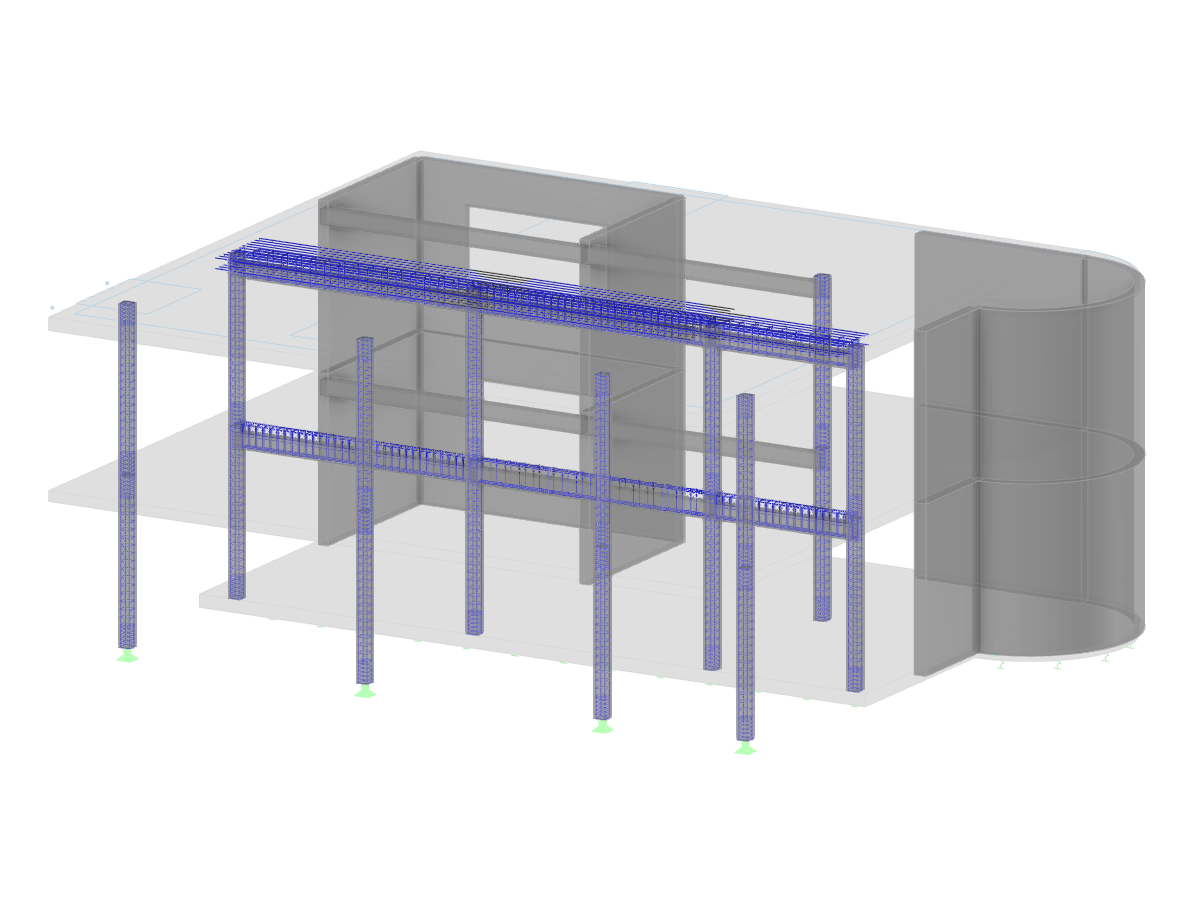
A family house with a remarkable roof structure was built in Upper Austria in 2014. The circular centerpiece of the building is covered by a tent roof. It was built as a visible wooden structure, and together with the light‑flooded glass facade, it is a real eye‑catcher.
Two Dlubal customers were involved in the project. The engineering office Wagner used RSTAB to create the structural analysis for the roof structure, and WIEHAG GmbH was responsible for the timber structures.
