System
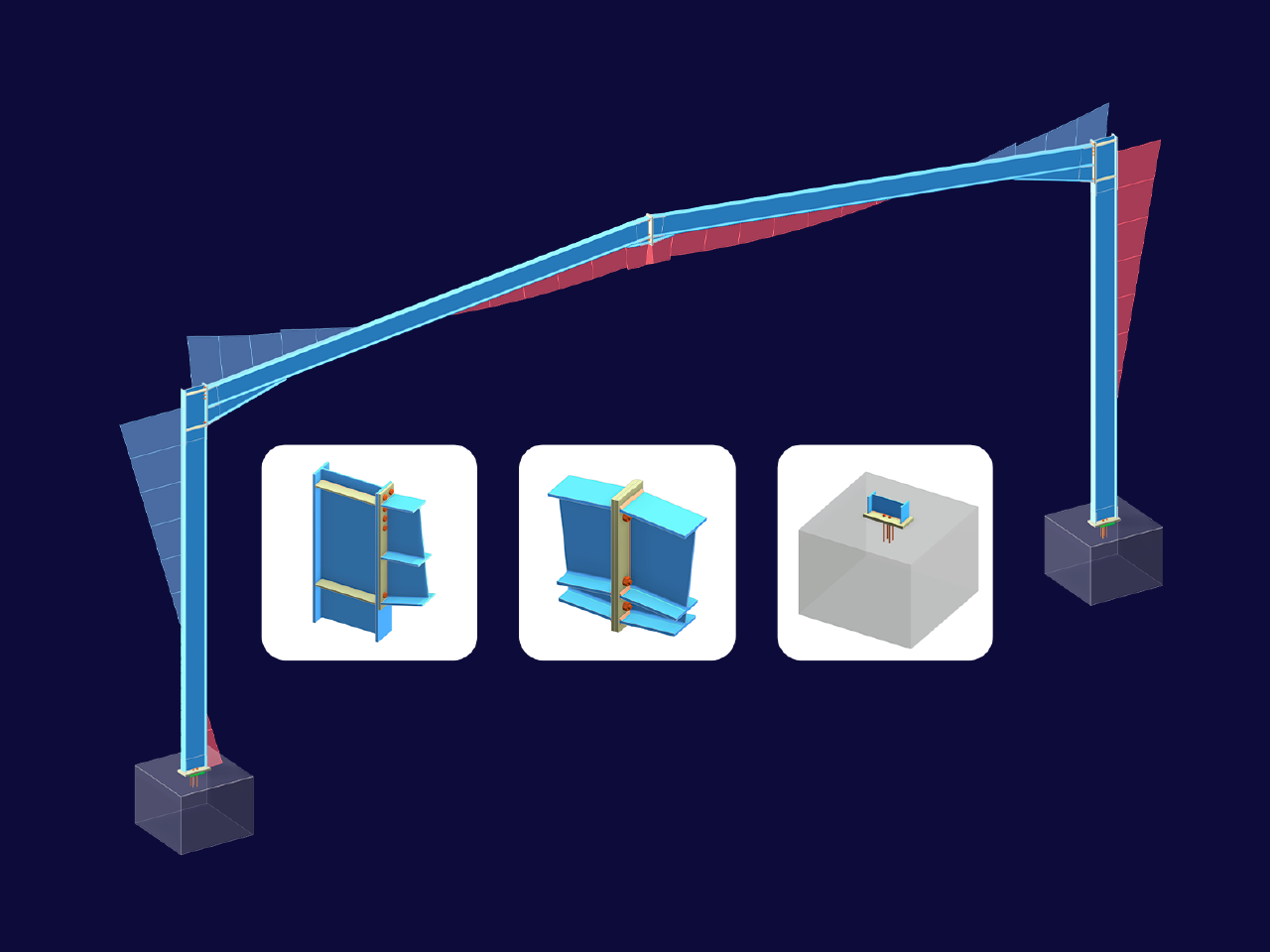
The entire structure is a simply supported half-frame, consisting of an IPE-160 beam with a length of 6 m and an IPE-200 column with a length of 4 m. The beam is connected to the column web with a welded, 5-millimeter-thick end plate by 4 x M12 bolts.
