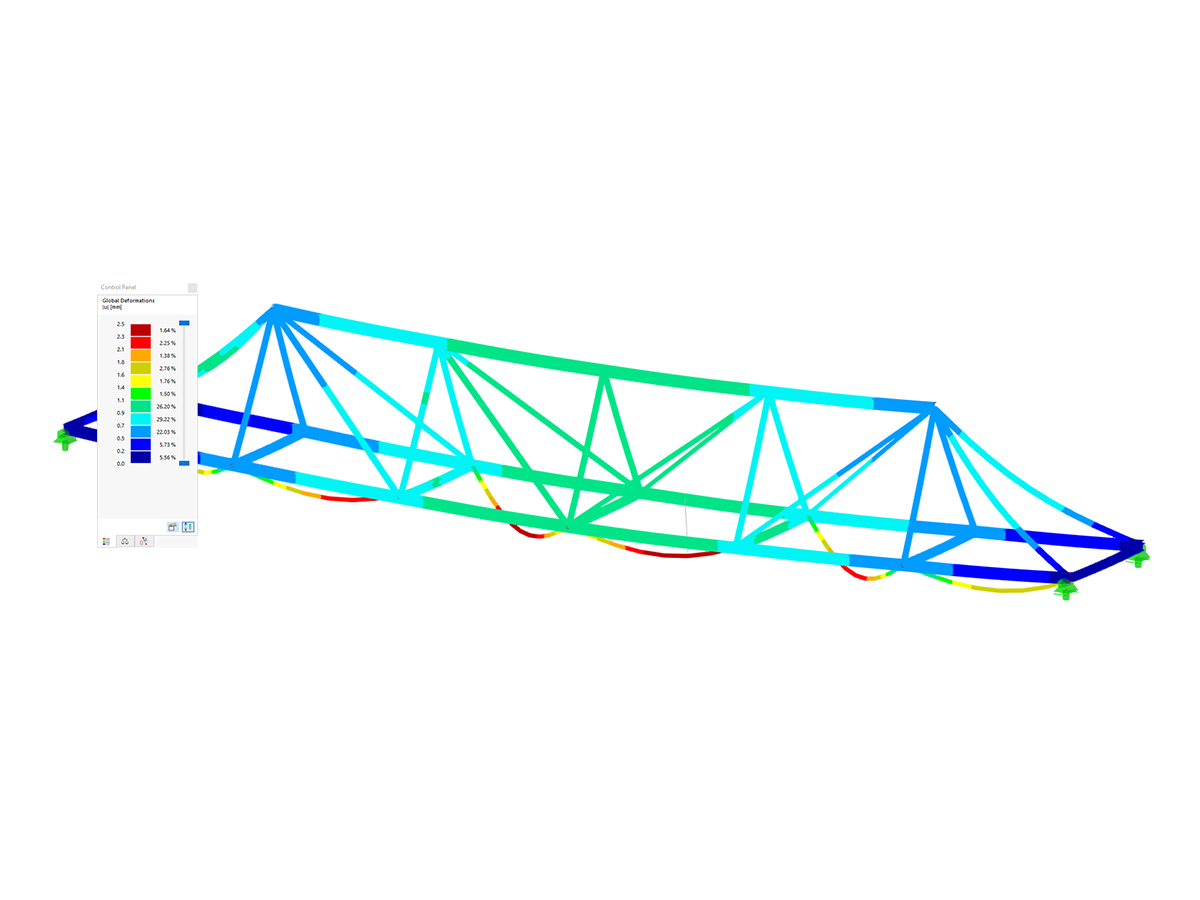
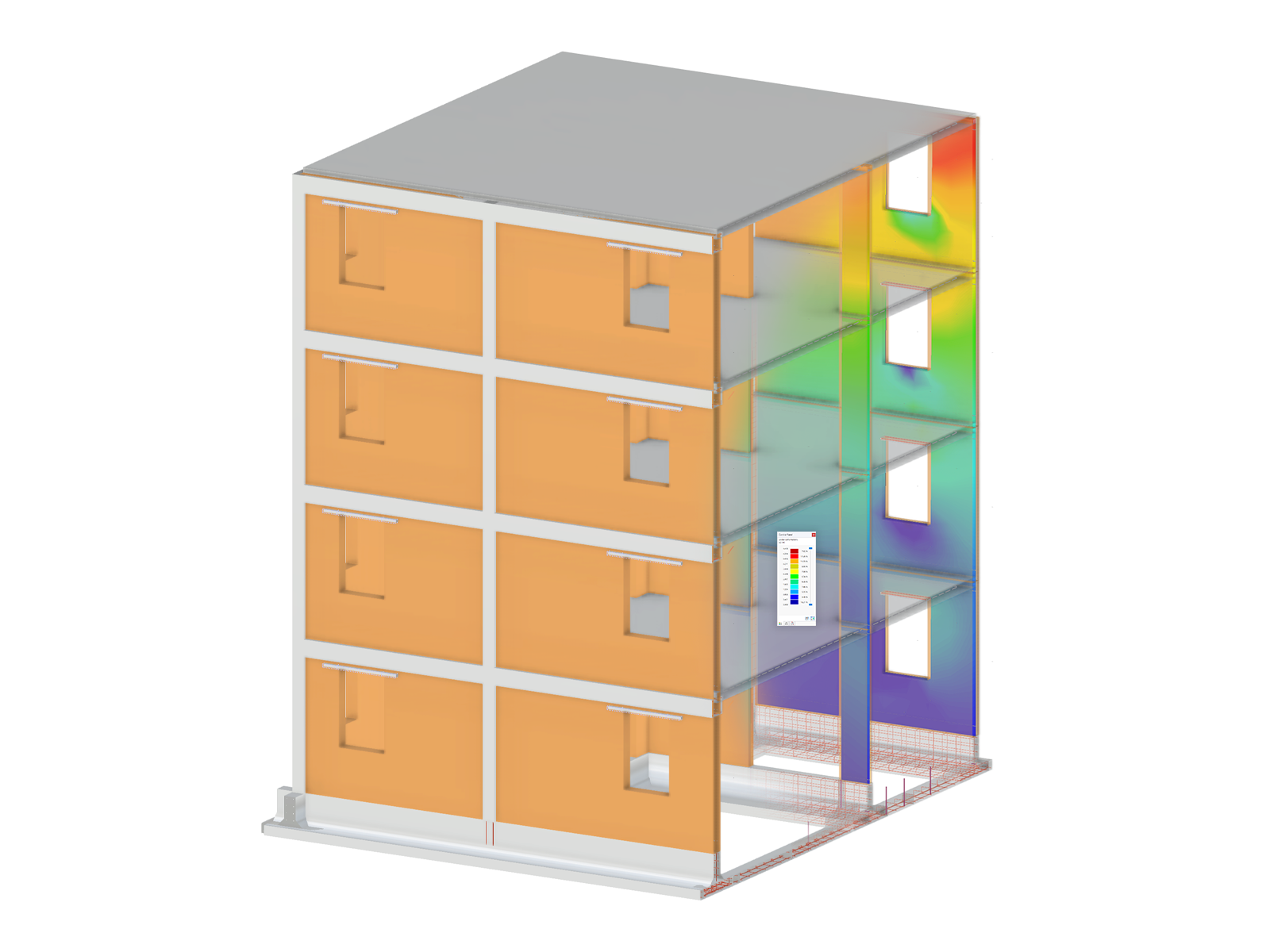
Dynamic analysis is a fundamental aspect of structural analysis, crucial for understanding how structures respond to time-dependent forces such as earthquakes, wind, machinery vibrations, and vehicular loads. Unlike static analysis, which assumes loads are applied gradually and remain constant, dynamic analysis accounts for inertia, damping, and energy dissipation effects. This makes it essential for designing resilient structures that can withstand seismic events, prevent excessive vibrations, and ensure long-term stability. Consequently, in civil engineering, dynamic analysis is used extensively in:
- Seismic design
- Vibration control
- Machine foundations
- Natural frequency analysis
Dlubal Software provides powerful solutions to tackle these dynamic challenges. With RFEM 6 and RSTAB 9, along with specialized add-ons for modal, response spectrum, pushover, and time history analysis, you can seamlessly perform seismic analysis, design vibration-resistant structures, evaluate machine foundations, and assess natural frequencies. The following text offers an overview of each add-on, along with valuable learning resources from the Dlubal website to support you in their practical application.