Roof Structure
Ing.-Büro Wagner GmbH, Gangkofen, Germany
s.wagner@ingbuero-wagner.com
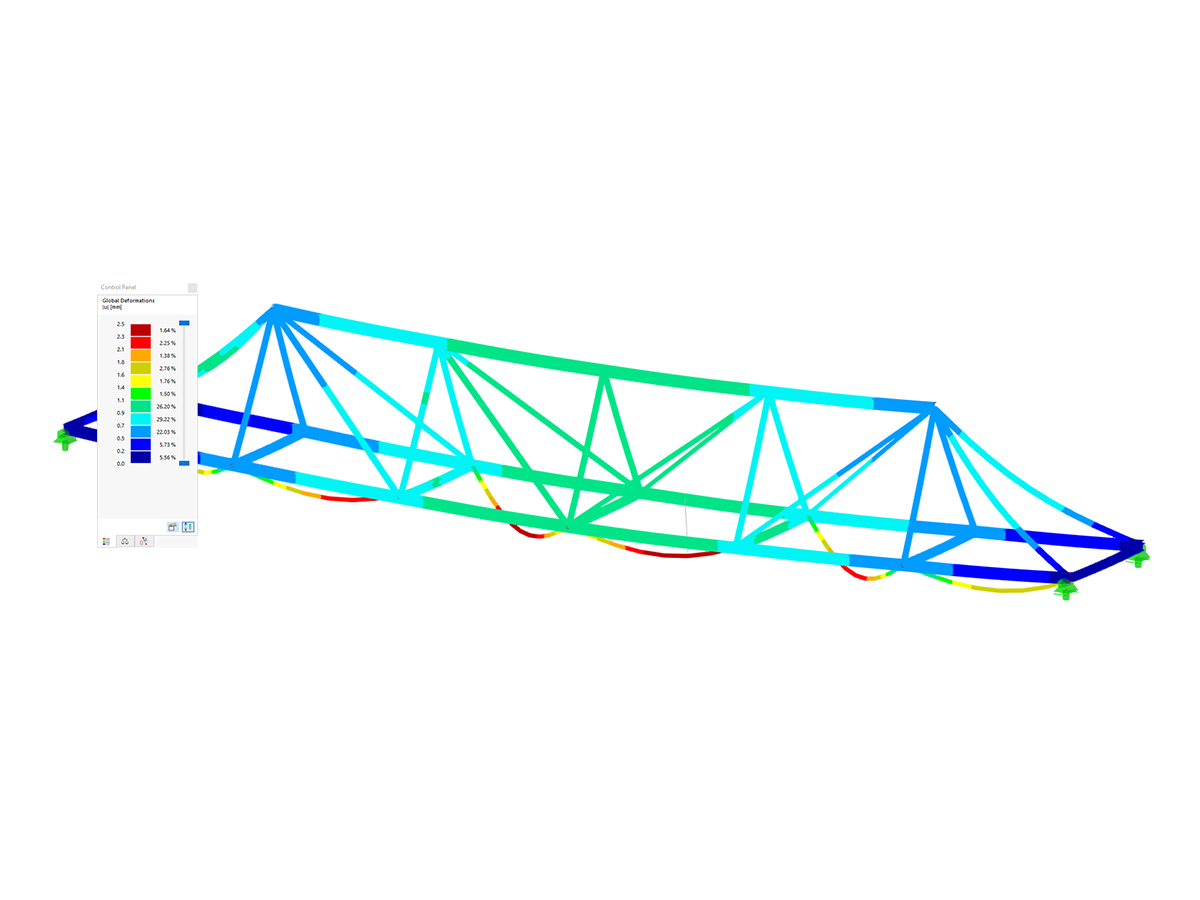
RSTAB Model of Tented Roof Connecting Two Pergolas (© IB Wagner)
| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Tented Timber Roof Structure, Austria
| Number of Nodes | 259 |
| Number of Members | 329 |
| Number of Load Cases | 9 |
