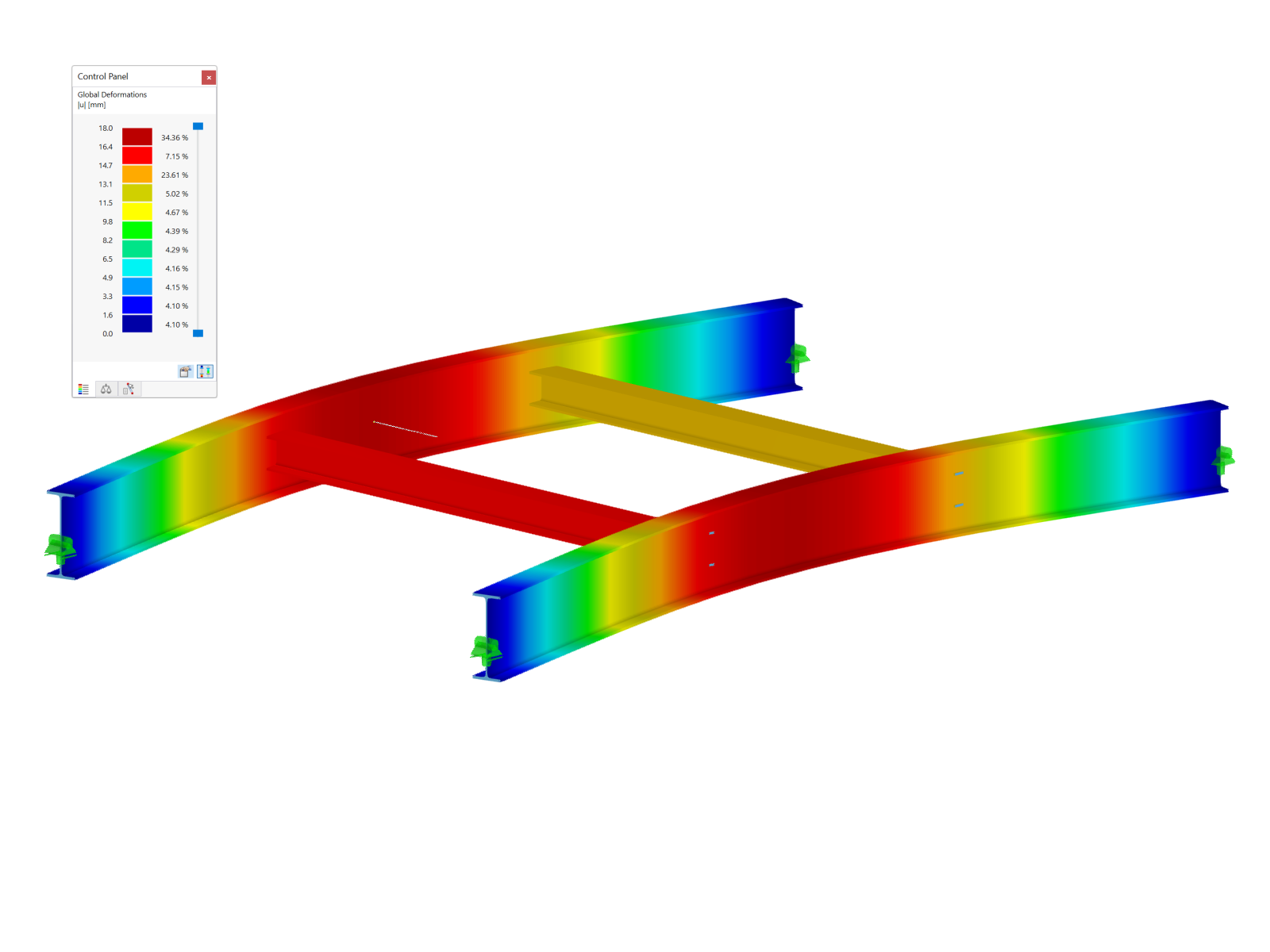
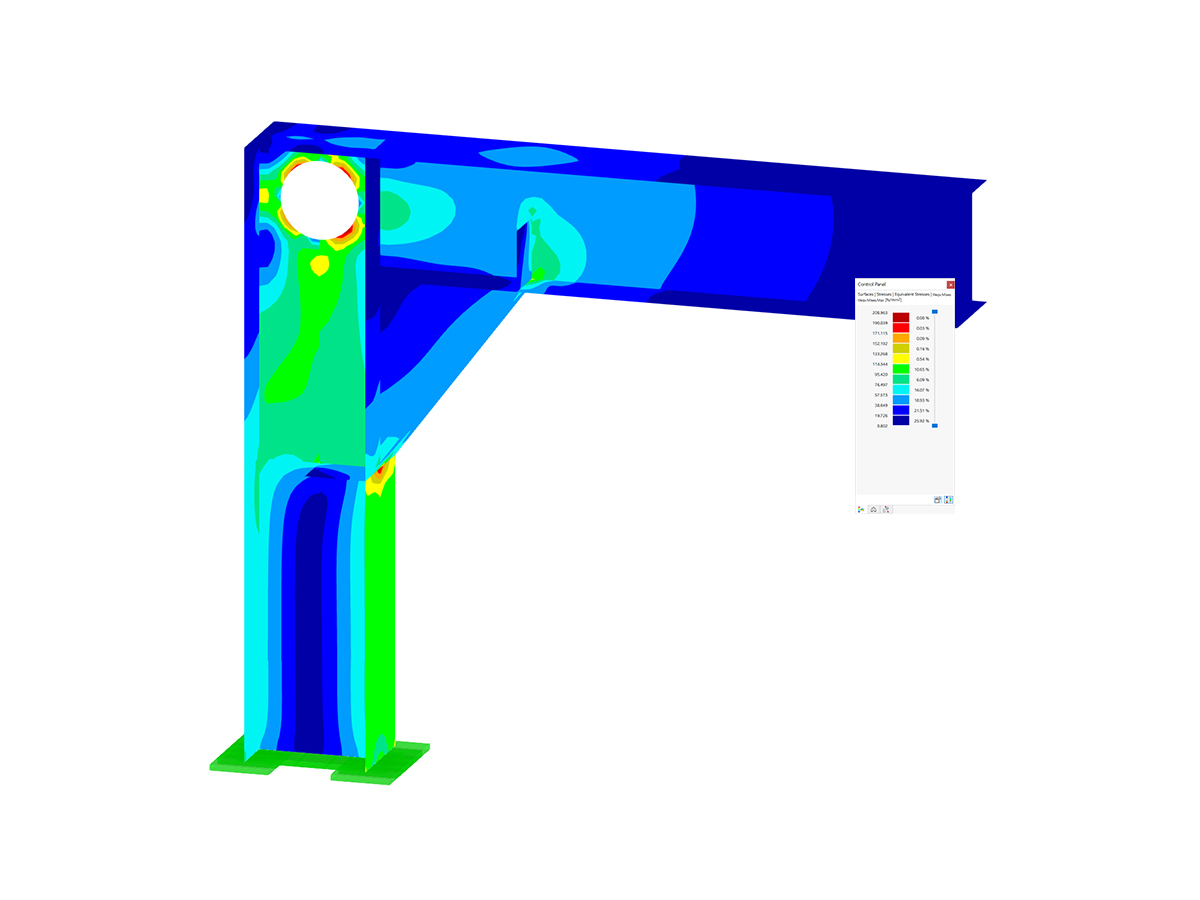
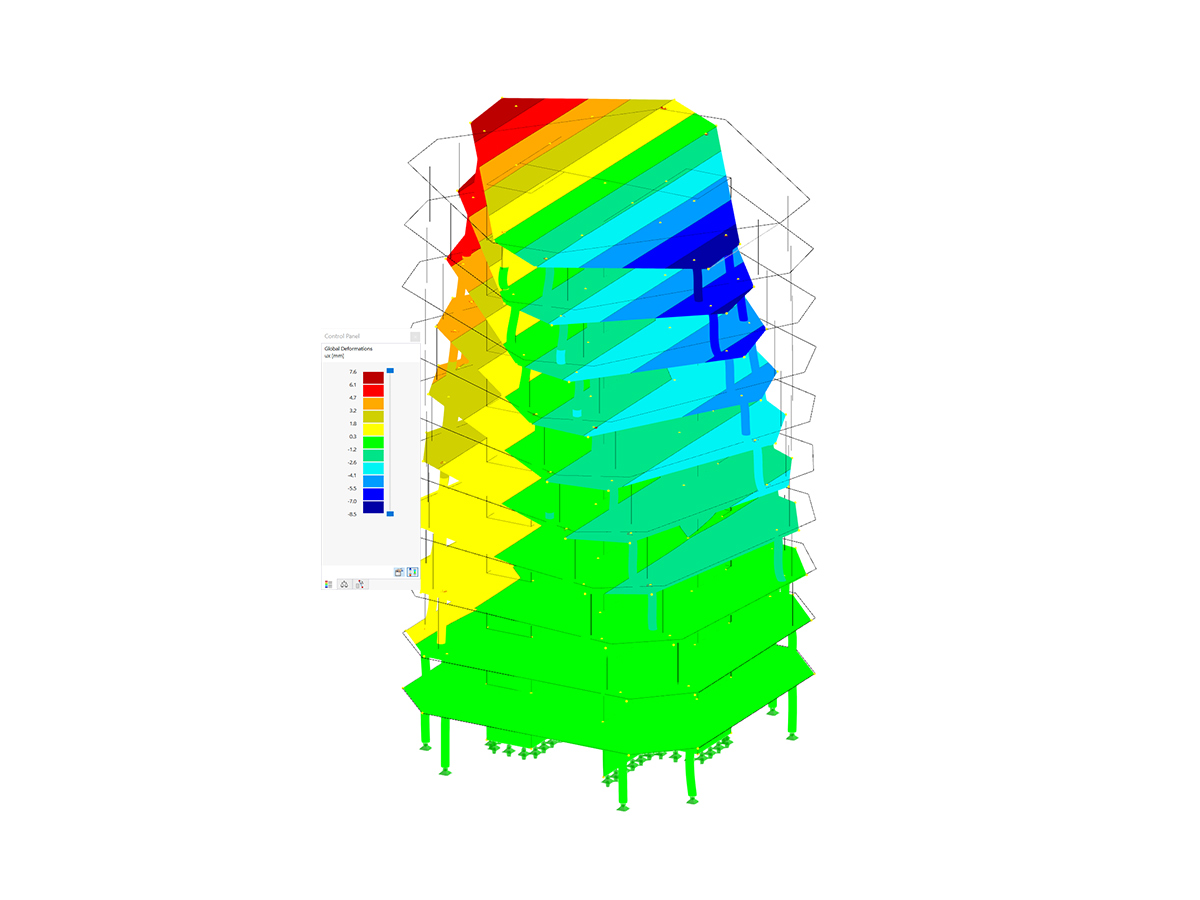
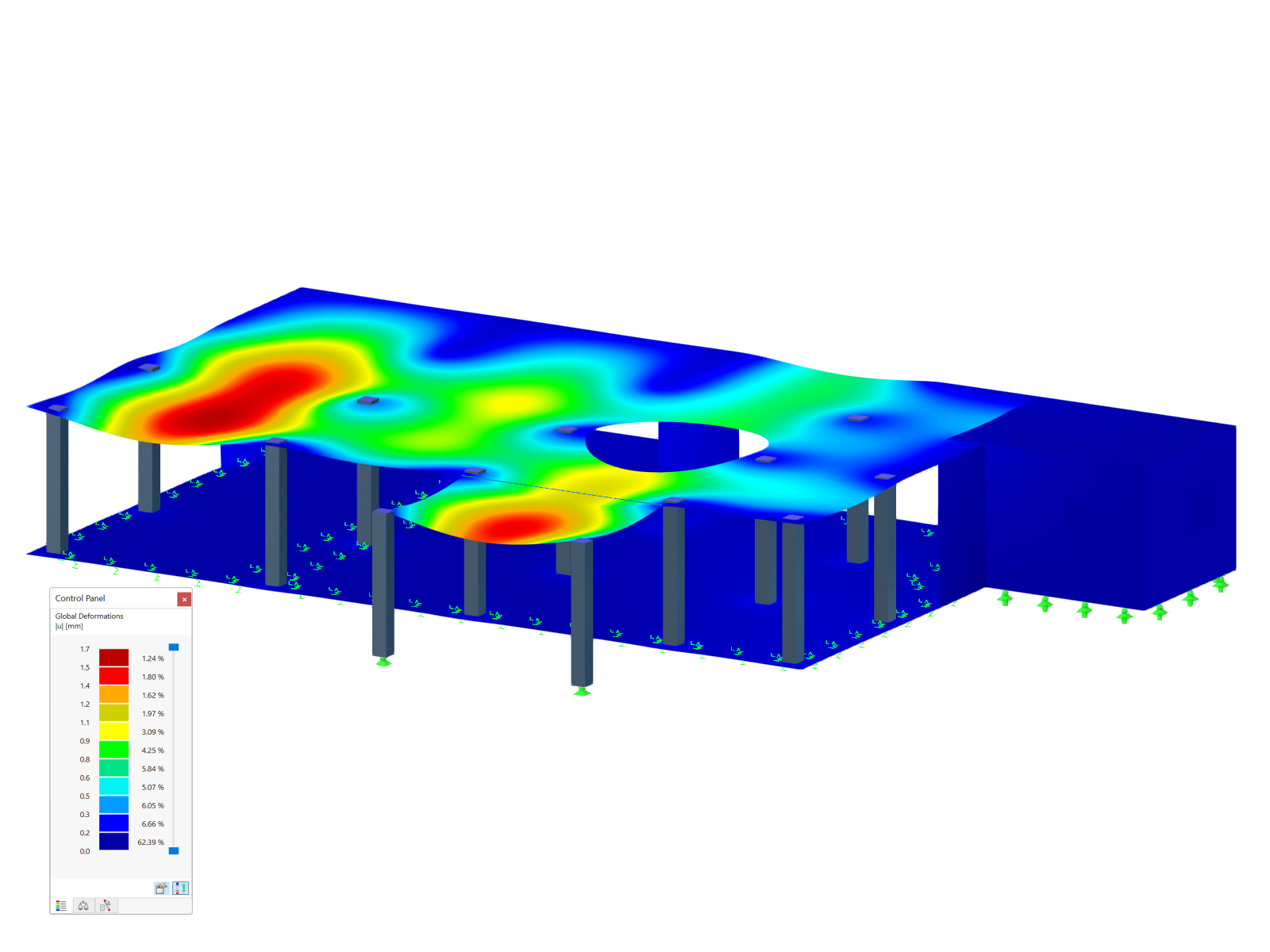
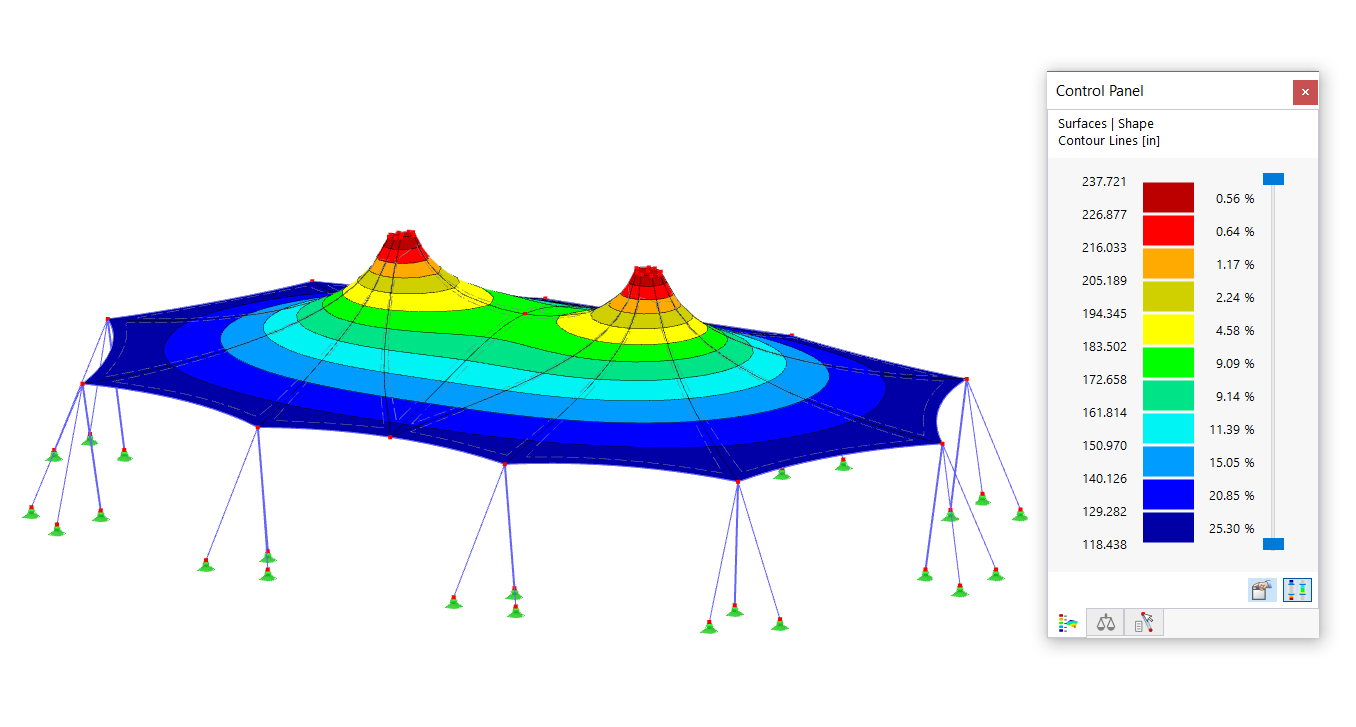