Modal Analysis Add-on
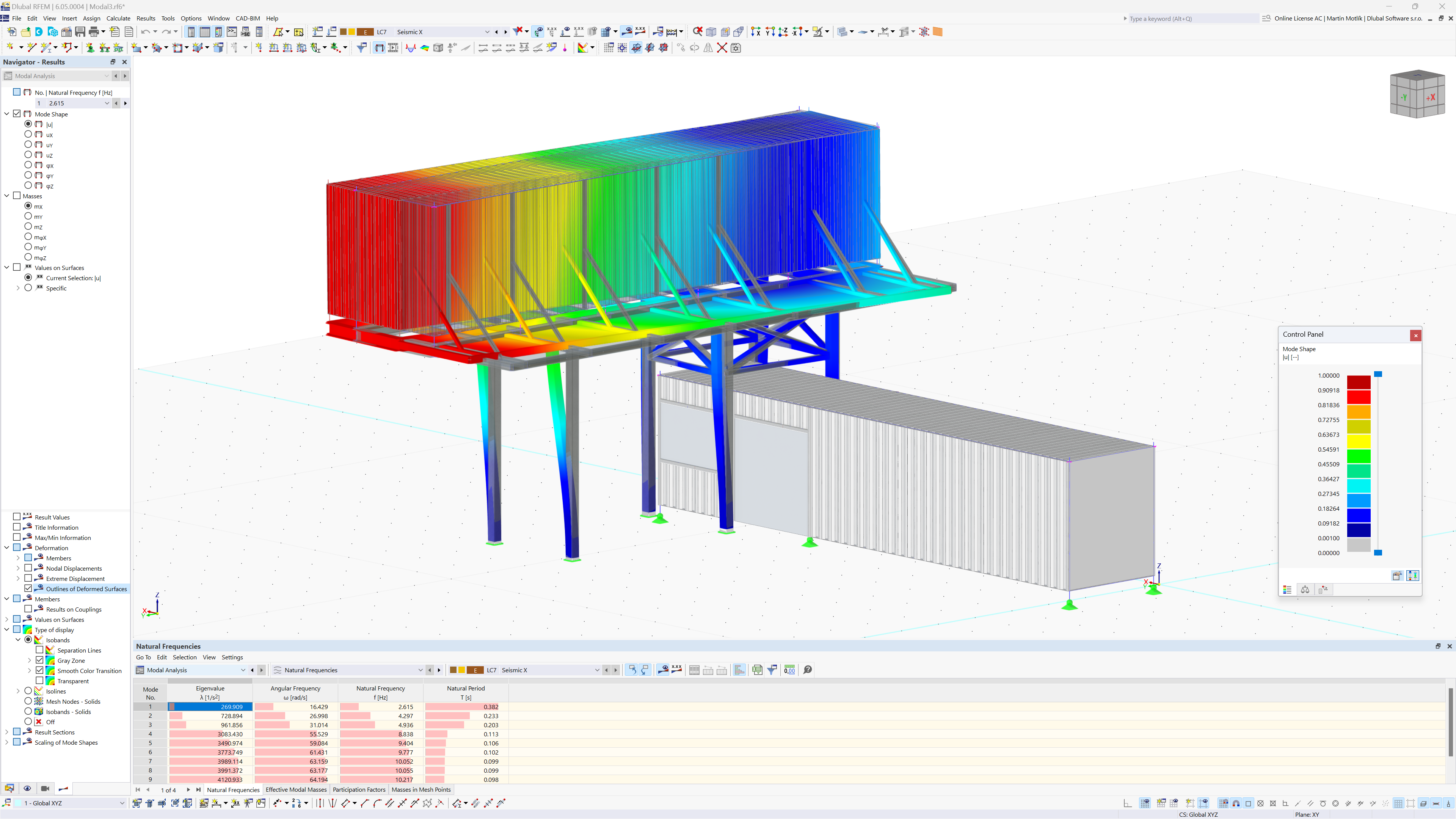
Modal analysis is a crucial tool in structural engineering, providing insights into a structure’s natural vibration characteristics. By identifying a structure's natural frequencies and mode shapes, engineers can prevent resonance, optimize design, and enhance overall stability and safety.