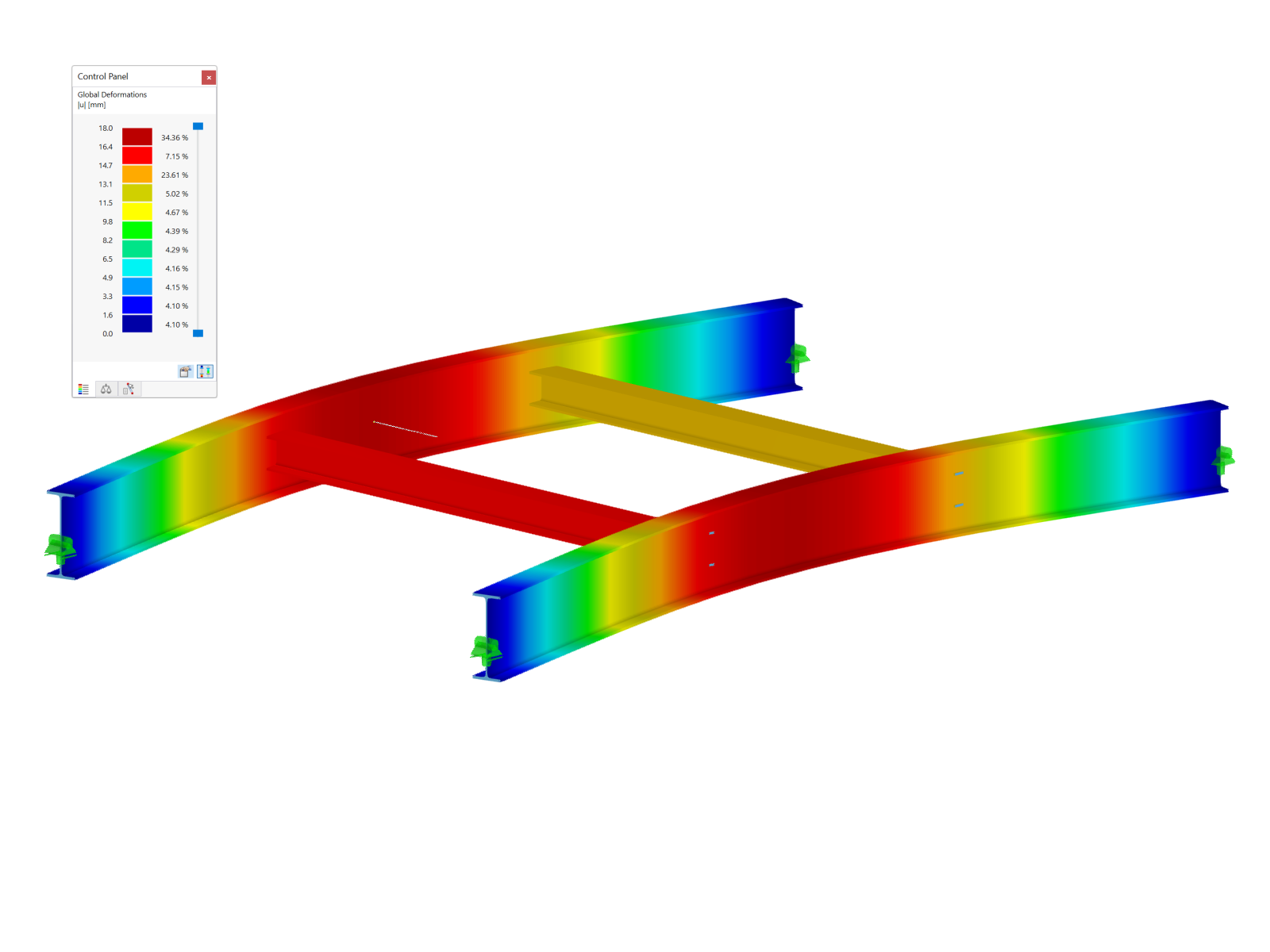
The loading of the structure is the self-weight as well as a distributed load of 8 kN/m oriented in the positive Z-direction (Image 01).
