General Description
Materials are required to define surfaces, cross-sections, and solids. The material properties are yielding into the stiffness of these objects.
A Color is assigned to each material, which is used for the display of objects in the rendered model (see 11.1.9 Rendering ).
For new models, RFEM presets the two materials that were last used.
Material Description
Any name can be chosen as a Description of the material. When the entered name corresponds to an entry of the library, RFEM imports the material properties.
Note
The import of materials from the library is described in the Opening the library section.
Modulus of Elasticity E
The modulus of elasticity E describes the ratio between normal stress and strain.
To adjust the settings for Materials, click Edit → Units and Decimal Places in the menu or use the corresponding button.
Shear Modulus G
The shear modulus G, also known as the sliding modulus, is the second parameter for describing the elastic behavior of a linear, isotropic, and homogenous material.
Note
The shear modulus of the materials listed in the library is calculated from the modulus of elasticity E and Poisson's ratio ν according to Equation 4.1. Thus, a symmetrical stiffness matrix is ensured for isotropic materials. The shear modulus values determined in this way may deviate slightly from the specifications in the Eurocodes.
Poisson's Ratio ν
The following relation exists between modulus E and G, as well as Poisson's ratio ν:
|
E |
Modulus of elasticity |
|
G |
Shear modulus |
|
ν |
Poisson's ratio |
Note
When you manually define the properties of an isotropic material, RFEM automatically determines Poisson's ratio from the values of the E and G modulus (or the shear modulus from E modulus and Poisson's ratio).
For isotropic materials, the Poisson's ratio is usually between 0.0 and 0.5. Therefore, for a value of 0.5 or higher (for example, rubber), it is assumed that the material is not isotropic. Before the calculation starts, a query appears asking if you want to use an orthotropic material model.
Specific weight γ
The specific weight γ describes the weight of the material per volume unit.
The specification is especially important for the load type "self-weight". The automatic self-weight of the model is determined from the specific weight and the cross-sectional areas of the used members or surfaces and solids.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion α
This coefficient describes the linear correlation between changes in temperature and axial strains (elongation due to heating, shortening due to cooling).
The coefficient is important for the "temperature change" and "temperature differential" load types.
Partial Factor γM
This coefficient describes the safety factor for the material resistance; therefore, the index M is used. Use the factor γM to reduce the stiffness in the calculation (see 7.3.1 Load Cases and Combinations ).
Do not confuse the factor γM with the safety factors for the determination of design internal forces. The partial safety factors γ on the action side take part in combining load cases for load and result combinations.
Material Model
Twelve material models are available for selection in the list.
Use the [Details] button in the dialog box or table to access dialog boxes where you can define the parameters of the selected model.
Note
If the add-on module
RF-MAT NL
you can only use the Isotropic Linear Elastic and Orthotropic Elastic 2D/3D material models.
Isotropic Linear Elastic
The linear-elastic stiffness properties of the material do not depend on directions. They can be described according to Equation 4.1. The following conditions apply:
- E > 0
- G > 0
- −1 < ν ≤ 0.5 (for surfaces and solids; no upper limit for members)
The elasticity matrix (inverse of stiffness matrix) for surfaces is the following:
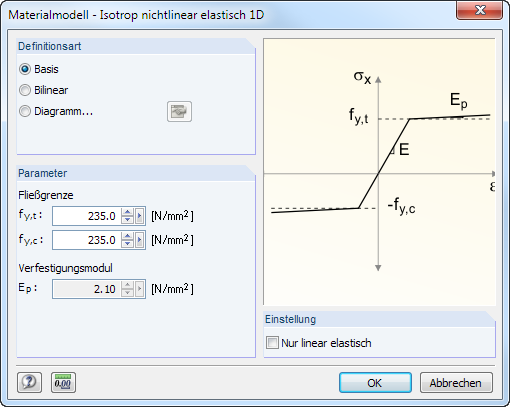
Isotropic Nonlinear Elastic 1D
You can define the nonlinear elastic properties of the isotropic material in a dialog box.
You have to define the yield strengths separately for tension (fy,t) and compression (fy,c) of the ideally or bilinearly elastic material. You can also define a stress-strain Diagram to display the material behavior realistically (see Figure 4.44).
