Unfortunately, I cannot find any information about how to design a strip foundation in RFEM. Is this not possible? What would be the alternative option?
Answer:
Currently, there is no RFEM add-on module for the design of strip foundations. RF-FOUNDATION PRO can only design independent foundations arranged on nodal supports.
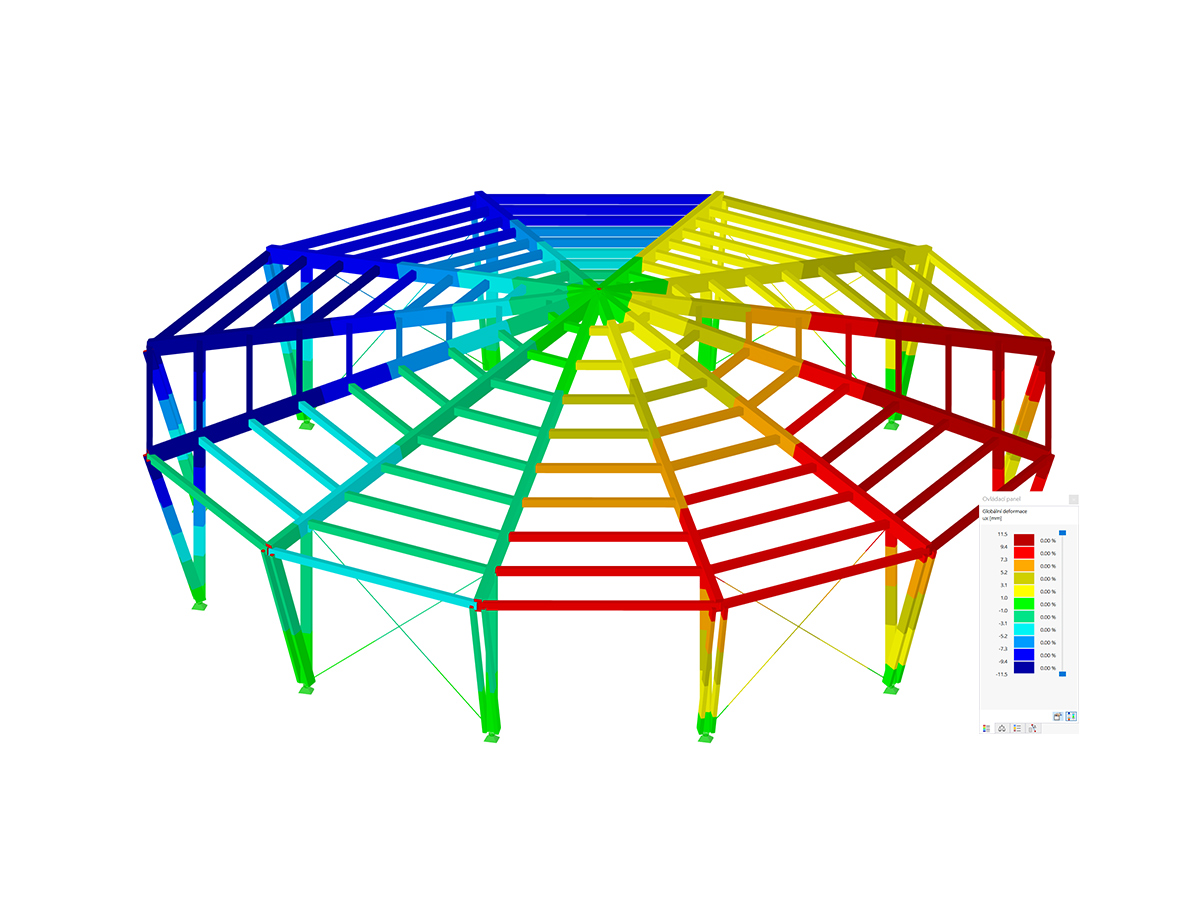
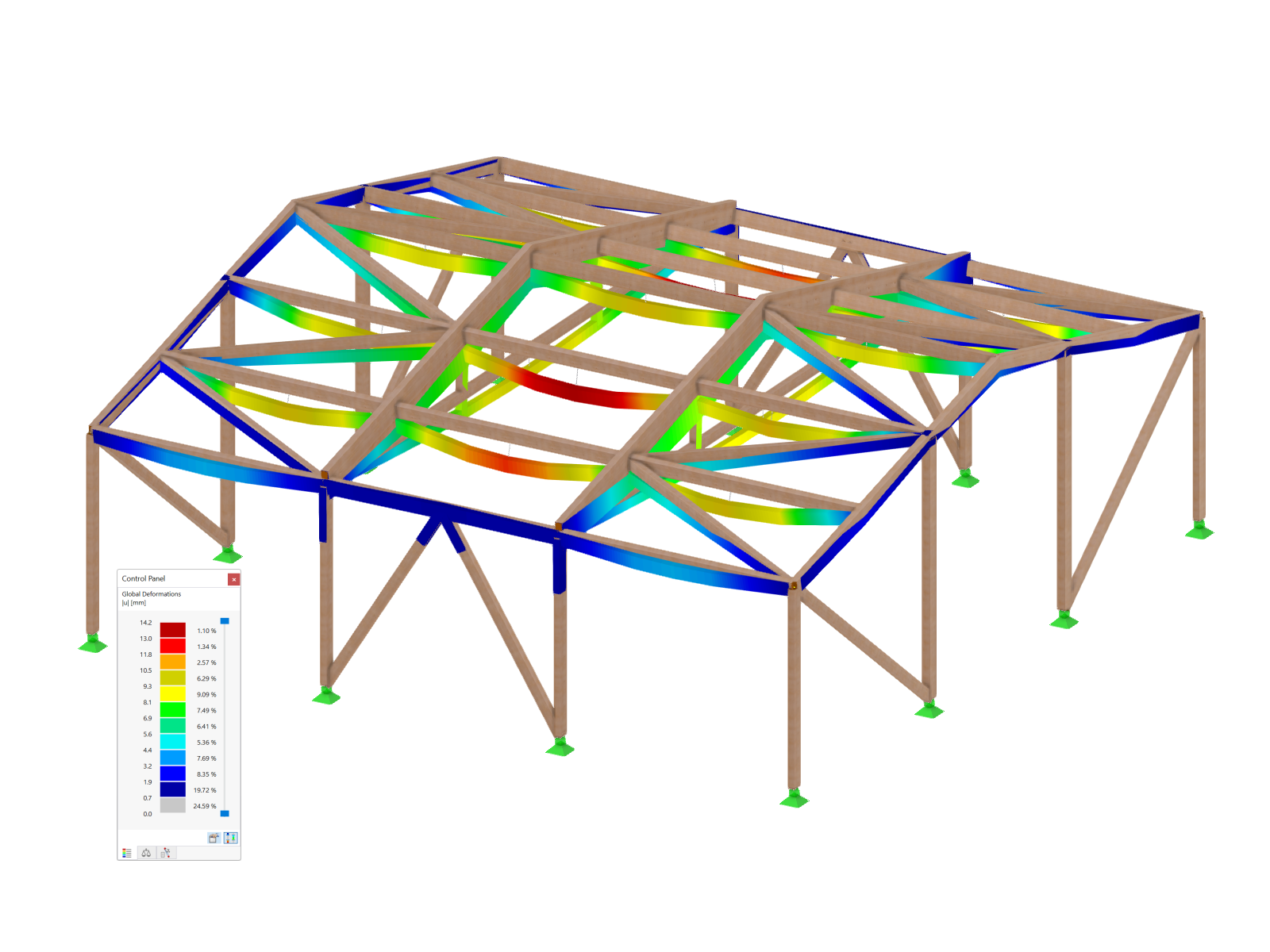
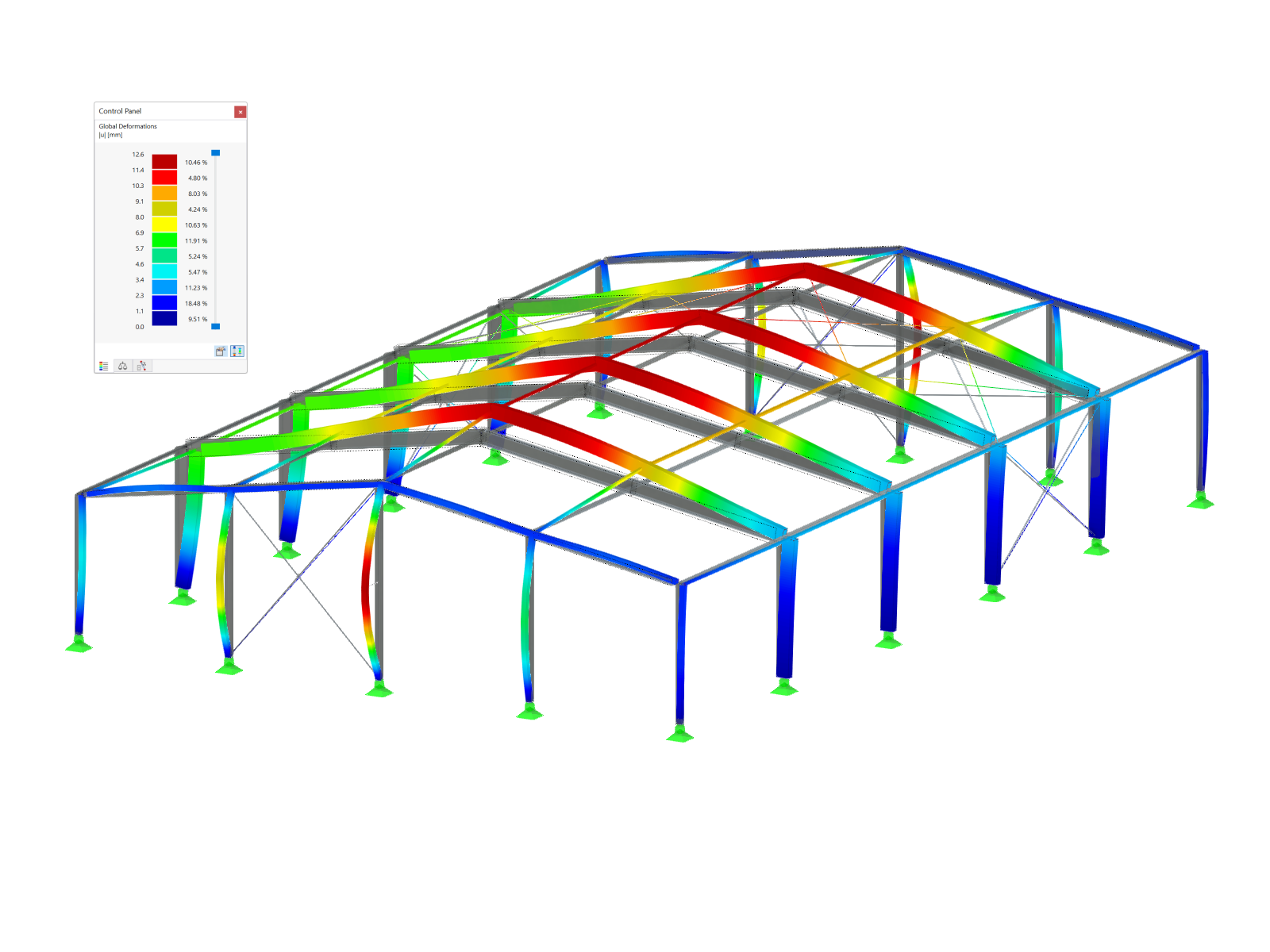
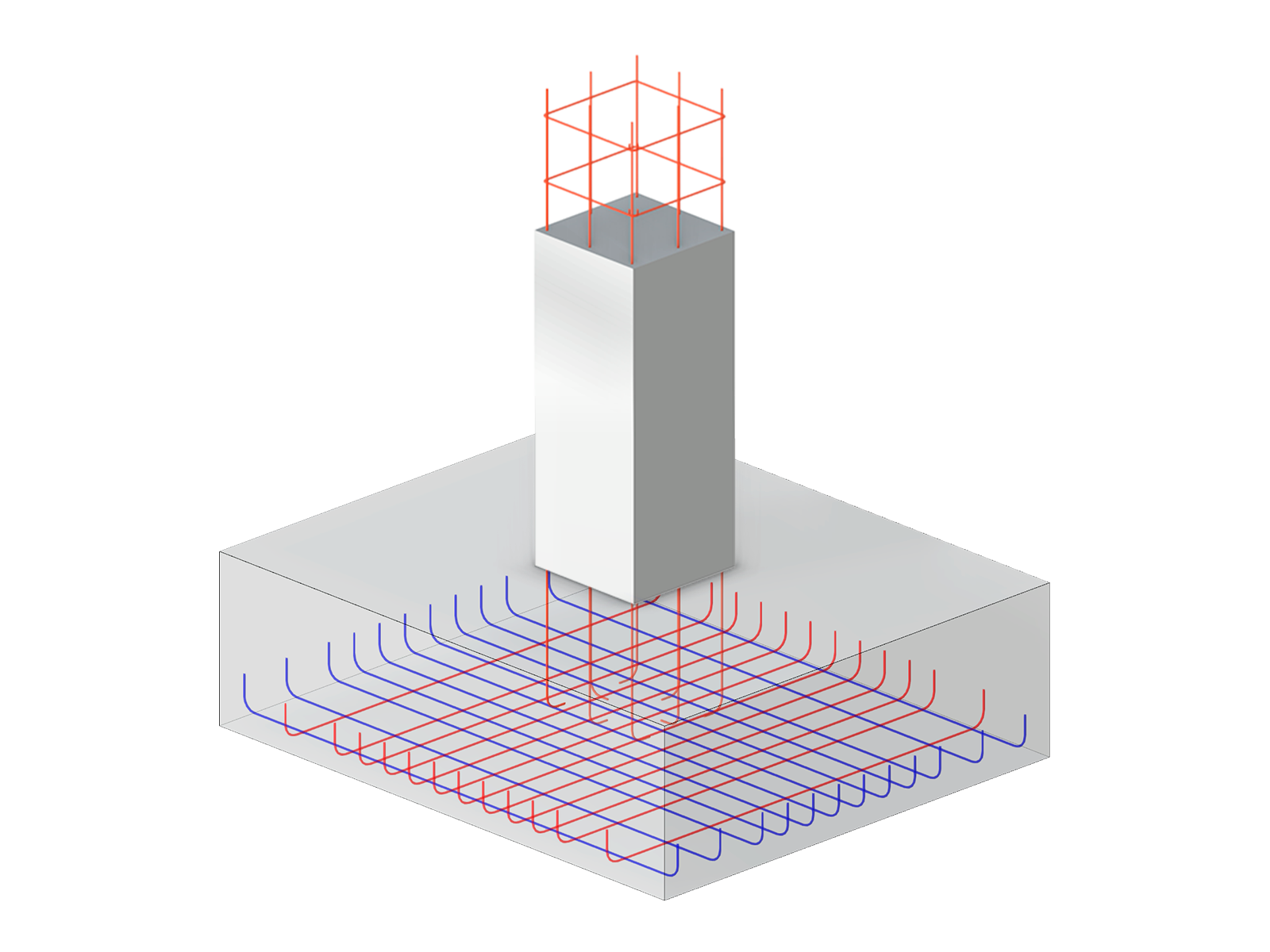
In most cases, line supports are used in the model; strip foundations are subsequently