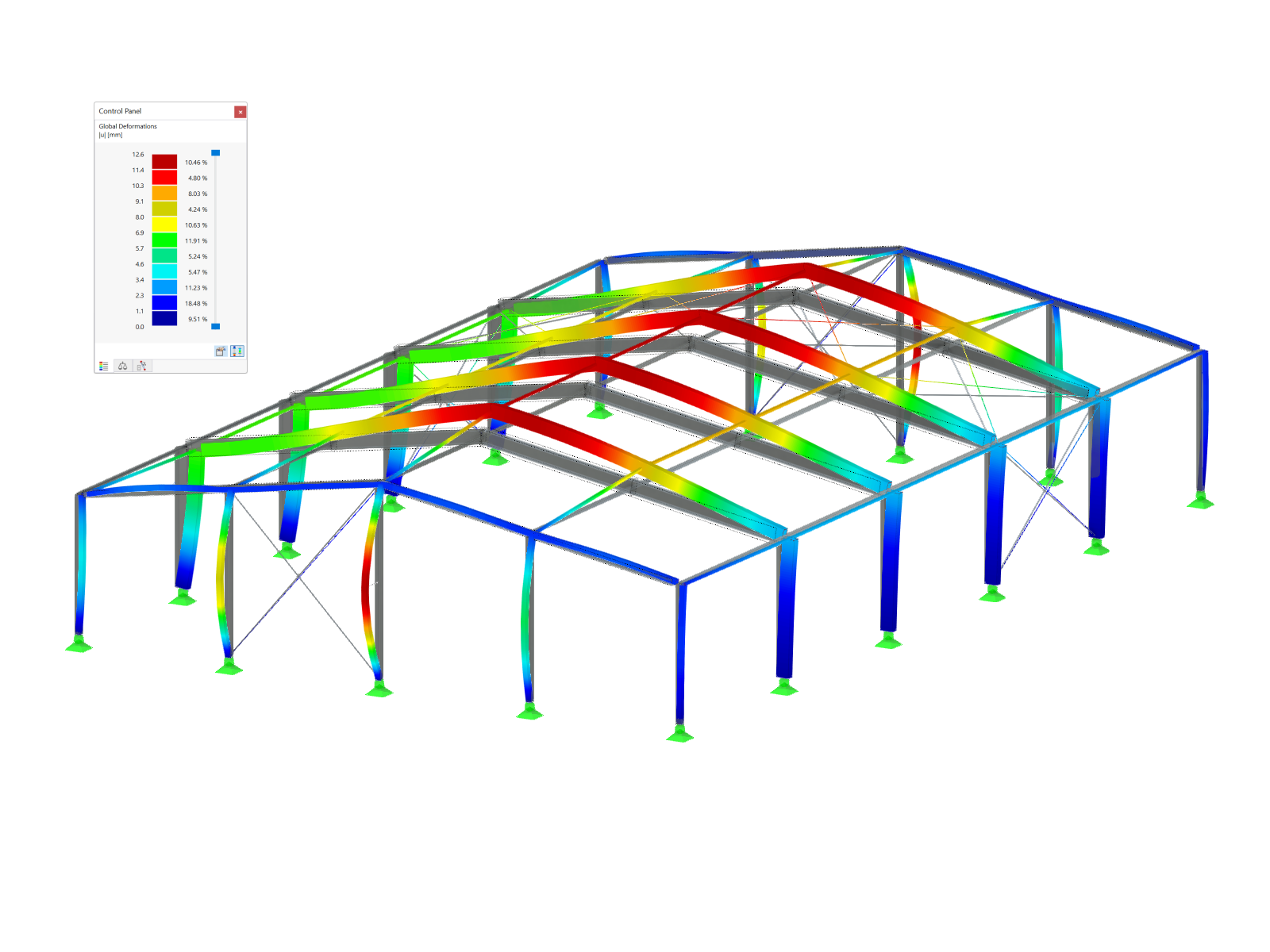
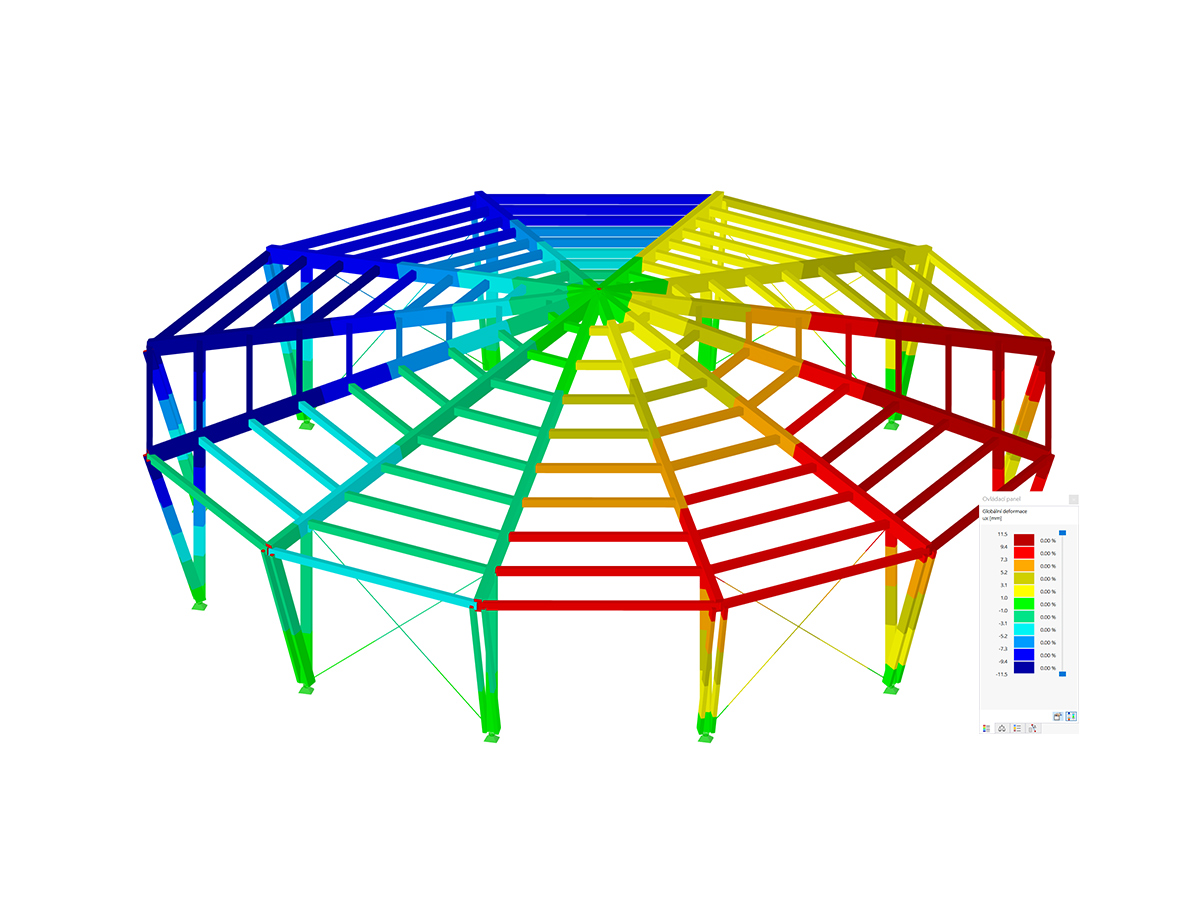
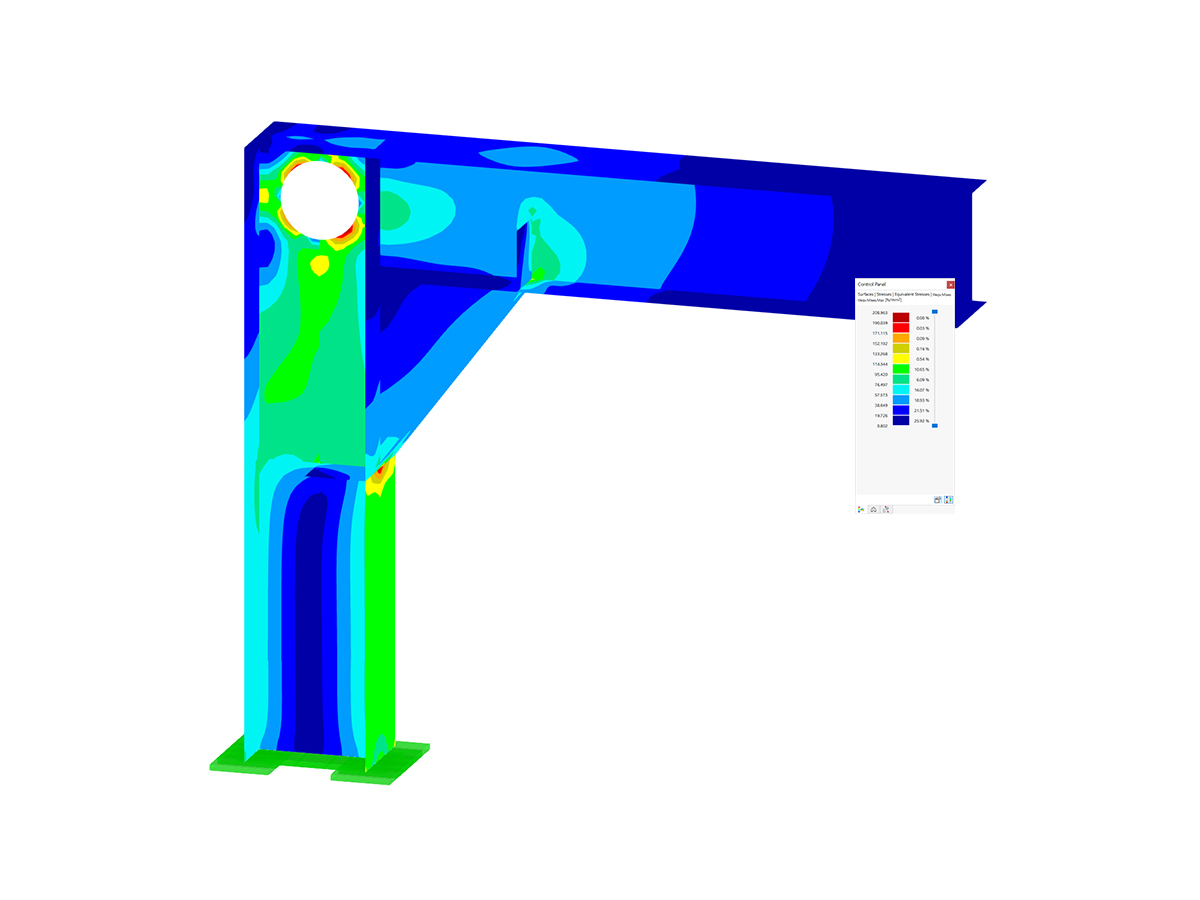
In Part 1, we have described the selection of layout criteria for dimensioning reinforcement for the serviceability limit state design in RF‑CONCRETE Members and CONCRETE. Now, we go into detail for the function "Find economical reinforcement for crack width design."