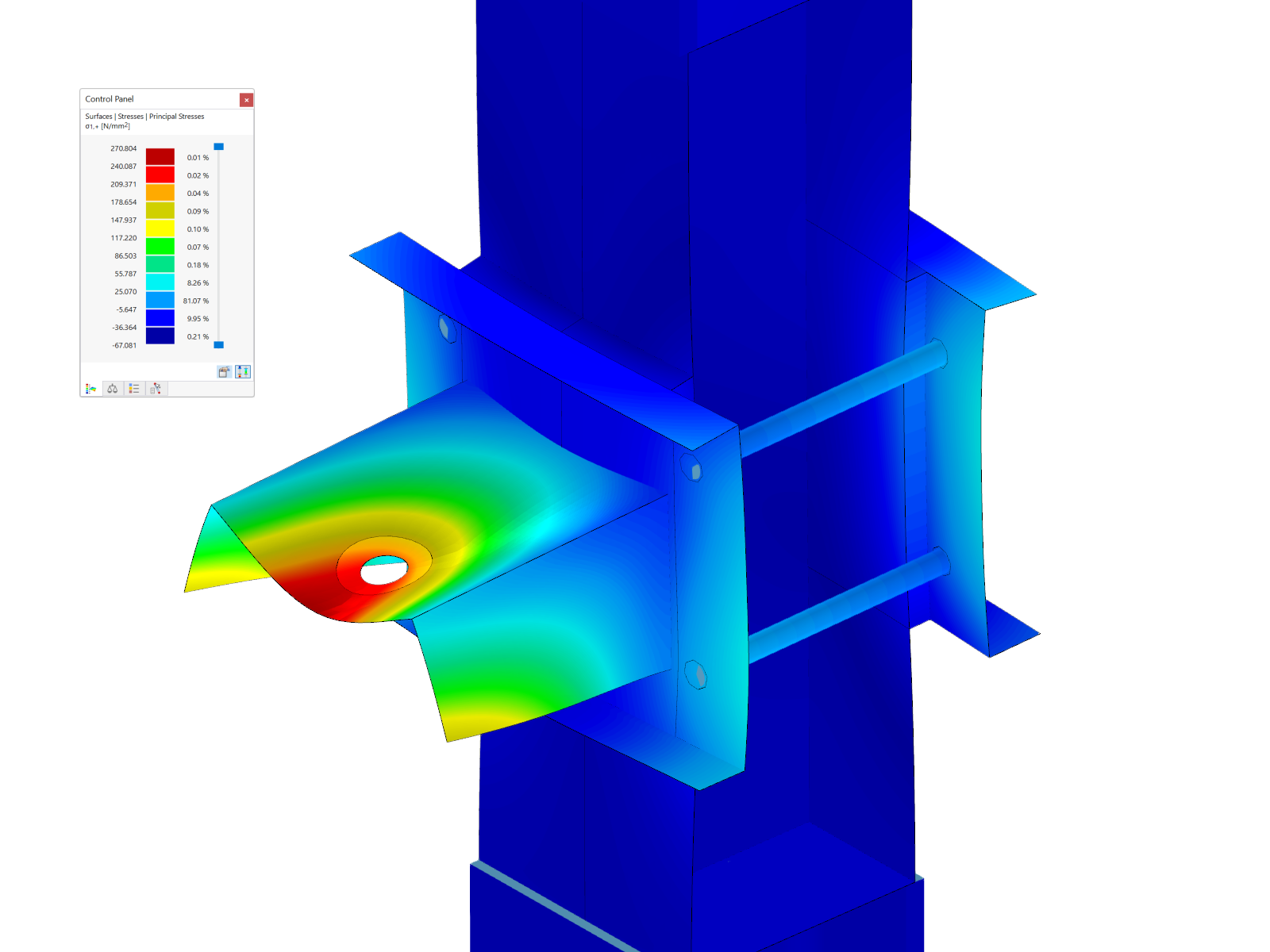
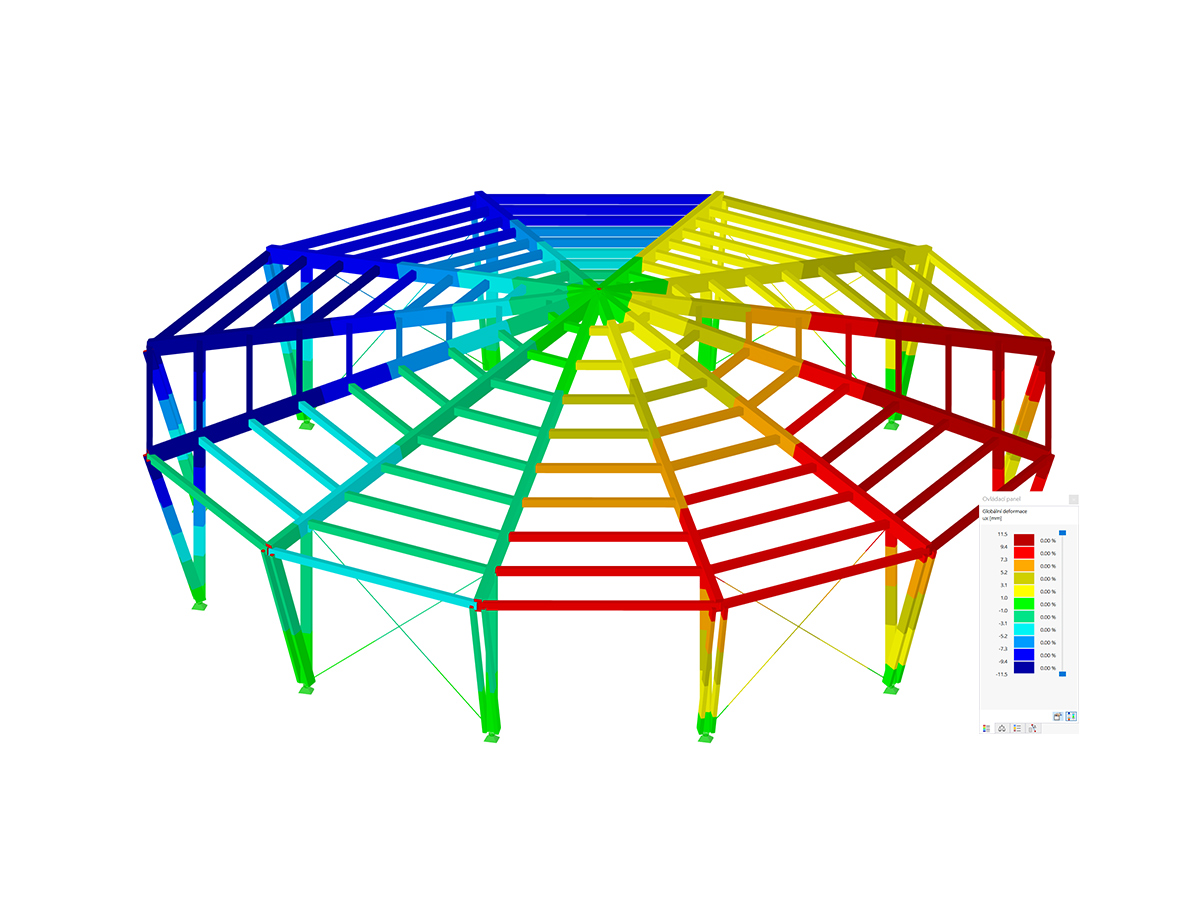
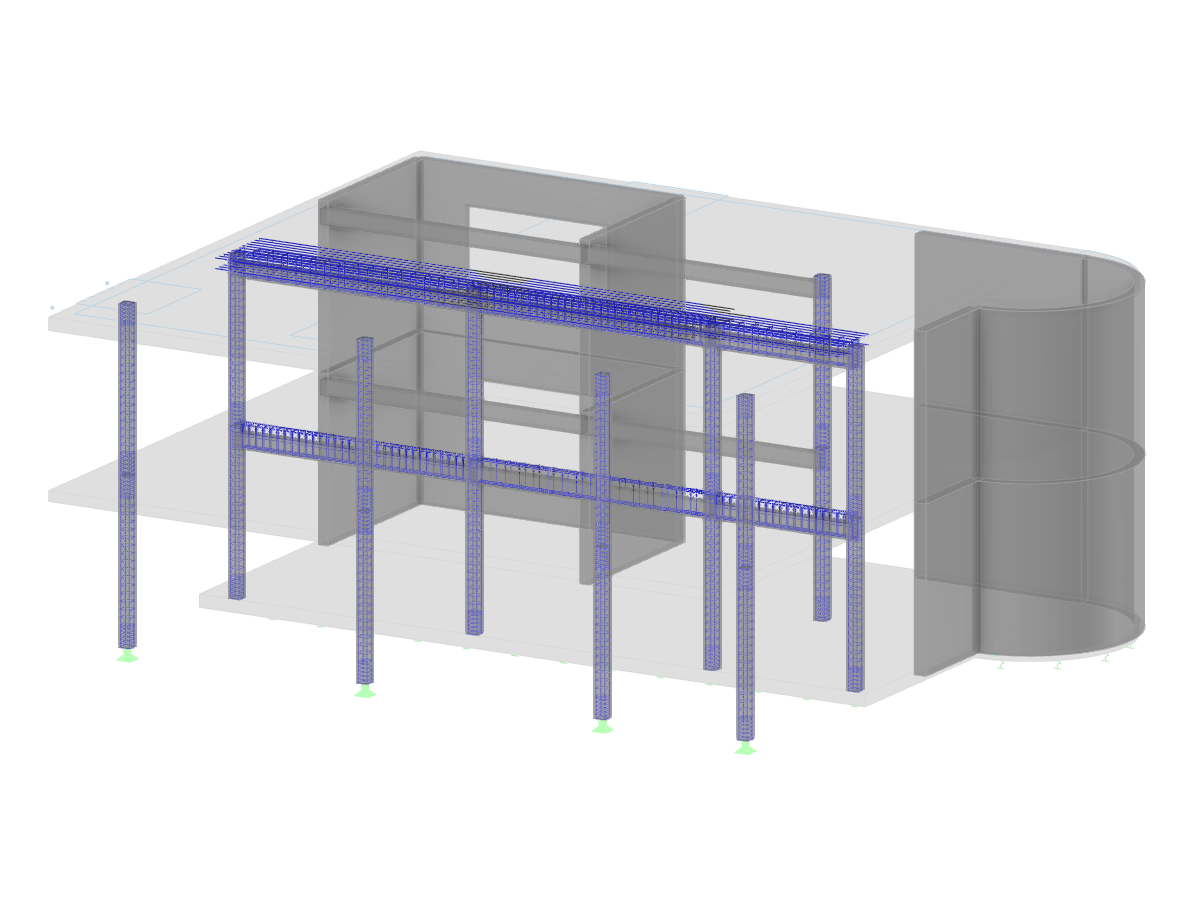
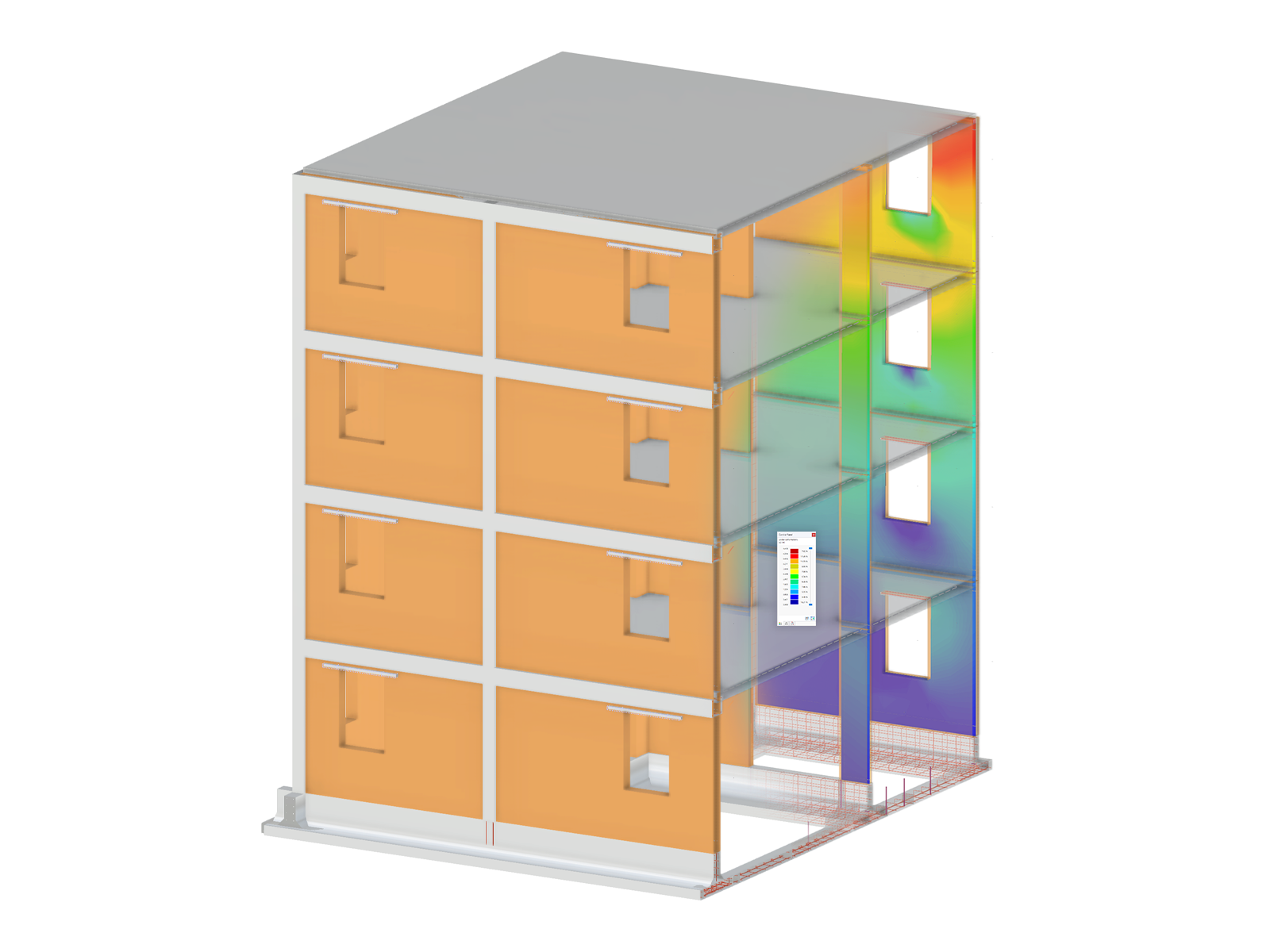
This model presents a comparative study of a steel building, incorporating variable-section PRS elements and cold-formed sections in accordance with Eurocode 3, as opposed to a conventional rolled-section solution. Designed as part of Graduation Thesis 000457, it integrates structural calculations performed with RSTAB 8, optimizing design performance and reliability. The visual illustration clearly shows the spatial configuration of the structure, highlighting connection details and the distribution of critical sections.
| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Steel Hall: Comparative Study According to EN 1993
| Number of Nodes | 237 |
| Number of Members | 408 |
| Number of Load Cases | 10 |
| Number of Load Combinations | 20 |
| Number of Result Combinations | 3 |
| Total Weight | 48.596 t |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 24.500 x 64.500 x 8.450 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 80.38 x 211.61 x 27.72 feet |
| Program Version | 8.24.01 |
You can download this structural model to use it for training purposes or for your projects. However, we do not assume any guarantee or liability for the accuracy or completeness of the model.

.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)
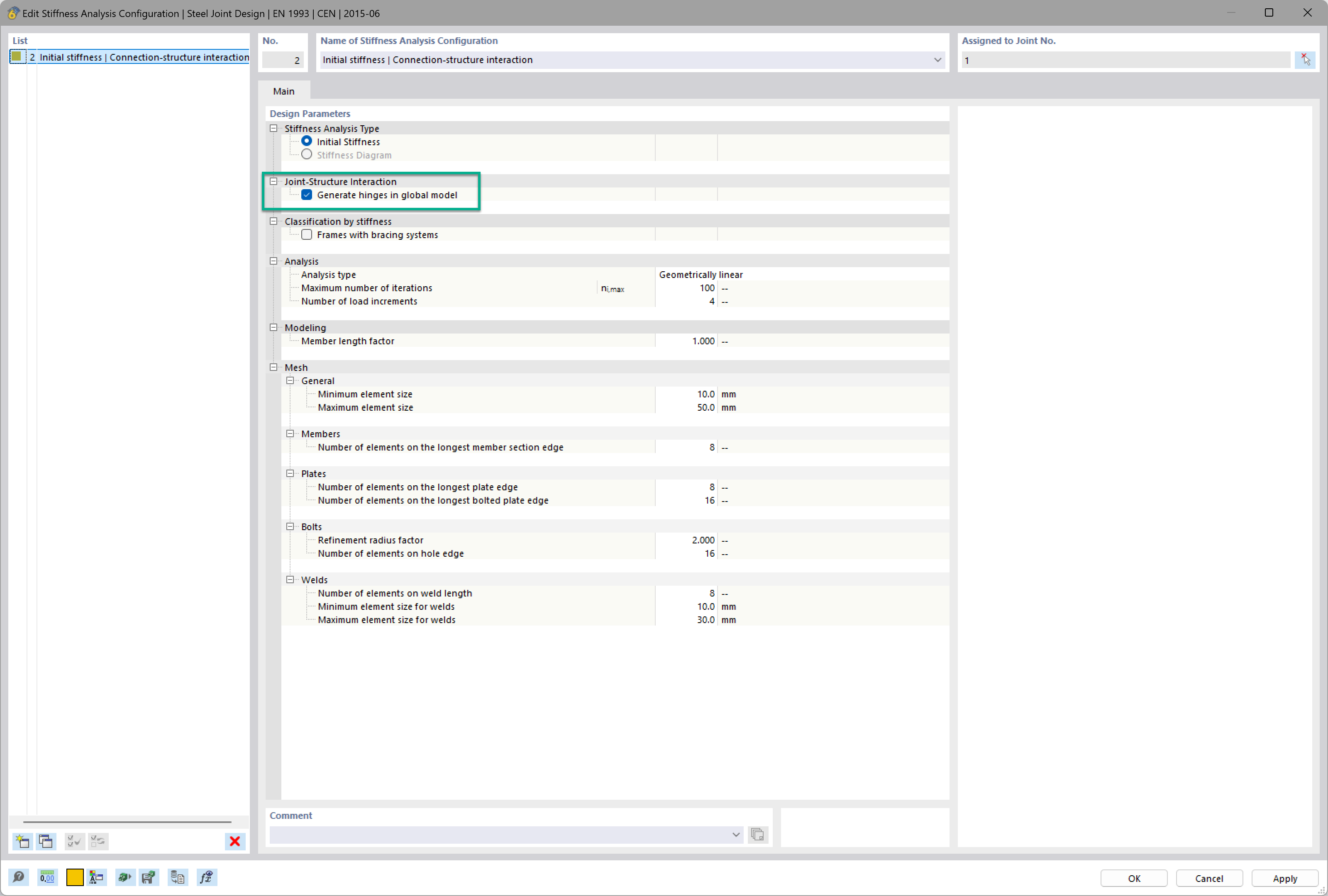
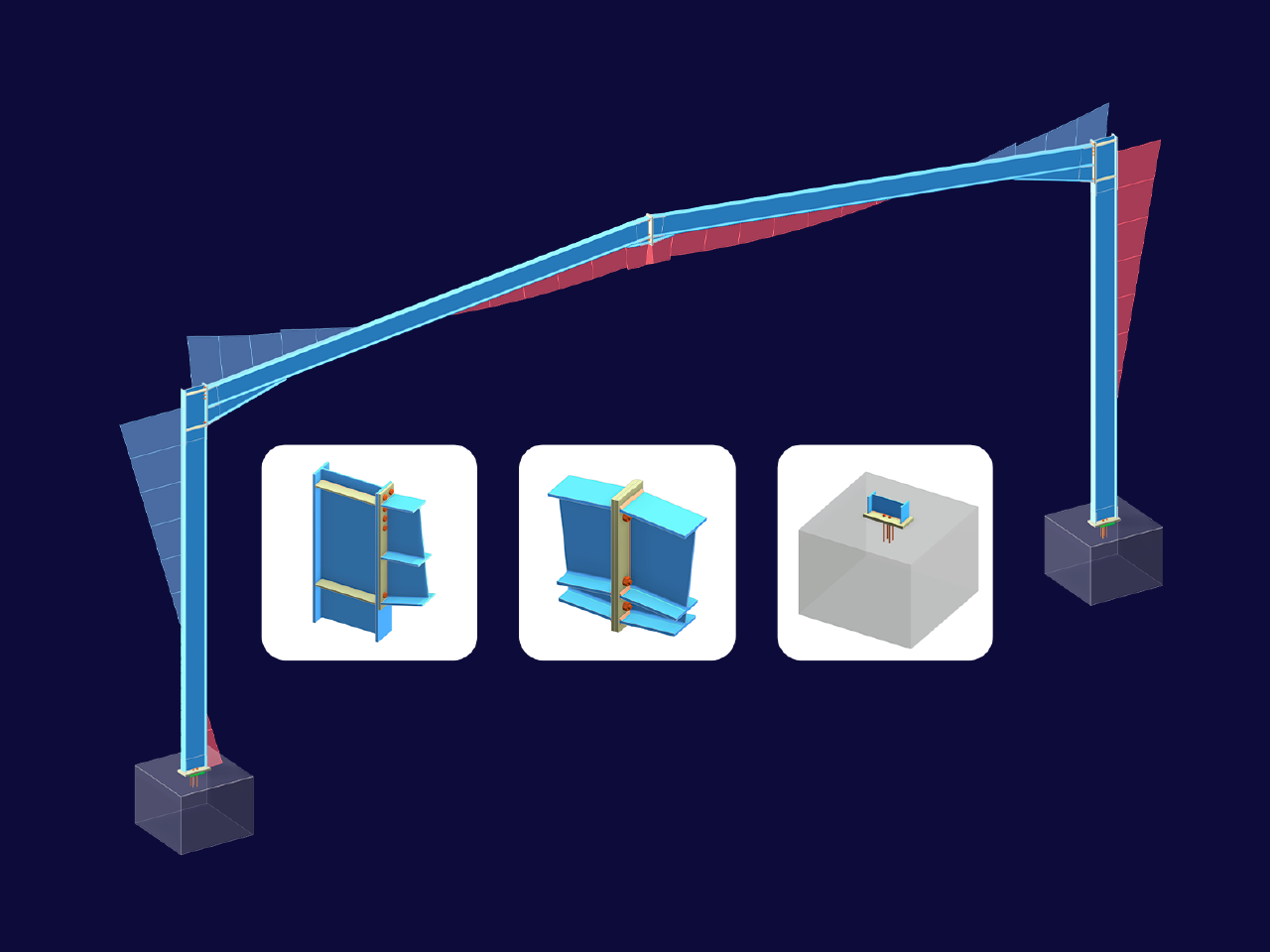
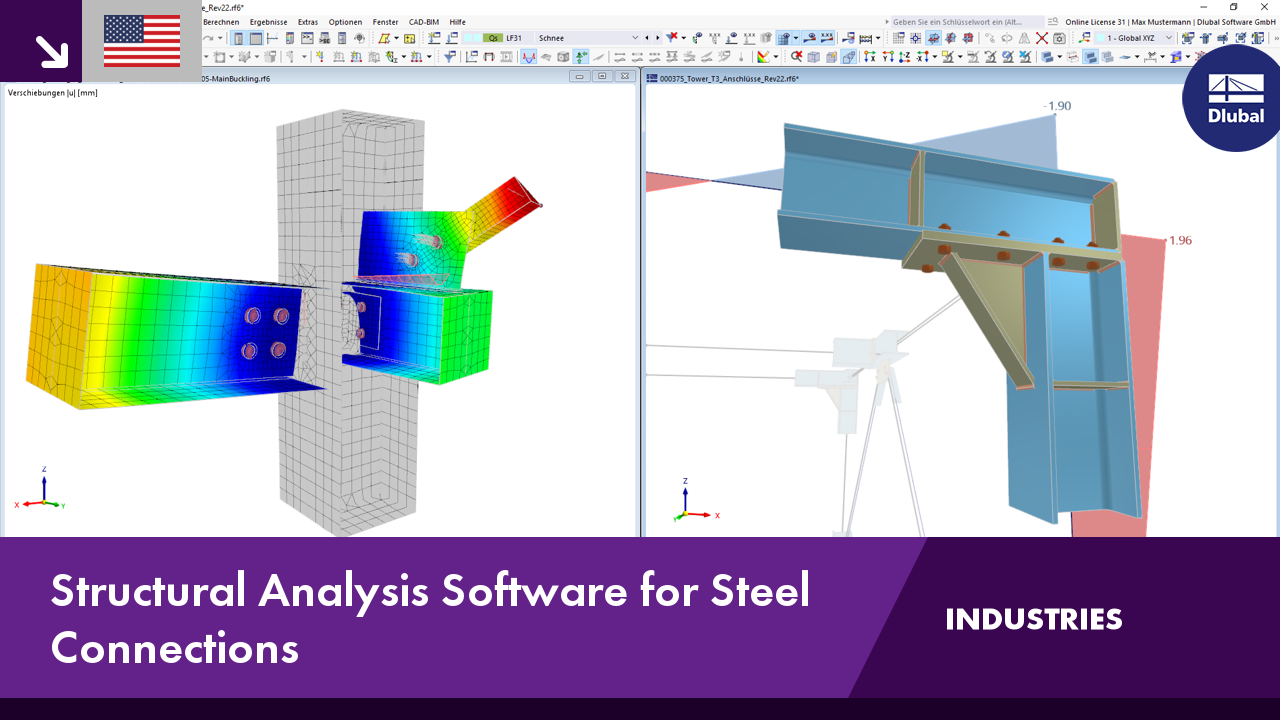
Want to automatically consider steel joint stiffness in your global RFEM model? Utilize the Steel Joints add-on!
Activate joint-structure interaction in the stiffness analysis of your steel joints. Hinges with springs are then automatically generated in the global model and included in subsequent calculations.
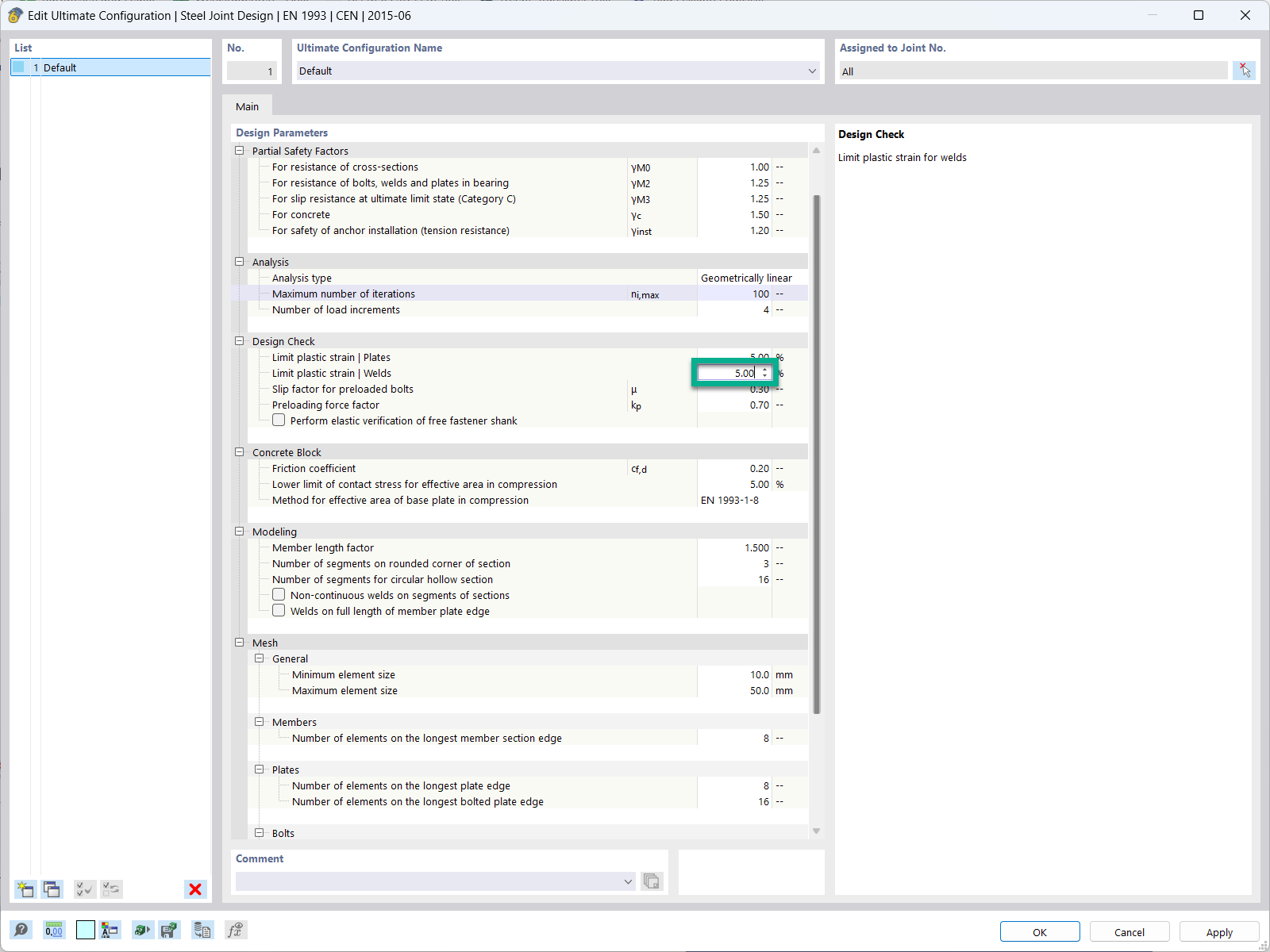
