The "prestress" load is treated by the program as an external load, like a member load, and it affects the entire structure. It "flows" off into the structural system and creates deformations and support reactions accordingly. The prestress is converted into a length change (a strain). Which axial force remains after the calculation depends on the deformation restraint of the member: if the stiffness of the connected system is soft, none or only very little of the prestress remains, but the deformation exists.
The prestress is thus comparable to a temperature change. It is expressed once with a force and once with a temperature.
In Example 2, the prestressing force is almost completely converted into the deformation, which results in much lower axial forces and thus also lower support forces.

























Dlubal_KohlA.png?mw=350&hash=6f6b192b31c8bbcb1c62aa6cf9fbfb1d9f859880)






.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)










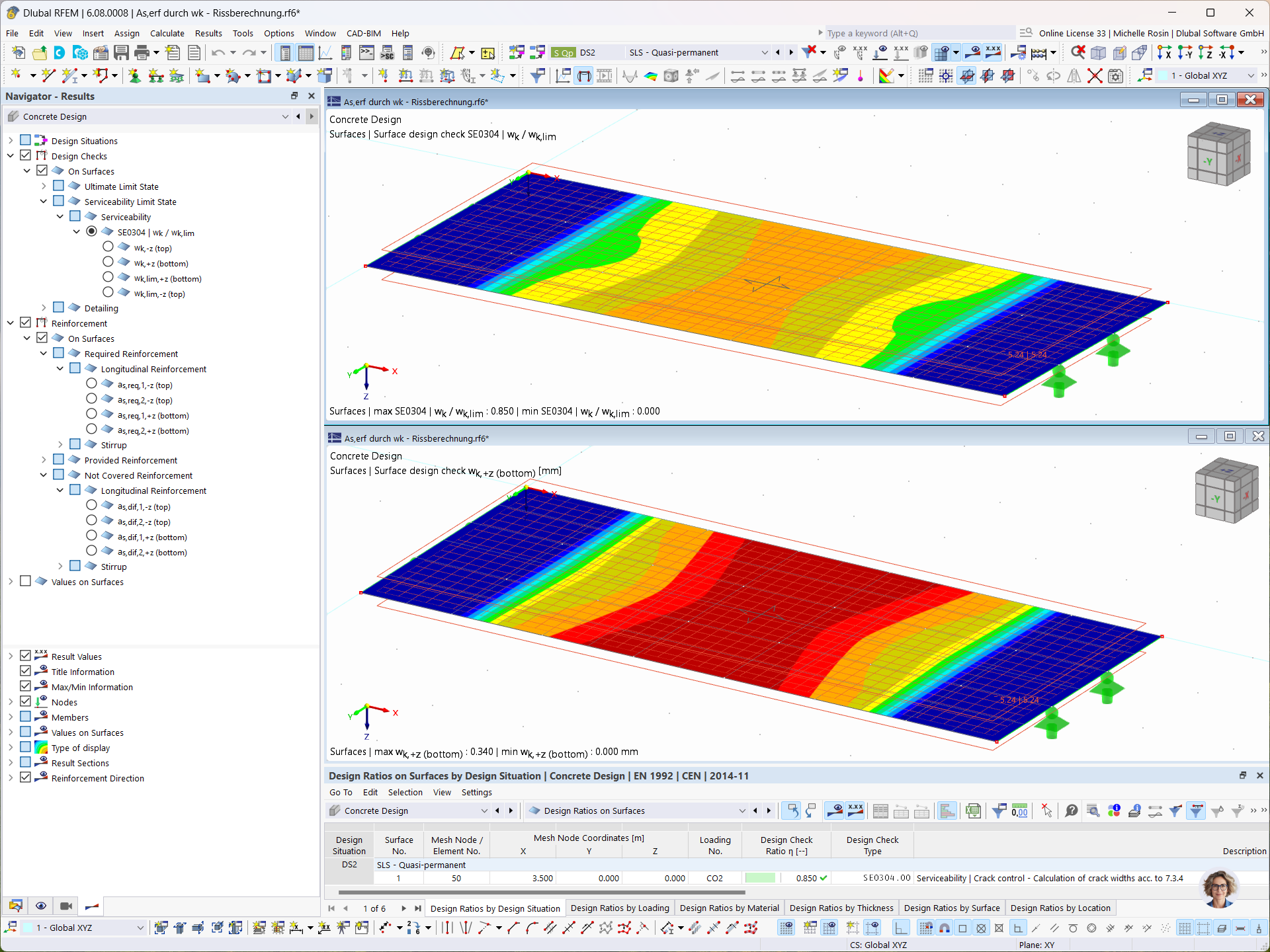

_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)