KB 000506 | Dimensioning of Longitudinal Reinforcement for Serviceability Limit State Design 2
.png?mw=512&hash=71474bbf484eff50cf2eb4da2f7c0a5d6103a65d)
.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)

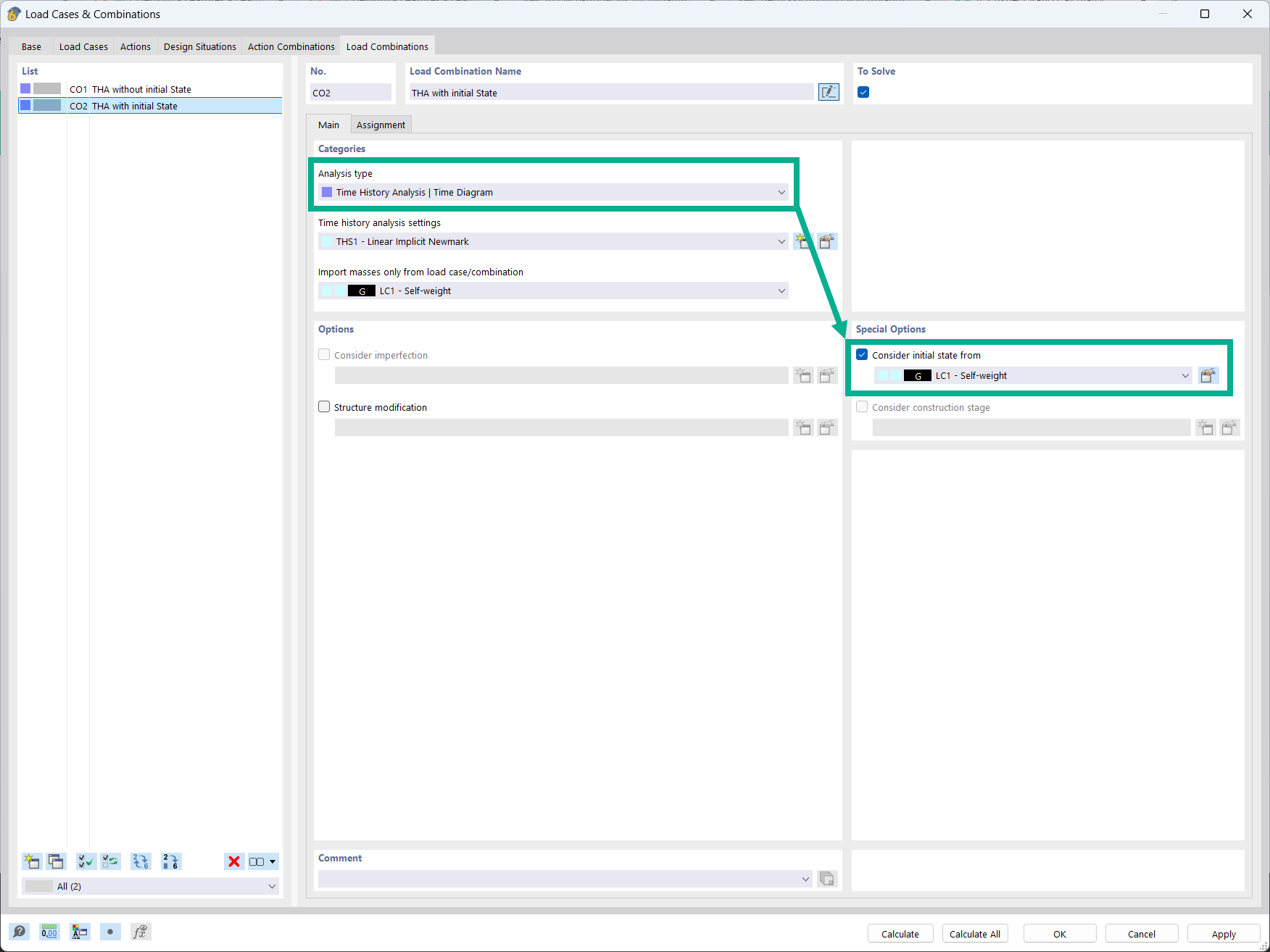
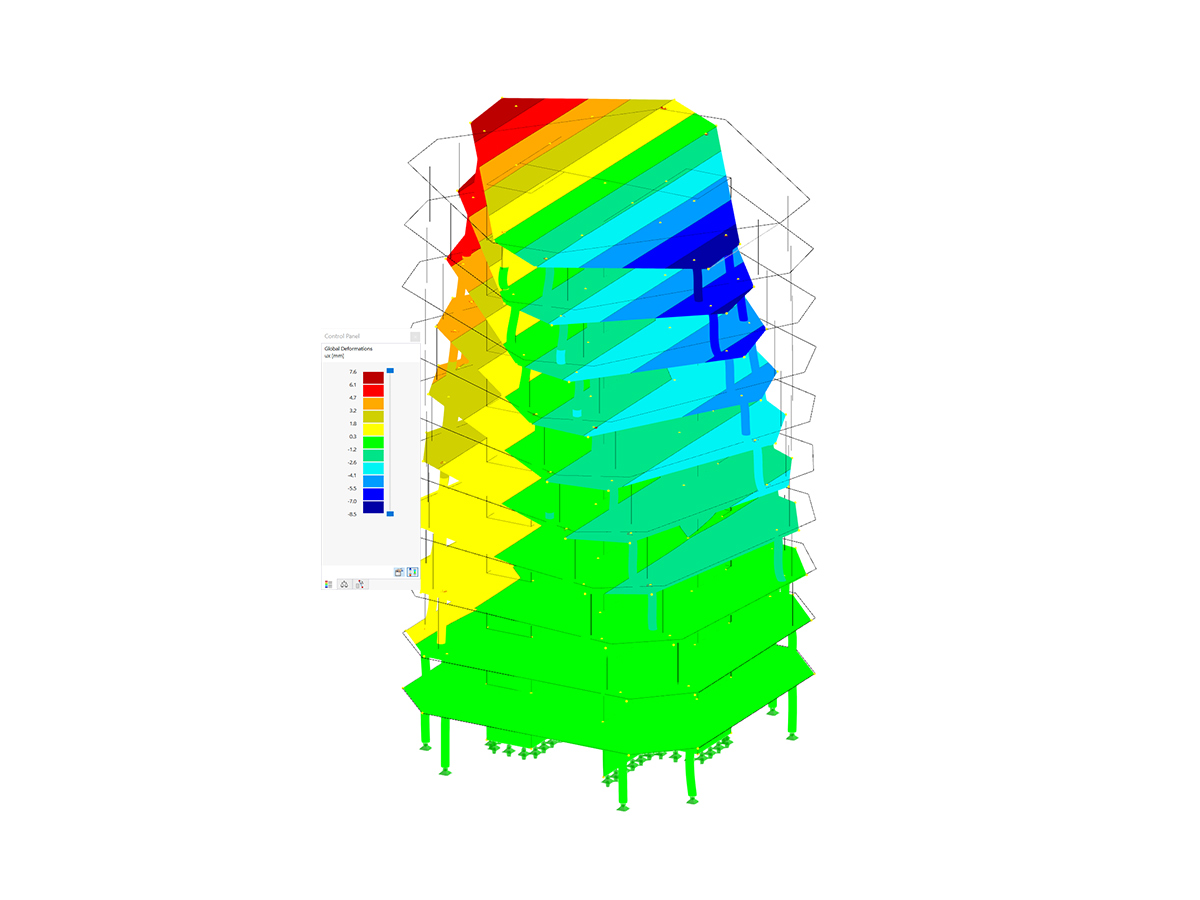
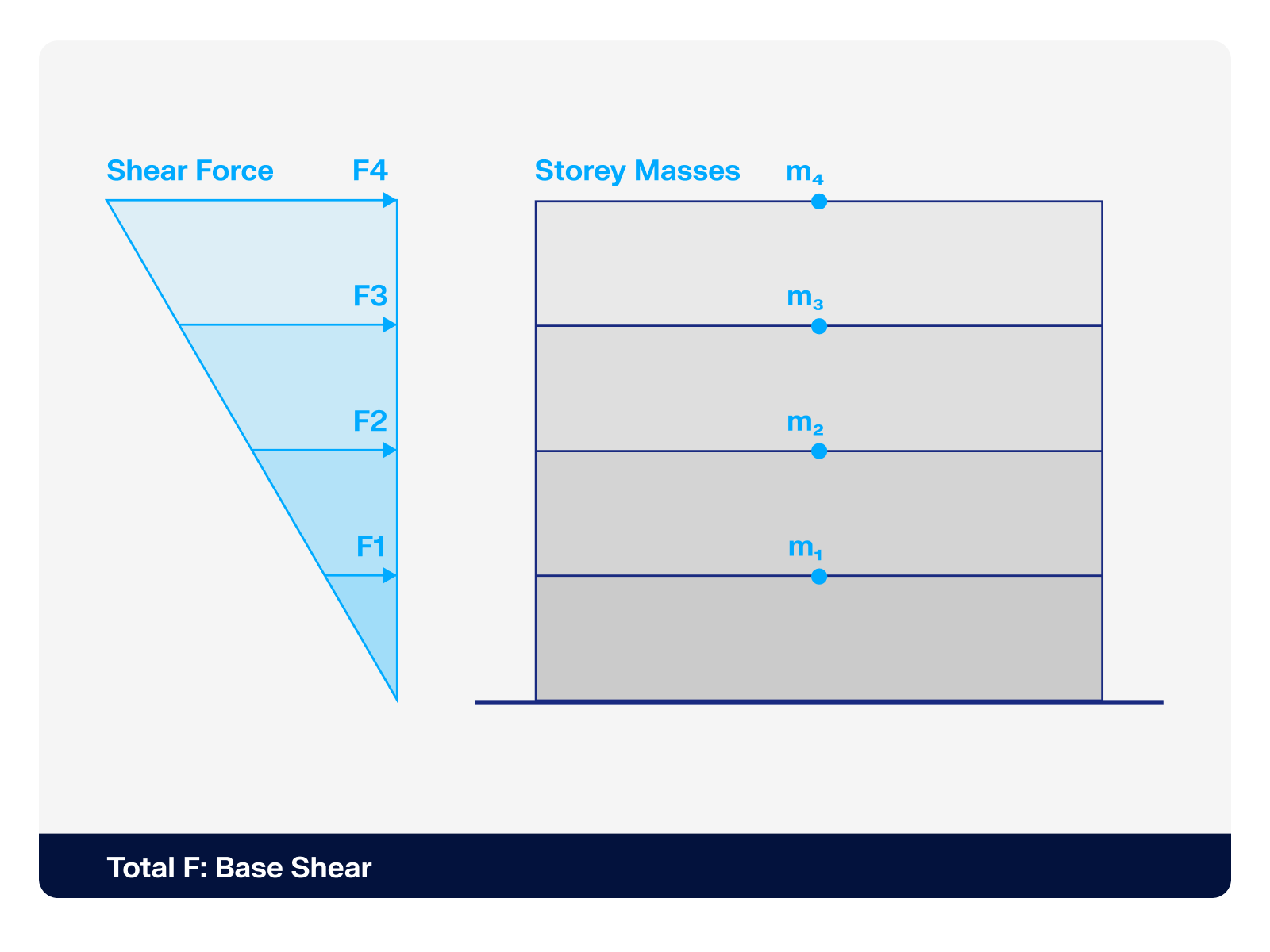
It is possible to consider initial states in the time history analysis.

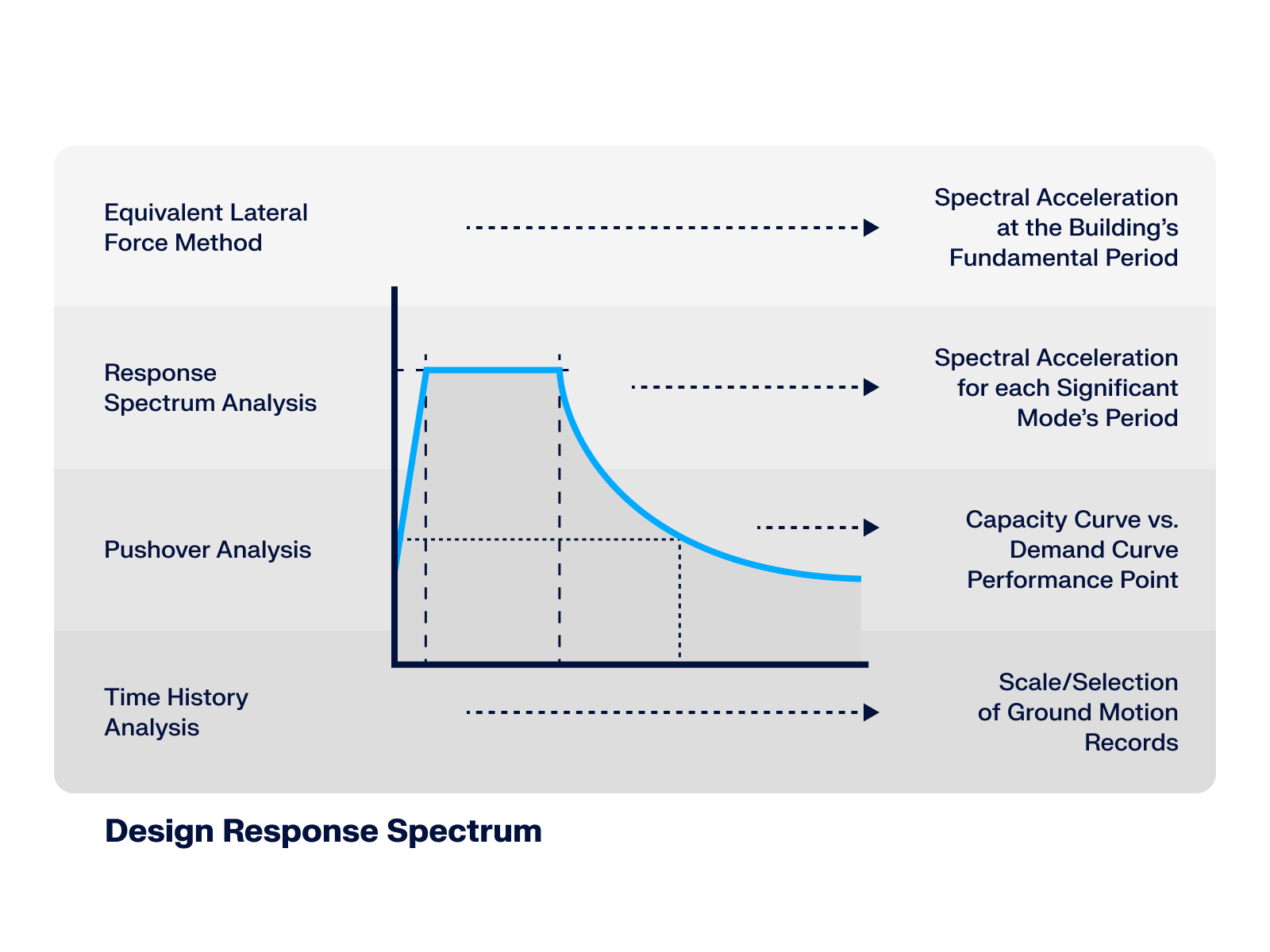
- Design of five types of seismic force-resisting systems (SFRS) includes Special Moment Frame (SMF), Intermediate Moment Frame (IMF), Ordinary Moment Frame (OMF), Ordinary Concentrically Braced Frame (OCBF), and Special Concentrically Braced Frame (SCBF)
- Ductility check of the width-to thickness ratios for webs and flanges
- Calculation of the required strength and stiffness for stability bracing of beams
- Calculation of the maximum spacing for stability bracing of beams
- Calculation of the required strength at hinge locations for stability bracing of beams
- Calculation of the column required strength with the option to neglect all bending moments, shear, and torsion for overstrength limit state
- Design check of column and brace slenderness ratios

The seismic design result is categorized into two sections: member requirements and connection requirements.
The "Seismic Requirements" include the Required Flexural Strength and the Required Shear Strength of the beam-to-column connection for moment frames. They are listed in the ‘Moment Frame Connection by Member’ tab. For braced frames, the Required Connection Tensile Strength and the Required Connection Compressive Strength of the brace are listed in the ‘Brace Connection by Member’ tab.
The program provides the performed design checks in tables. The design check details clearly display the formulas and references to the standard.