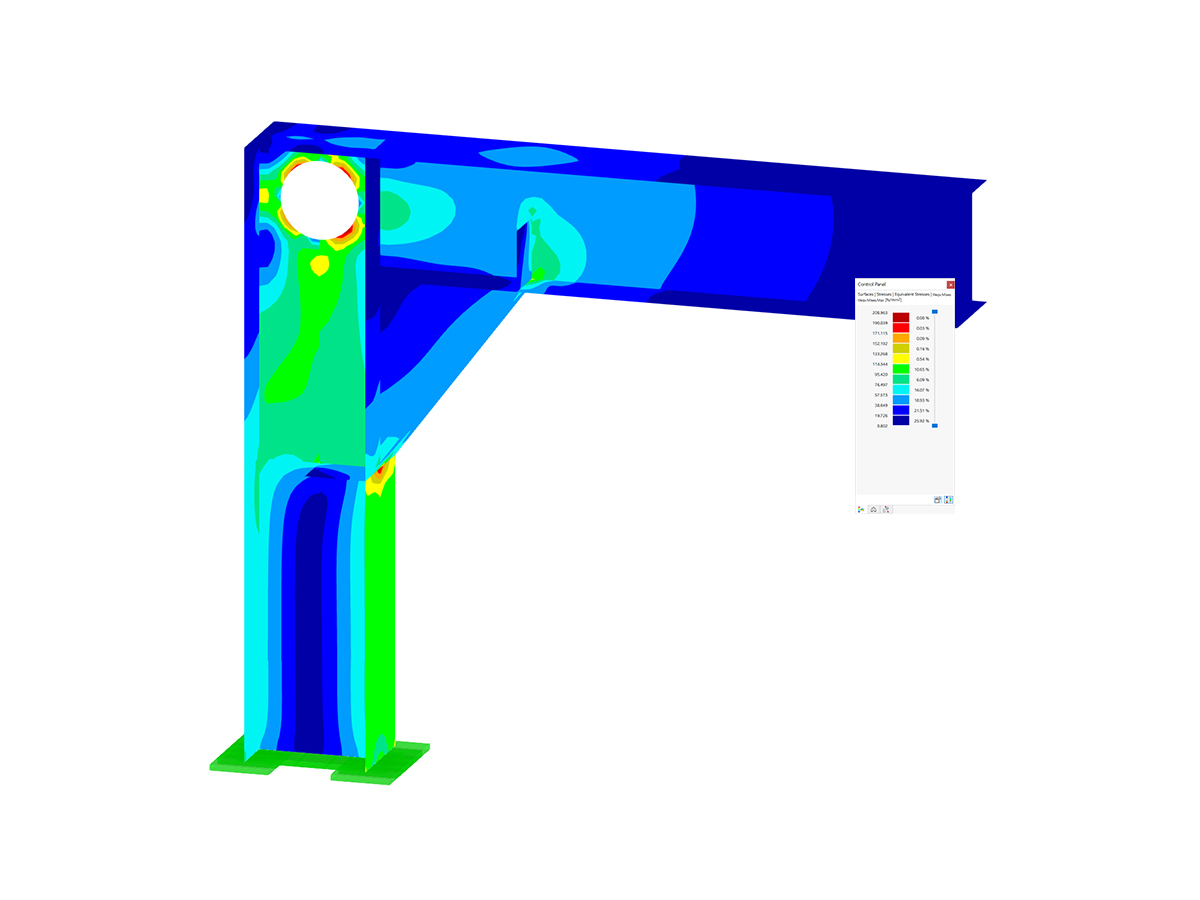
The end plate has the dimensions of w/h = 82/160 mm. The edge distances of the bolts amount to e1/e2 = 44/20.5 mm (Image 02).