The Modal Analysis add-on by Dlubal Software enables fast and efficient evaluation of natural frequencies and mode shapes for models containing members, surface, and solids, and it is a prerequisite for all other dynamic add-ons. All necessary input data are seamlessly imported from the main program RFEM 6 / RSTAB 9. Upon successful calculation, the mode shape, eigenvalue, angular frequency, natural frequency, period, effective modal mass, and participation factor for each mode are provided and fully integrated into the main program interface.
- KB 1739 | Modal Analysis in RFEM 6 Using Practical Example
- KB 1891 | Methods for Determining Number of Mode Shapes in Modal Analysis Add-on
- KB 1878 | Key Elements of Structural Dynamics: Mode Shape, Natural Period, and Modal Mass
Response Spectrum Analysis Add-on
The Response Spectrum Analysis add-on in RFEM 6 and RSTAB 9 enables efficient seismic analysis using the multi-modal response spectrum method. Users can either select predefined spectra based on international standards or define custom spectra as needed. The add-on also allows for the consideration of accidental torsion, ensuring a more comprehensive analysis. By combining the deformation shapes of individual modes with the corresponding accelerations from the response spectrum, the software calculates the system’s deformations and internal forces directly—eliminating the need to generate equivalent static loads.
- Seismic Design in RFEM 6 and RSTAB 9 According to Eurocode
- KB 1721 | Seismic Analysis in RFEM 6
- KB 1860 | NBC 2020 Modal Response Spectrum Analysis and Base Shear Considerations in RFEM 6
- KB 1823 | Superposition of Modal Responses in Response Spectrum Analysis Using Equivalent Linear Combination in RFEM 6 / RSTAB 9
- KB 1833 | Using Nonlinearities in Response Spectrum Analysis in RFEM 6
Pushover Analysis Add-on
The Pushover Analysis add-on offers a powerful tool for assessing the impact of earthquakes on a model, helping predict deformations and potential structural damage. It enables users to define parameters such as horizontal load distribution, load direction, constant loads, and response spectra for determining target displacement.
During the analysis, horizontal loads are applied in incremental steps, with a nonlinear static analysis performed at each step until a predefined limit is reached. The results obtained provide all the standard results of a static analysis, with data available for each load step. The results for each step can then be used to create a capacity curve of the structure, typically presented in a force-deformation diagram.
Furthermore, the capacity of the structure can be transferred to the acceleration-displacement (AD) format together with the response spectrum. This results in the creation of both the capacity spectrum and the acceleration-displacement response spectrum (ADRS). A unified presentation format allows a direct comparison between the capacity of the structure and the seismic demand within the same graph.
The target displacement is automatically calculated based on the analysis results, which can be reviewed both graphically and in table form. This facilitates the evaluation of individual acceptance criteria, not only for the target displacement load step but also for all other load steps. Additionally, static analysis results for each step are available for further detailed assessment.