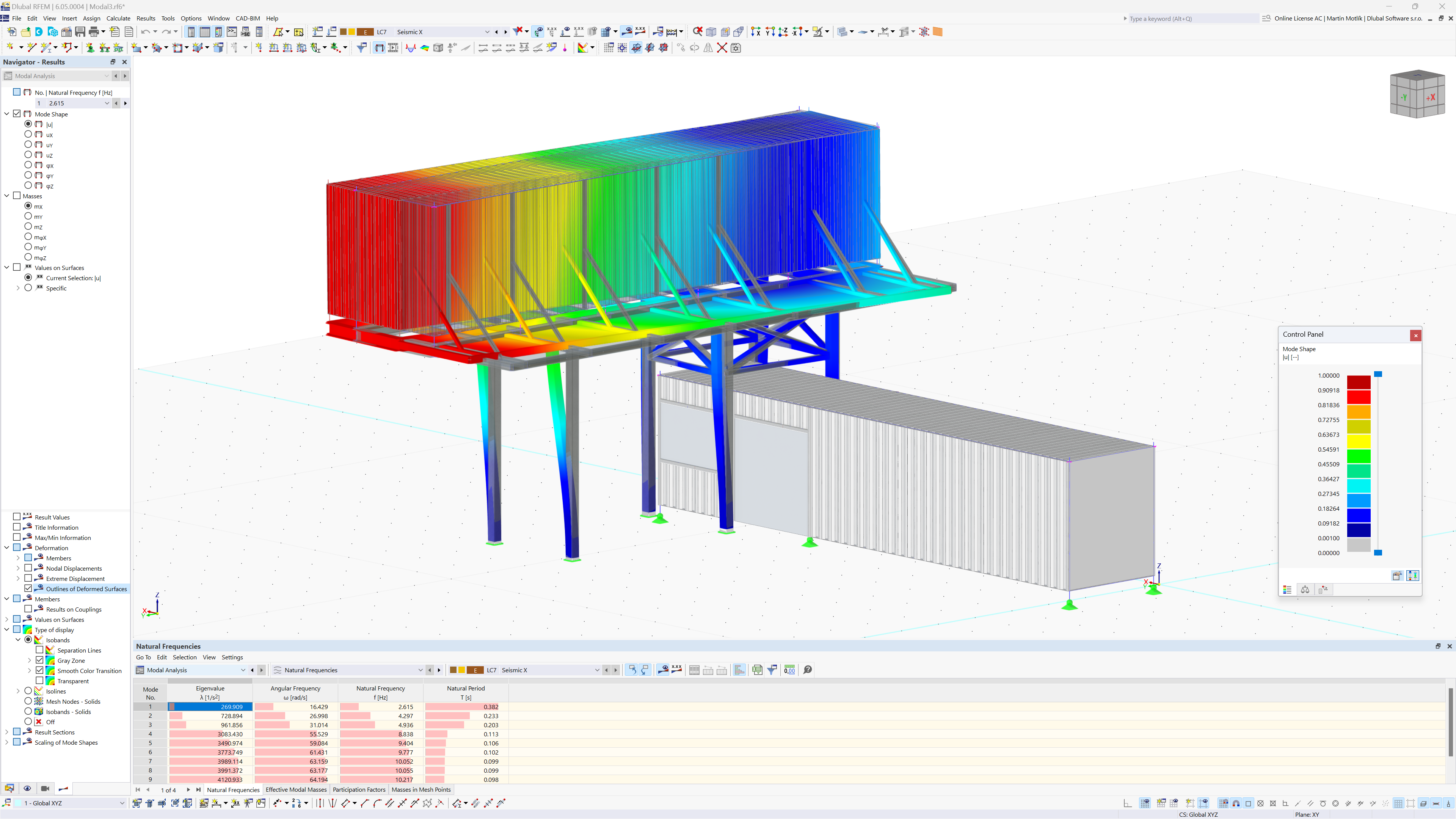
Using the "Damper" member type, you can define a damping coefficient, a spring constant, and a mass. This member type extends the possibilities within the Time History Analysis.
With regard to viscoelasticity, the "Damper" member type is similar to the Kelvin-Voigt model, which consists of the damping element and an elastic spring (both connected in parallel).




































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)