Option 1: Design of Connection with RF-JOINTS Steel – Pinned
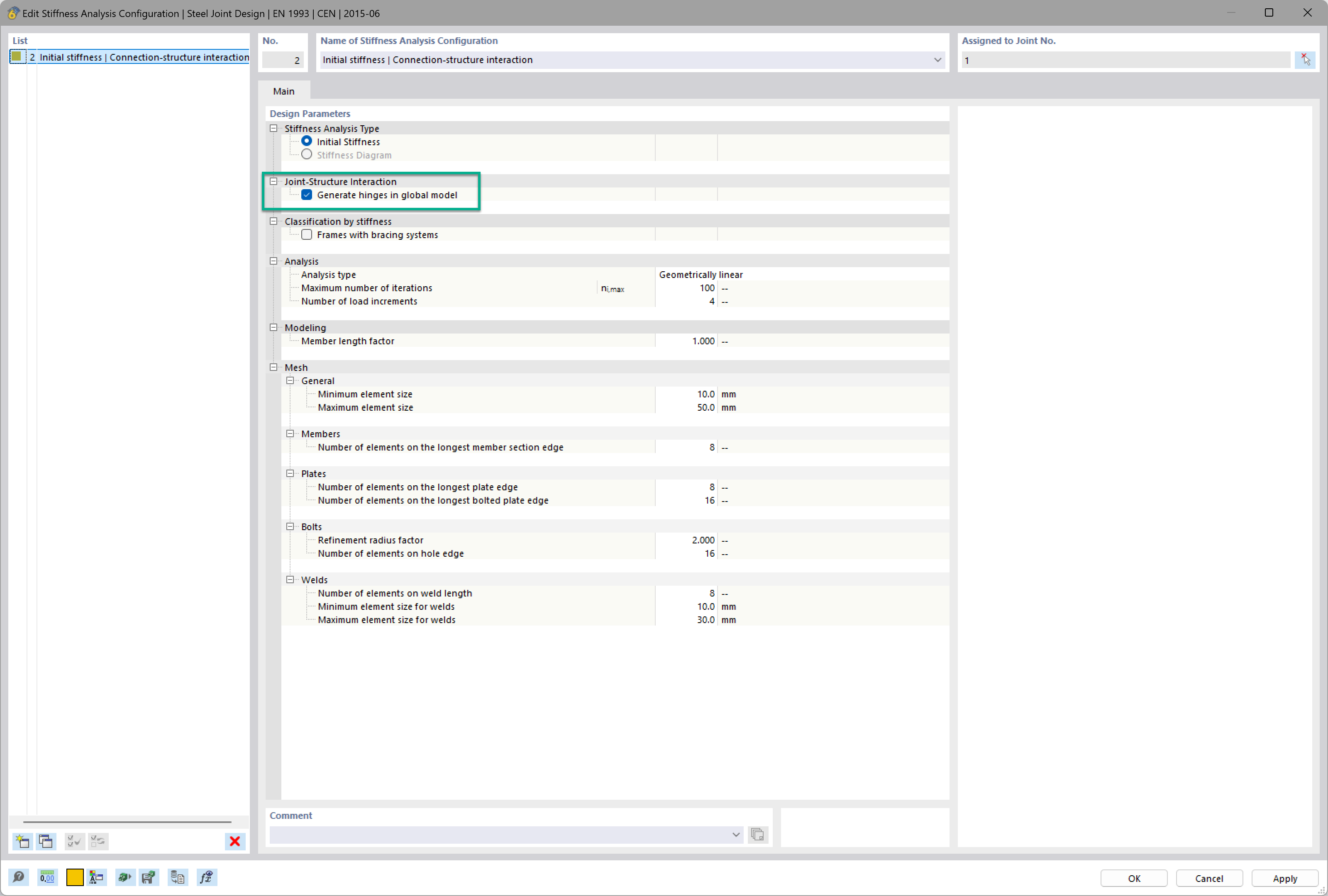
After having modeled the structure in RFEM, including load case and loading, the RF-JOINTS Steel – Pinned add-on module can be opened. The corresponding input data can then be defined in the add-on module so that the design of this connection can be performed within a short period of time.