designed for these supports. As a solution, you could create an equivalent model and apply the governing support forces resulting for a "3.28-foot strip" as a load on a short member (for example, rigid member, since there is no additional dead load). This way, you obtain support forces on a nodal support for this 1m strip of the wall (see Image 01).
For these nodal support forces, you could then perform a single foundation design in RF‑FOUNDATION Pro according to EN 1997‑1 by defining the "strip foundation" as a 3.28-foot-wide plate foundation.
Another alternative would be to replace the line support with a reinforced concrete slab with an elastic foundation. Then, you could design the plate that represents the strip foundation in RF‑CONCRETE Surfaces. However, the design of the static equilibrium, soil pressure stresses, and so on, must then be performed manually using the RFEM results (for example, the evaluation of contact stresses σz).
You can find more information on the design of independent foundations in RF‑FOUNDATION Pro (see Links) in the technical article in our Knowledge Base.
| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Equivalent Model of Strip Foundations
| Number of Nodes | 6 |
| Number of Lines | 5 |
| Number of Members | 1 |
| Number of Surfaces | 1 |
| Number of Load Cases | 1 |
| Total Weight | 0.900 tons |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 3.250 x 0.500 x 2.250 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 10.66 x 1.64 x 7.38 feet |
| Program Version | 5.23.01 |
You can download this structural model to use it for training purposes or for your projects. However, we do not assume any guarantee or liability for the accuracy or completeness of the model.