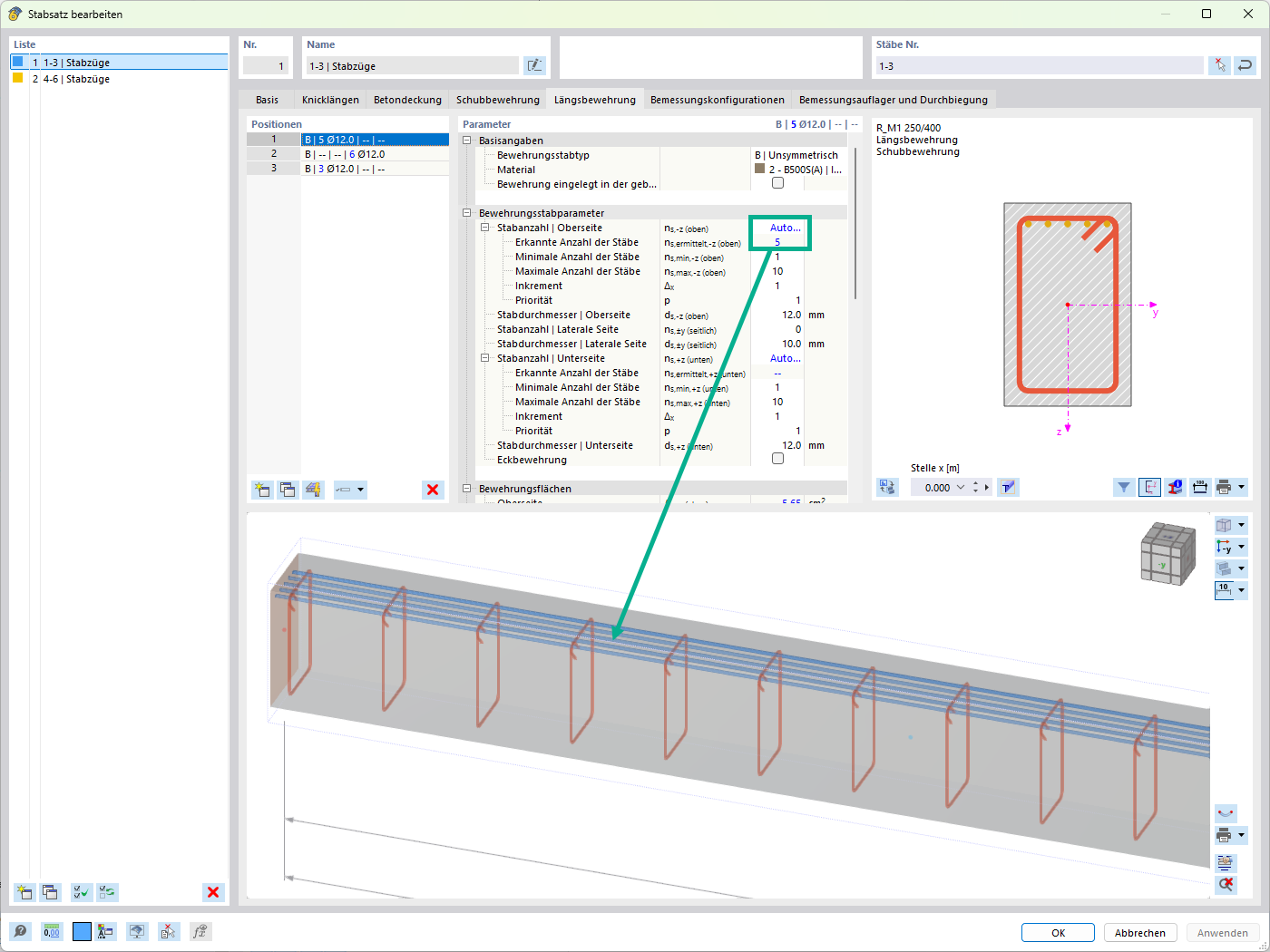
-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)