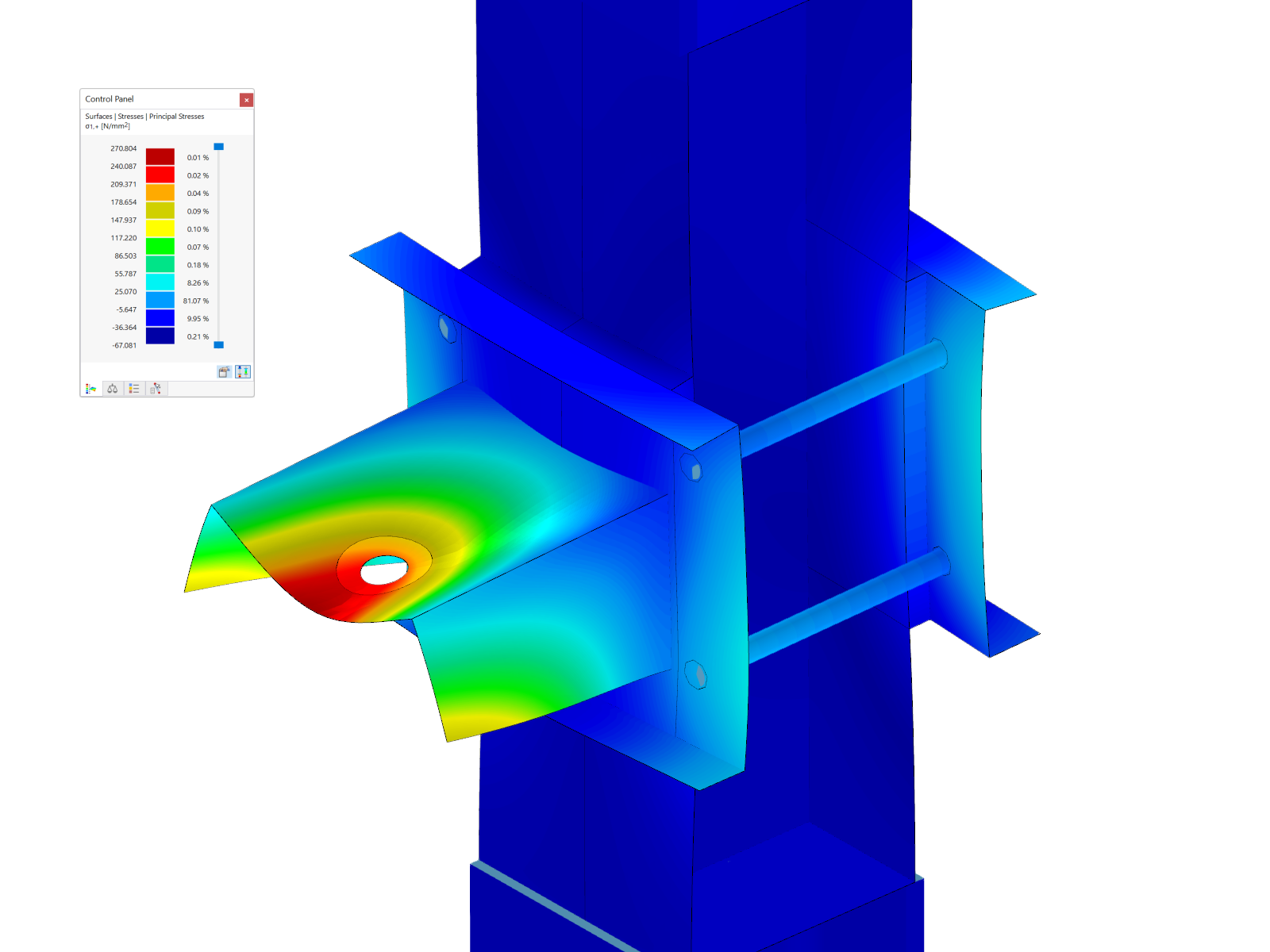
In this example, the carrying capacity of bolts in shear is the governing design (ratio 47%, Image 03). The maximum existing shear force Fn,Ed of a single bolt amounts to 6.12 kN.