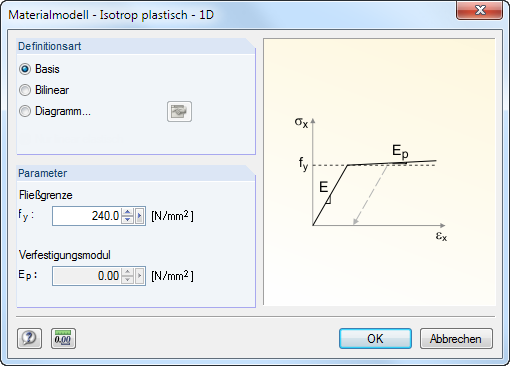
Isotropic Plastic 1D
If you have set the 3D model type (see Figure 12.23), you can define the plastic properties of the isotropic material in a dialog box. RFEM takes these properties for member elements into account, for example for the plastic calculation of a kinematic chain.
Note
The nonlinear material behavior is only determined correctly in the calculation if a sufficient number of FE nodes are created on the member. For this purpose, the following options are available:
- Divide Member Using n Intermediate Nodes dialog box (see Figure 11.91), method of division: Place new nodes on the line without dividing it
- FE Mesh Settings dialog box (see Figure 7.10), option: Use division for straight members with a Minimum number of member divisions of 10
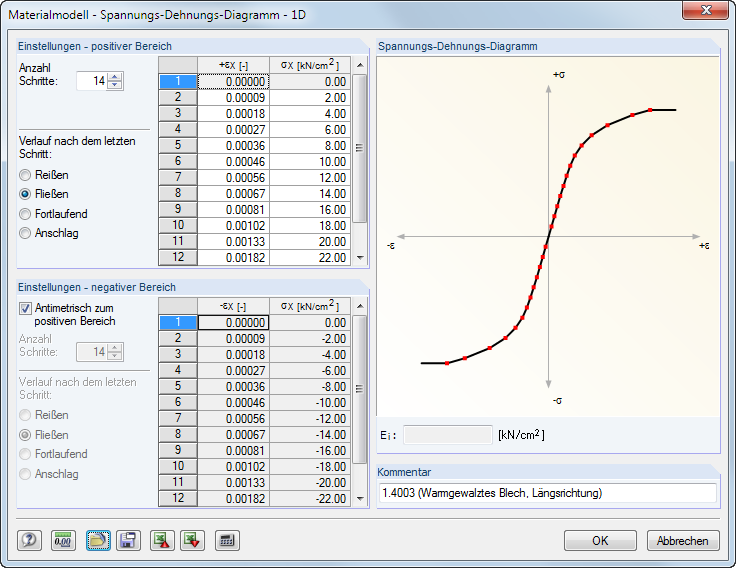
Specify the parameters of the ideally or bilinearly plastic material. You can also define a stress-strain Diagram to display the material behavior realistically.
The material properties can be defined separately for the positive and the negative zones. The Number of steps determines the number of definition points respectively available. Enter the strains ε and the corresponding normal stresses σ into the two lists.
There are several options for the Diagram after last step: Tearing for material failure when exceeding a certain stress, Yielding for restricting the transfer of a maximum stress, Continuous as in the last step, or Stop for restricting to a maximum allowable deformation.
It is also possible to import parameters from an [Excel] worksheet.
Watch the dynamic graphic in the Stress-Strain Diagram dialog section to check the material properties. The dialog field Ei below the graphic shows the modulus of elasticity E for the current definition point.
Use the
![]() button in the dialog box to save the stress-strain diagram so that you can apply it to different models. The
button in the dialog box to save the stress-strain diagram so that you can apply it to different models. The
![]() button allows you to create user-defined diagrams.
button allows you to create user-defined diagrams.
Note
For members with isotropic plastic material properties, the Activate shear stiffness of members (cross-sectional areas Ay, Az) check box in the Calculation Parameters dialog box (see Figure 7.25) has no effect. This material model uses the beam theory according to Euler-Bernoulli where shear distortions are neglected.
Isotropic Nonlinear Elastic 2D/3D
With this material model, you can display the properties of nonlinear materials for surfaces and solids. No energy is delivered to the model (conservative analysis). As the same stress-strain relations apply for loading and relief of load, no permanent plastic distortions are available after a relief.