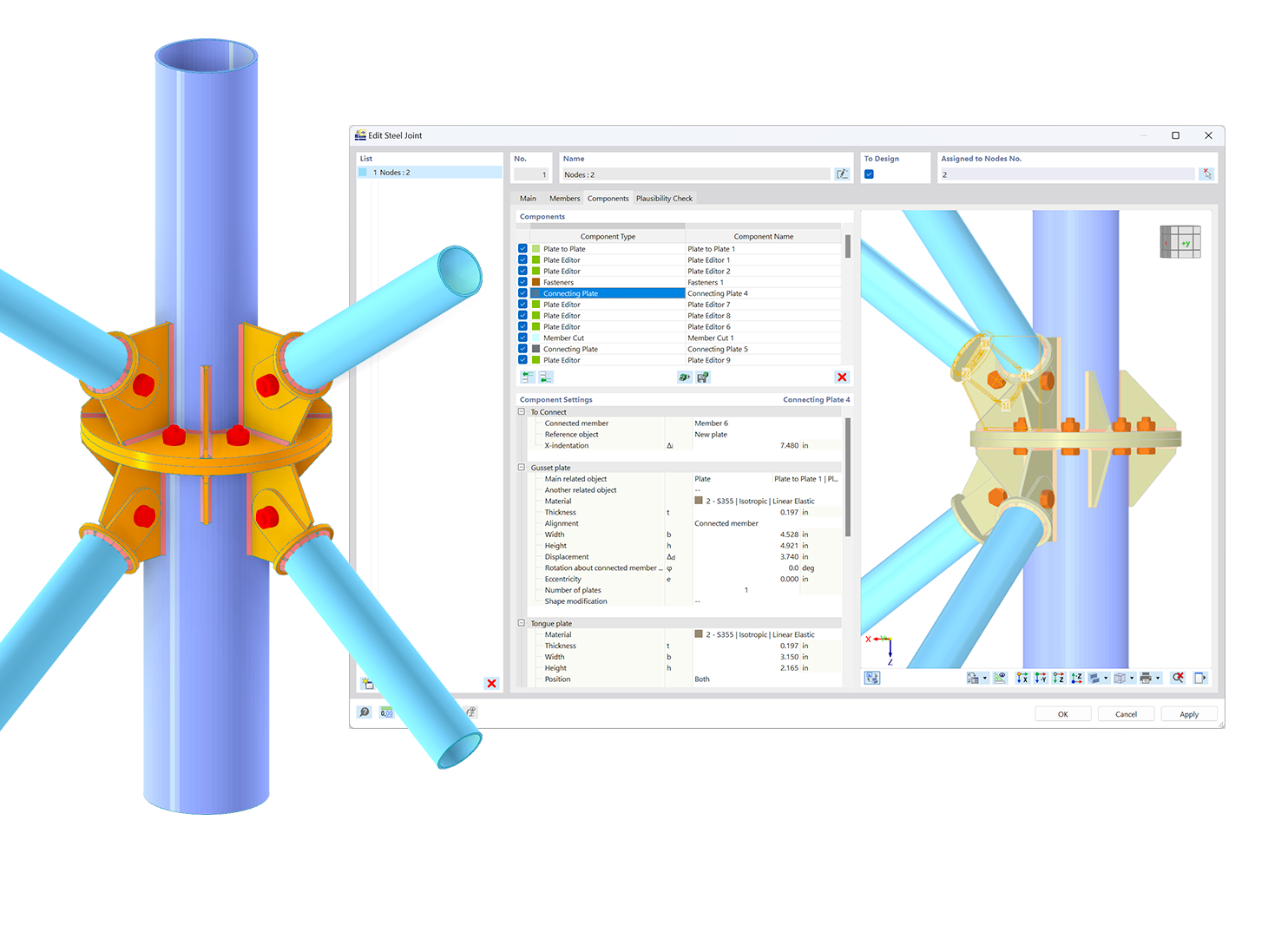
In the ultimate configuration of the steel joint design, you have the option to modify the limit plastic strain for welds.
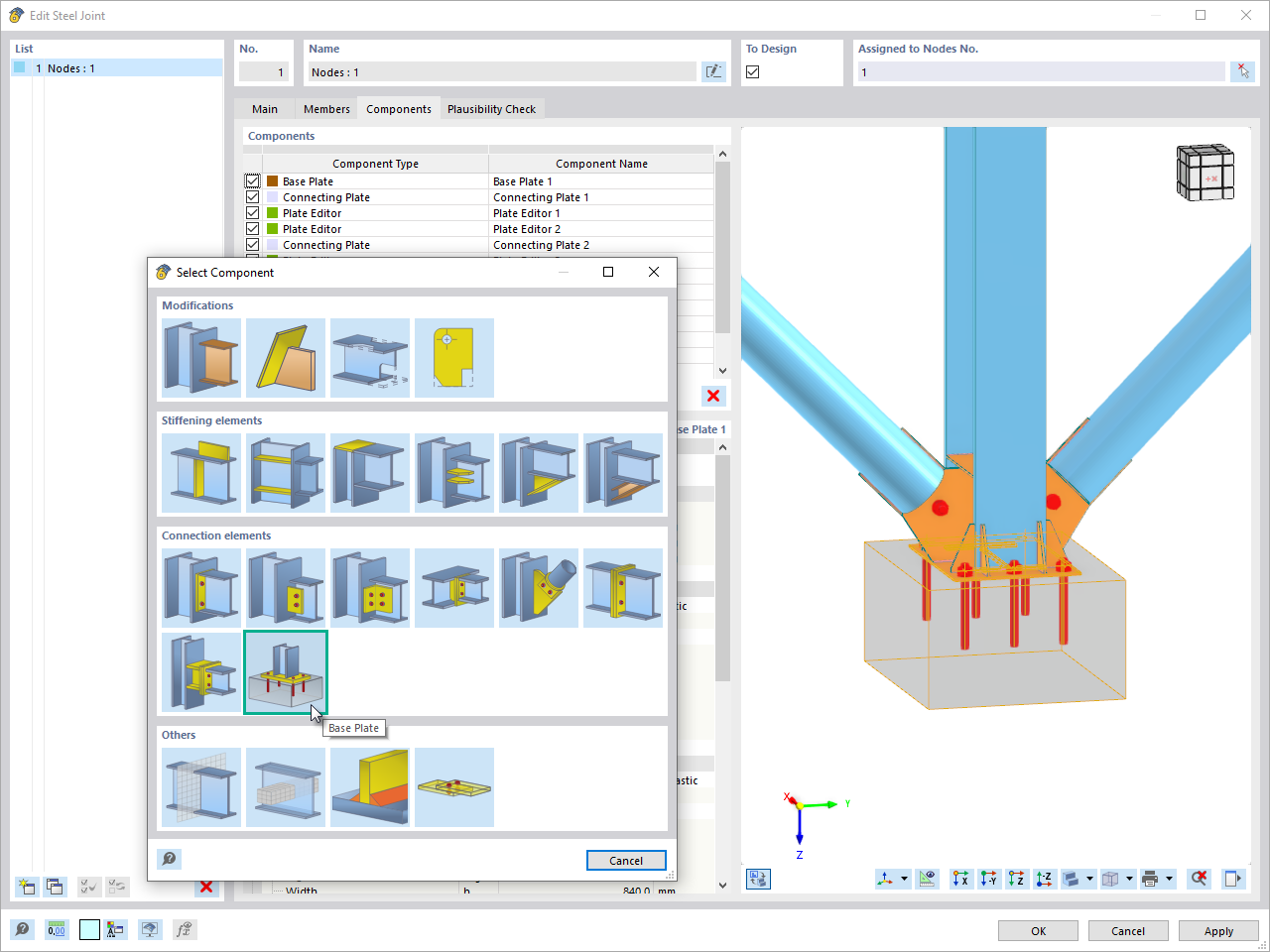
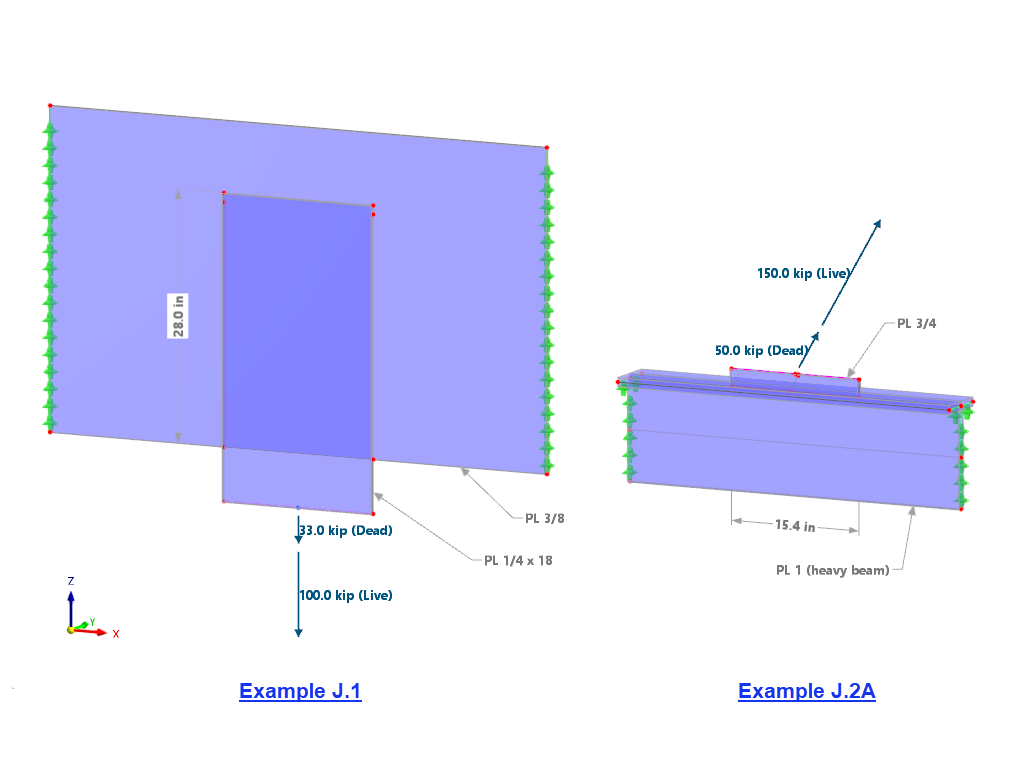
The "Base Plate" component allows you to design base plate connections with cast-in anchors. In this case, plates, welds, anchorages, and steel-concrete interaction are analyzed.
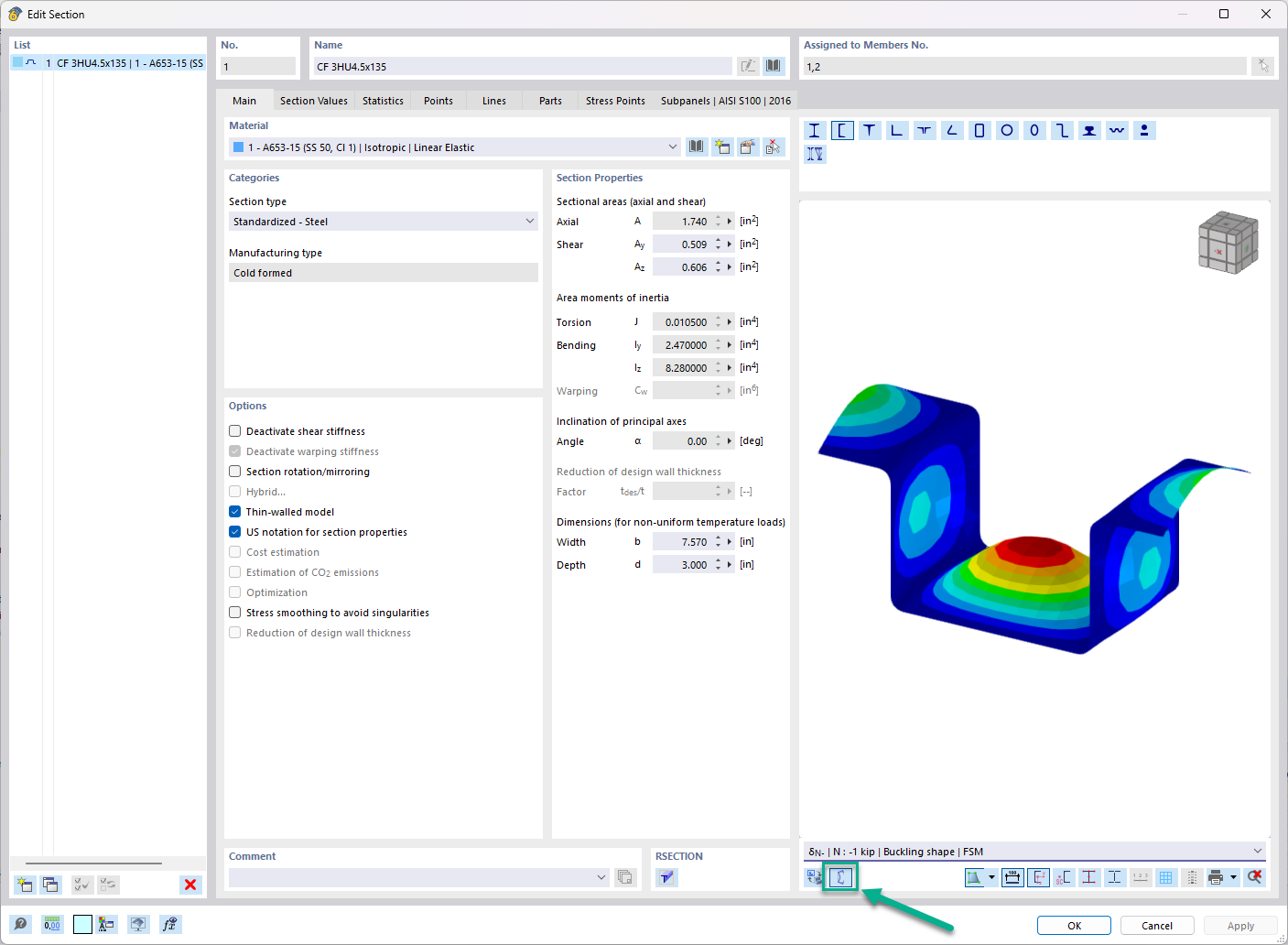
In the "Edit Section" dialog box, you can display the buckling shapes of the Finite Strip Method (FSM) as a 3D graphic.
In the Steel Joints add-on, I get high utilization ratios for preloaded bolts in the tension design. Where do these high utilization ratios come from and how can I evaluate the load-bearing reserves of the bolt?
How can treating a connection as fully rigid result in an uneconomical design?
Is it possible to consider shear panels and rotational restraints in the global calculation?















.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)
























_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)






.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)