Option 2: Modeling of Connection in RFEM
The alternative modeling of the connection in RFEM takes place in the following steps:
- Copy of the model, to be on the safe side.
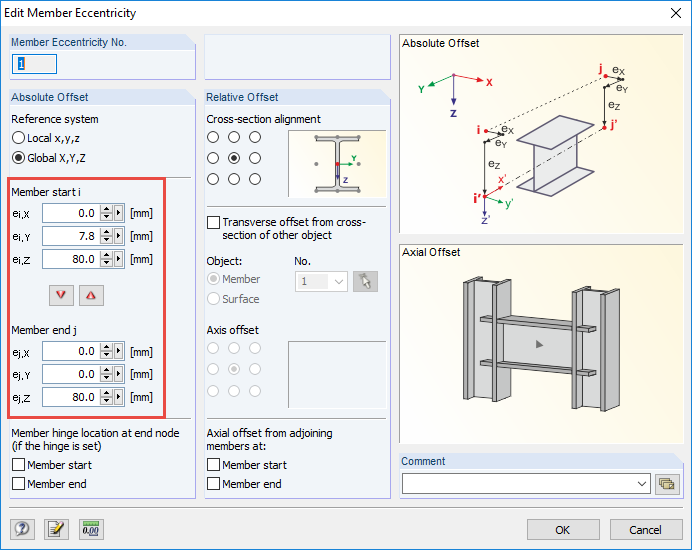
- Definition of the member eccentricity at the beam (half height of the beam in the Z direction, end plate thickness + half thickness of the column web in the Y direction, only at the end of the connection, see Image 04).
- Right-click on Members → "Generate Surfaces from Member".
- Deletion of nodal support, definition of hinged line supports at the bottom edge of the girder flange and at the end of the column web (see Image 05).
- Deletion of member load (8 kN/m) and conversion to surface load (97.6 kN/m² on the girder flange).
Connection:
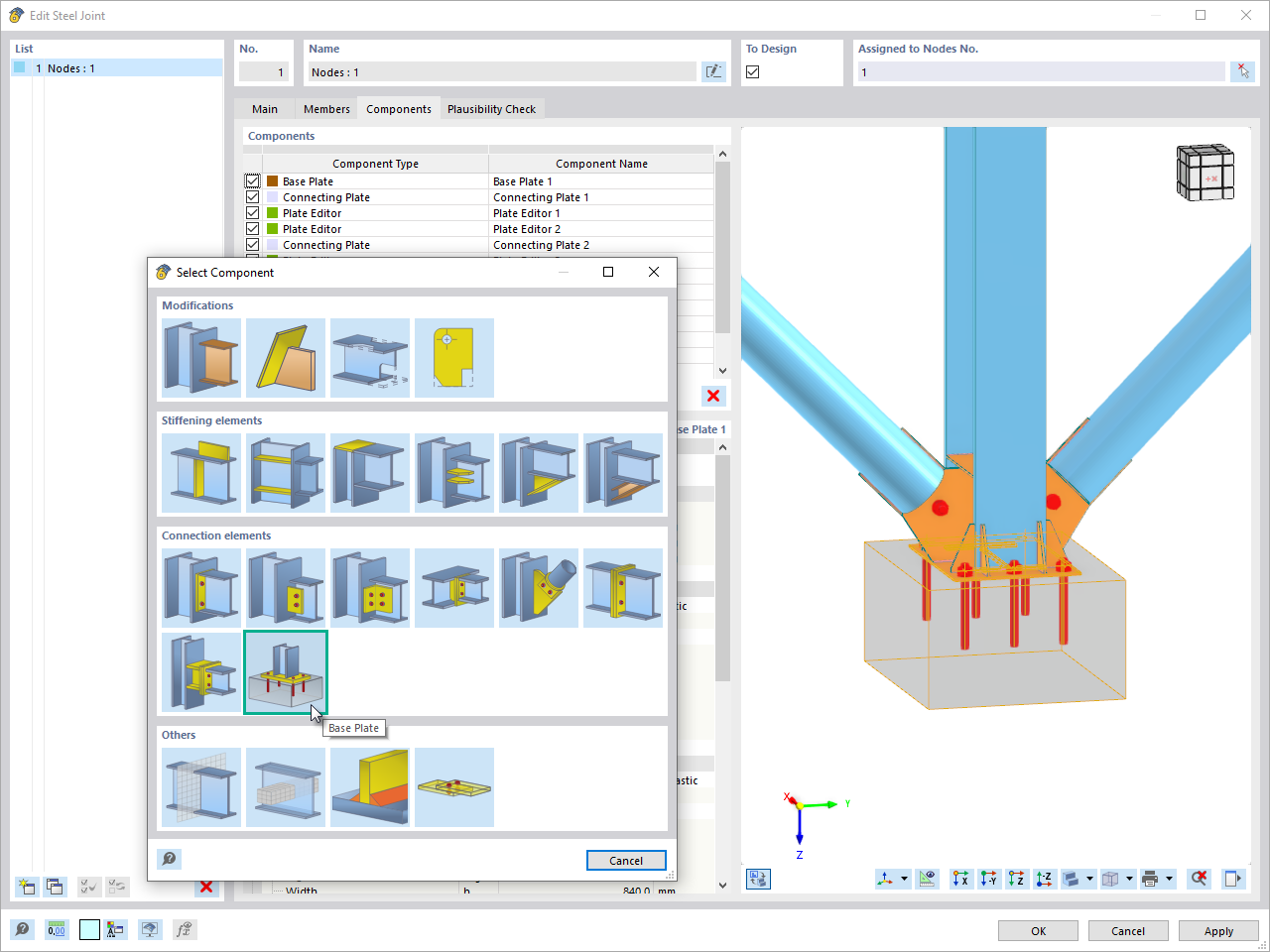
- Modeling an end plate as a solid element (cuboid, see Image 06).
- Insertion of the bolt holes with openings. See this article: KB | Inserting Openings, Holes, Drilled Holes in Solids
- Copy of solid end plate to the end of the girder. Please note: The end plate should have no contact with the surface of the column web due to the pinned joint; the force transmission is only carried out by the bolts (see Image 07).
- Copy of the openings of the end plate (bolt holes) to the surface of the column web.
- To ensure that no contact is present between the end plate and the surface of the column web, the calculation can be started at this point. A message about instability should appear.
- The four bolts can each be modeled as a cylindrical solid, consisting of circular and quadrangular surfaces.
- In order to receive member internal forces for the bolts, it is necessary to place a result beam in the middle of each bolt (see Image 08). In this example, a 12 mm round bar is used as the cross-section for simplification purposes. More information about the result beams is available in our Knowledge Base.
The calculation results in a maximum shear force in a bolt of Vz = 6.69 kN (see Image 09).
Conclusion
The results from the main program RFEM and the RF-JOINTS Steel – Pinned add-on module are relatively close and are therefore comparable. In this example, it becomes apparent that there are many options for modeling in RFEM. Compared to the fast design in the RF-JOINTS Steel – Pinned add-on module, the effort is, however, relatively high when modeling is performed manually so that the user has to decide individually which design option is used.



















.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)














.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)













_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)






.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)