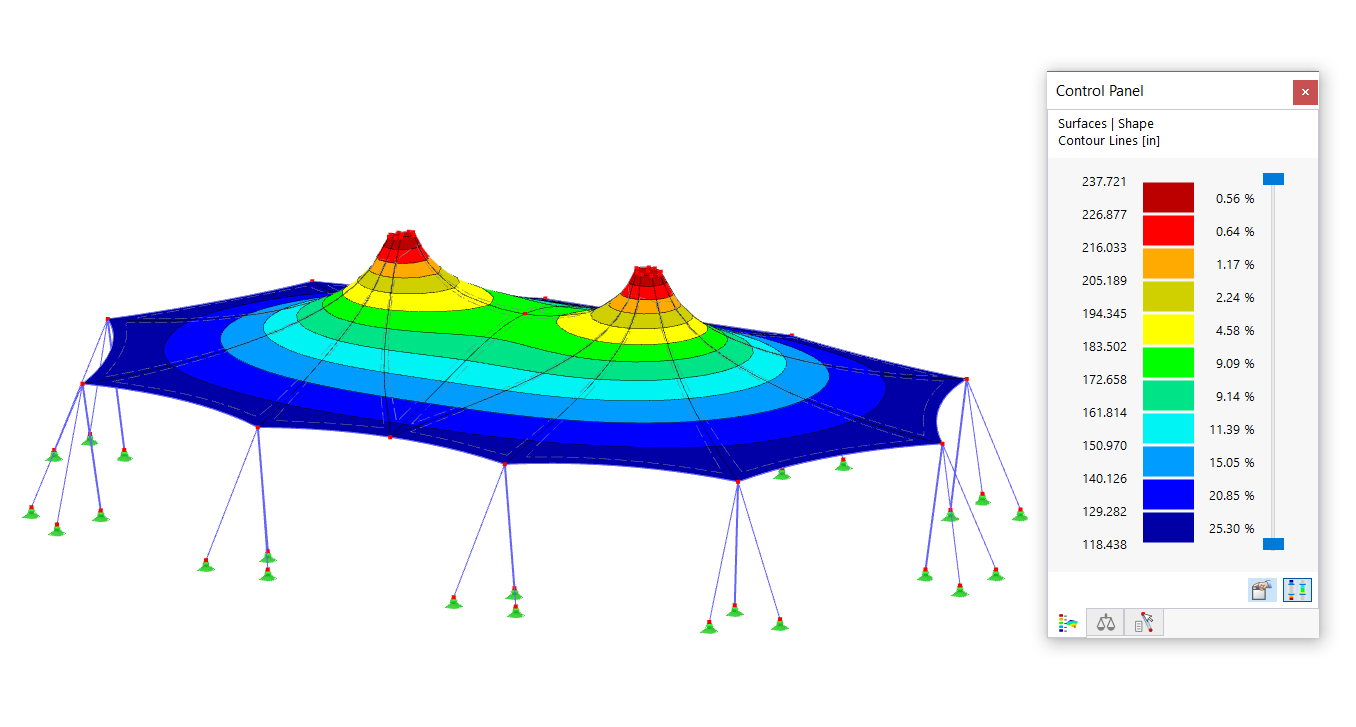
![Basic Shapes of Membrane Structures [1]](/en/webimage/009595/2419502/01-en-png-png.png?mw=512&hash=6ca63b32e8ca5da057de21c4f204d41103e6fe20)
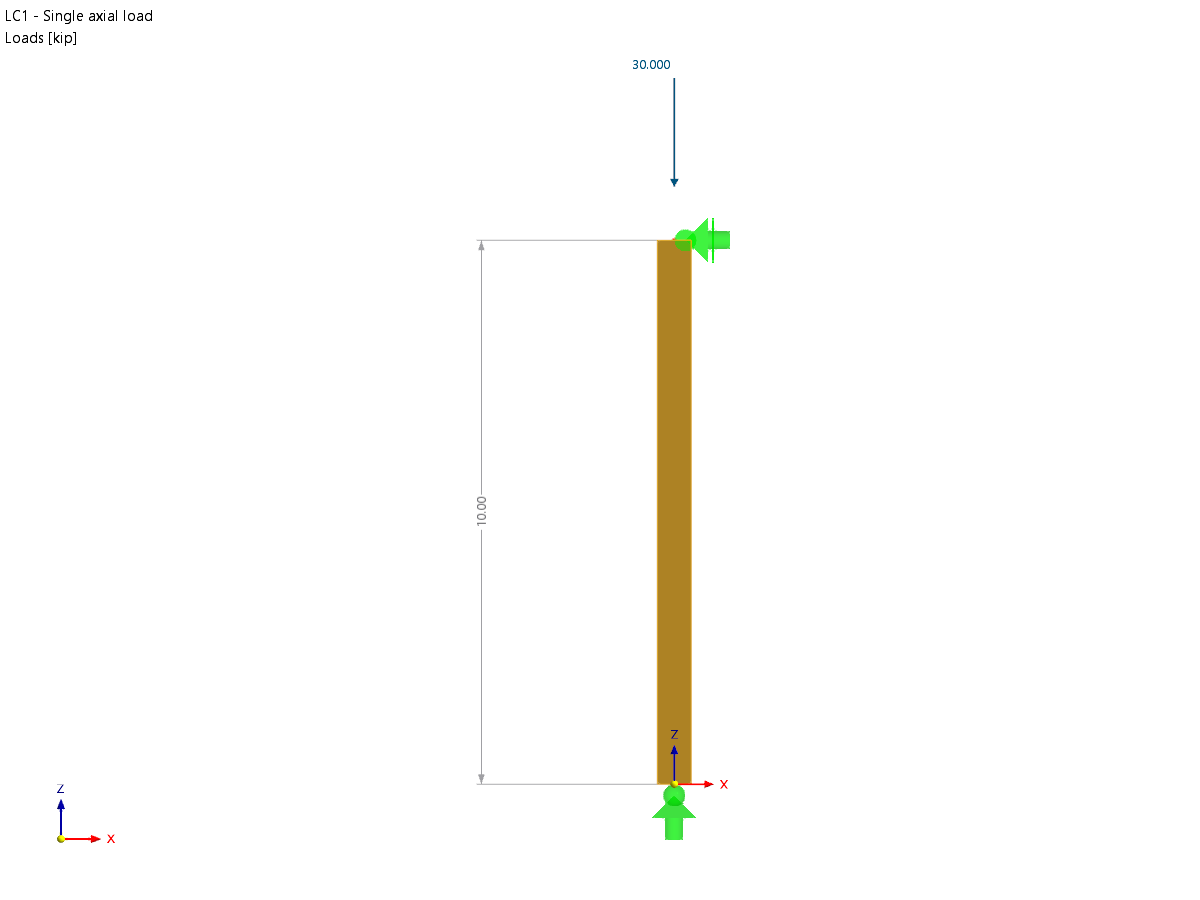
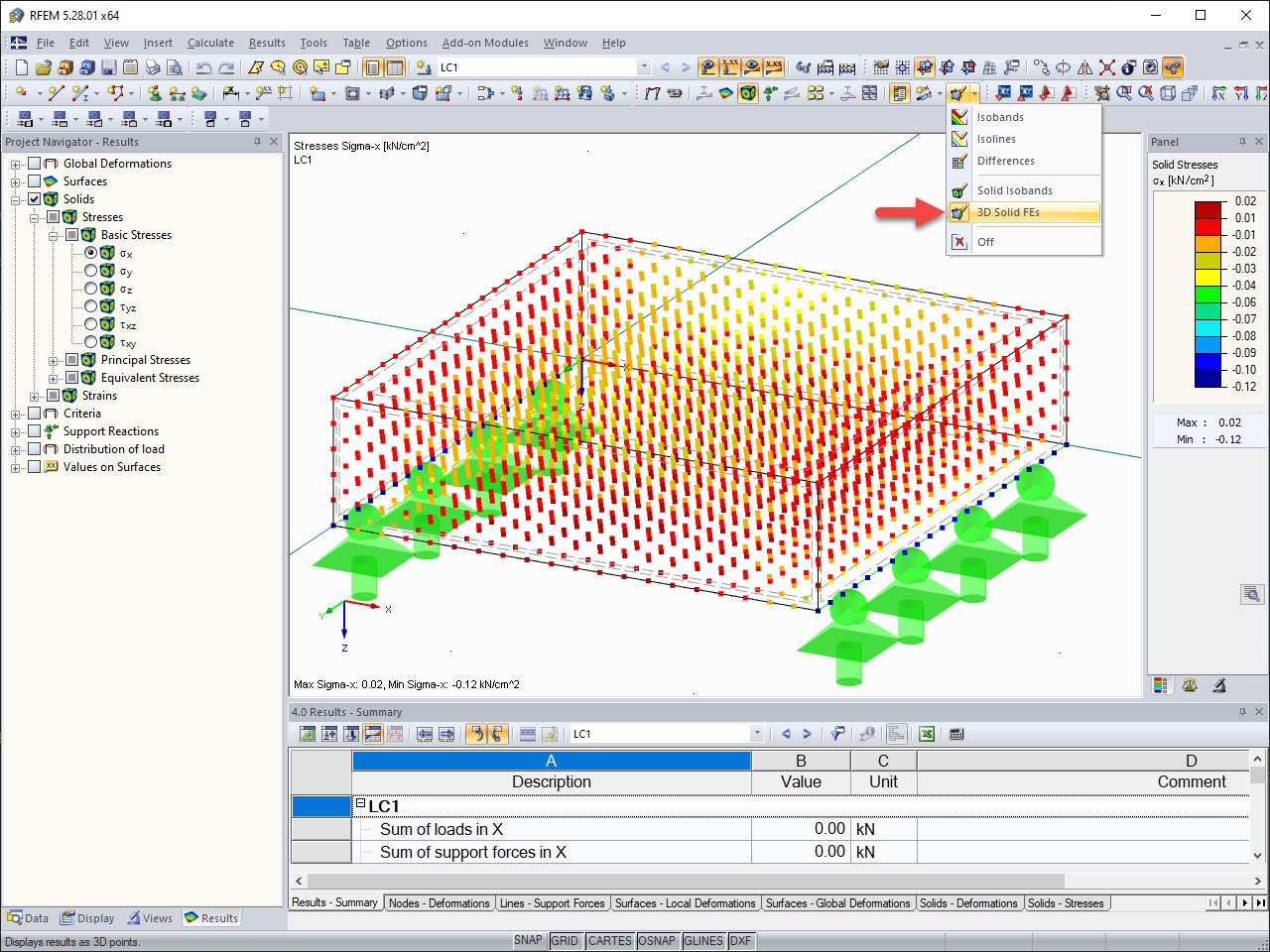
The results of solid stresses can be displayed as colored 3D points in the finite elements.
.png?mw=512&hash=ea9bf0ab53a4fb0da5c4ed81d32d53360ab2820c)
The number of degrees of freedom in a node is no longer a global calculation parameter in RFEM (6 degrees of freedom for each mesh node in 3D models, 7 degrees of freedom for the warping torsion analysis). Thus, each node is generally considered with a different number of degrees of freedom, which leads to a variable number of equations in the calculation.
This modification speeds up the calculation, especially for models where a significant reduction of the system could be achieved (for example, trusses and membrane structures).

Display extended strains of members, surfaces, and solids (for example, the important principal strains, equivalent total strains, and so on) in the Project Navigator - Results in RFEM as well as in Table 4.0.
For example, you can display governing plastic strains when performing the plastic design of connections with surface elements.

RFEM and RSTAB models can be saved as 3D glTF models (*.glb and *.glTF formats). View the models in 3D in detail with a 3D viewer from Google or Babylon. Take your VR glasses, such as Oculus, to "walk" through the structure.
You can integrate the 3D glTF models into your own websites using JavaScript according to the instructions (as on the Dlubal website Models to Download): "Easily display interactive 3D models on the web & in AR" .
Where can I find the update reports for RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, SHAPE-THIN, SHAPE-MASSIVE, RX-TIMBER, CRANEWAY, PLATE-BUCKLING, COMPOSITE-BEAM?
For my NVIDIA graphics card, I need to select between a driver from the "Production Branch" and a "New Feature Branch." Which driver is best suited for RFEM/RSTAB?
Why do I get an error message about invalid material when defining timber surfaces?



.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)























_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)















.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)