- Webinar | Introduction to the New Pushover Analysis Add-on
- KB 1829 | Determining Bilinearization for Pushover Curve (N2 Method)
Time History Analysis Add-on
The Time History Analysis add-on enables dynamic structural analysis for external excitations, such as seismic loads, machine-induced vibrations, impact forces, and explosions. Users can enter force-time or acceleration-time diagrams and define calculation parameters, including the analysis method and maximum calculation time. The analysis is conducted using either modal analysis or the linear implicit Newmark method. Note that this add-on is limited to linear structural systems, meaning nonlinear elements are either ignored or converted to linear equivalents.
An essential extension of the Time History Analysis capabilities is the use of the Damper member type. This feature allows for the integration of local energy dissipation systems, such as tuned mass dampers, significantly enhancing the structure’s ability to mitigate dynamic responses.
Once the calculation is complete, the results are organized in tables and can be viewed for each time step or as an envelope. Additionally, the results can be displayed graphically, such as in calculation diagrams, and animated for further analysis.
- Webinar | Introduction to Time History Analysis in RFEM 6 (USA)
- Webinar | Analysis of Induced Vibrations in Time History Analysis Add-on in RFEM 6
- Webinar | Analysis of Pedestrian-Induced Vibrations Using Linear Time History Analysis in RFEM 6
Enhanced Seismic Analysis with Building Model Add-on in RFEM 6
The Building Model add-on in RFEM 6 can also play a significant role in seismic analysis. This add-on facilitates story-based modeling with rigid floor slabs, ensuring efficient mass distribution and an accurate assessment of the structural response. By utilizing the "rigid diaphragm" floor modeling approach, the model is further simplified by concentrating masses at the floor level, which can also be represented visually in the software.
A key advantage of the Building Model add-on is its capability to determine interstory drift, a critical parameter in seismic design. Story drift evaluation is essential to maintaining structural performance by limiting excessive displacement, which can lead to system instability or damage to nonstructural components such as partitions. With this functionality, engineers can also compute stability factors and interstory drift sensitivity coefficients, allowing them to determine whether P-delta effects need to be considered in the seismic analysis. These effects can then be incorporated directly into RFEM 6 alongside the Response Spectrum Analysis add-on for a more comprehensive assessment.
- KB 1877 | ASCE 7-22 and NBC 2020 Seismic P-Delta Considerations in RFEM 6
- KB 1866 | Determination of Sensitivity Coefficient to Investigate Need for Second-Order Analysis in Dynamic Analyses
Conclusion
Dynamic analysis plays a vital role in structural engineering, ensuring that buildings and infrastructure can effectively withstand dynamic forces such as earthquakes, wind, machinery vibrations, and vehicular loads. RFEM 6 and RSTAB 9, together with their specialized add-ons, offer a comprehensive and efficient approach to conducting these analyses. The Modal Analysis add-on forms the basis of dynamic evaluations by identifying natural frequencies and mode shapes. The Response Spectrum Analysis add-on allows engineers to model seismic loading using multi-modal response spectrum methods, while the Pushover Analysis add-on assesses structural behavior and potential damage under increasing lateral forces. For more advanced time-dependent studies, the Time History Analysis add-on enables the simulation of machinery-induced vibrations and other dynamic effects.
Furthermore, the Building Model add-on enhances seismic design by supporting story-based modeling, interstory drift assessments, and P-delta effect evaluations. Its seamless integration with other add-ons ensures that seismic analysis results are efficiently organized and presented within RFEM 6.
By utilizing these advanced tools, engineers can refine structural designs, improve resilience against dynamic forces, and ensure adherence to seismic design standards, ultimately contributing to safer and more reliable infrastructure.
.png?mw=760&hash=90990fc10b779d88590f165264d767957a74ebb6)