| Number of Load Combinations | 159 |
| Number of Result Combinations | 2 |
| Total Weight | 8.052 tons |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 16.648 x 24.997 x 5.131 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 54.62 x 82.01 x 16.83 feet |
| Program Version | 8.02.00 |
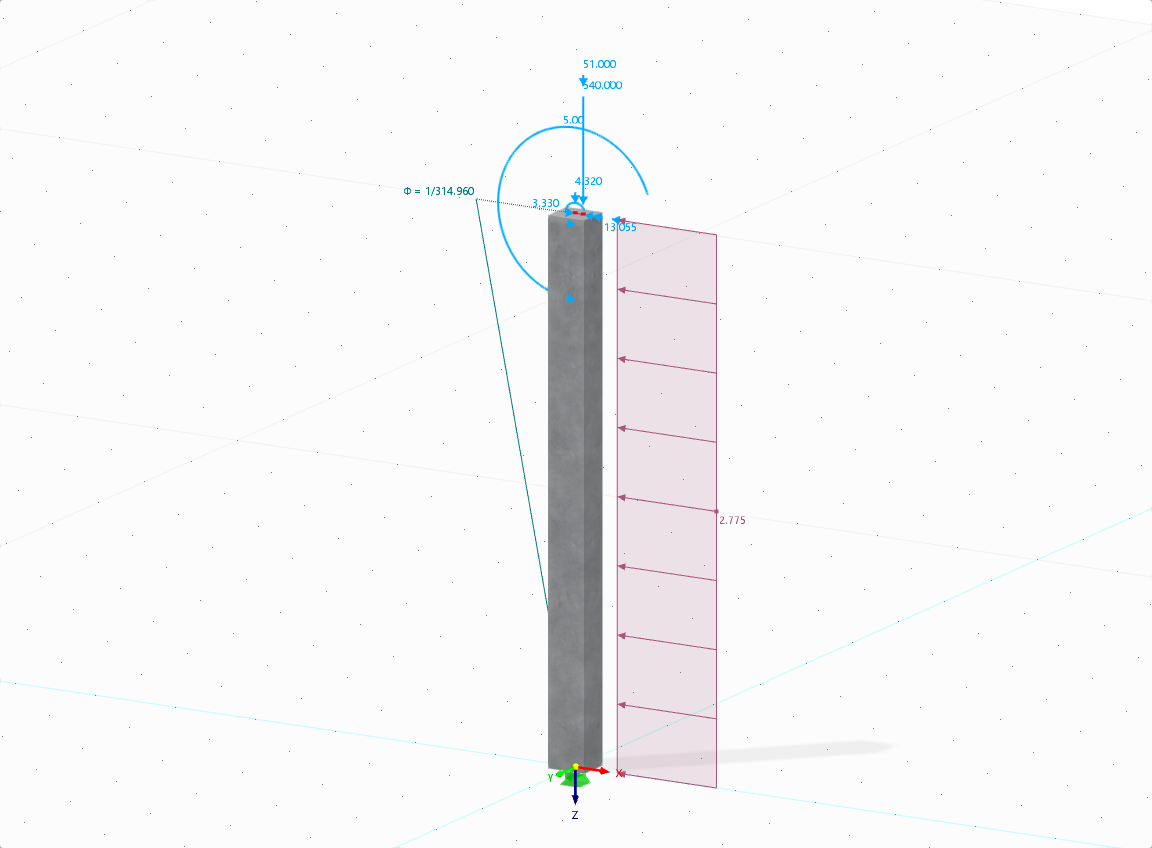
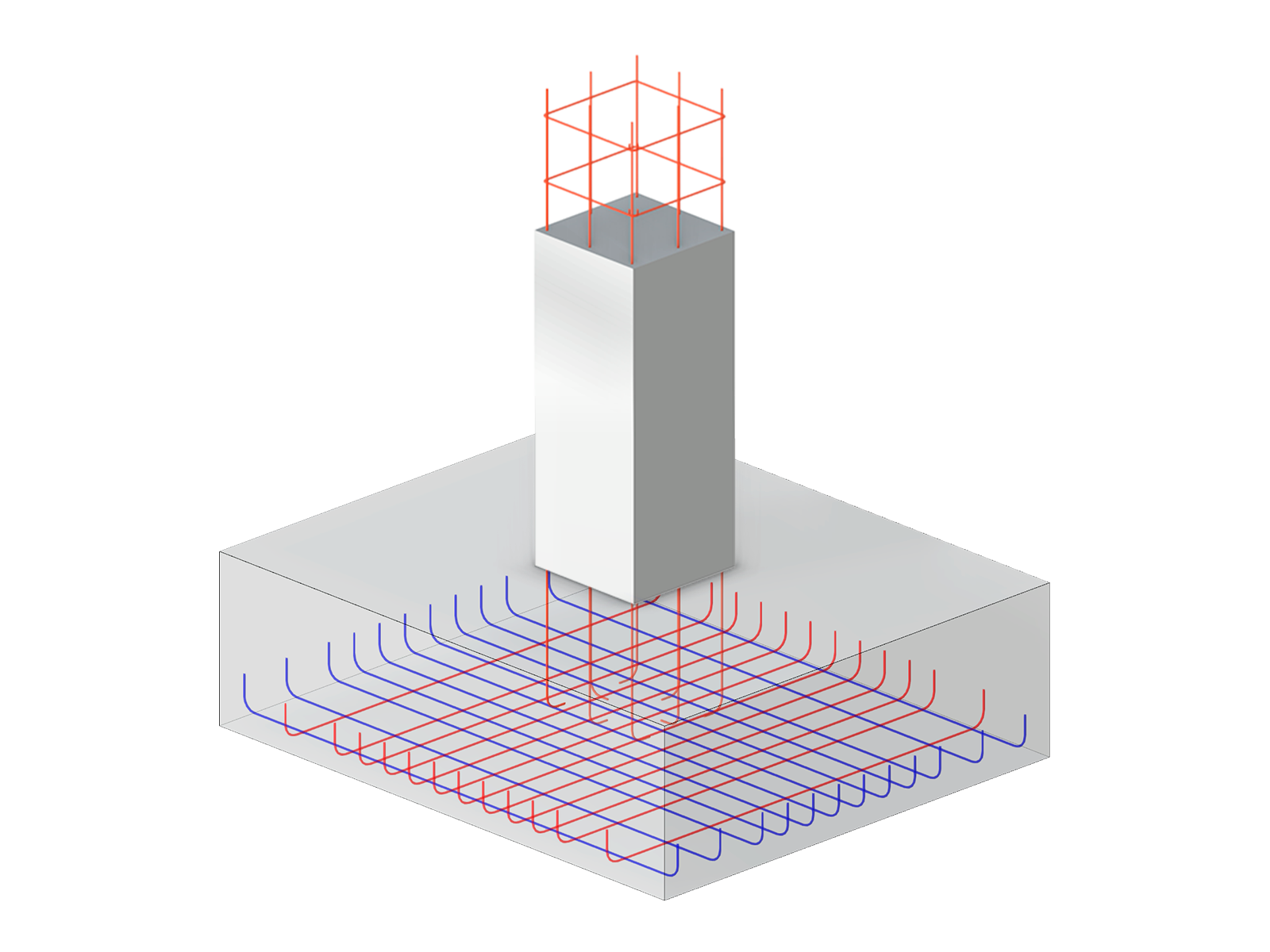
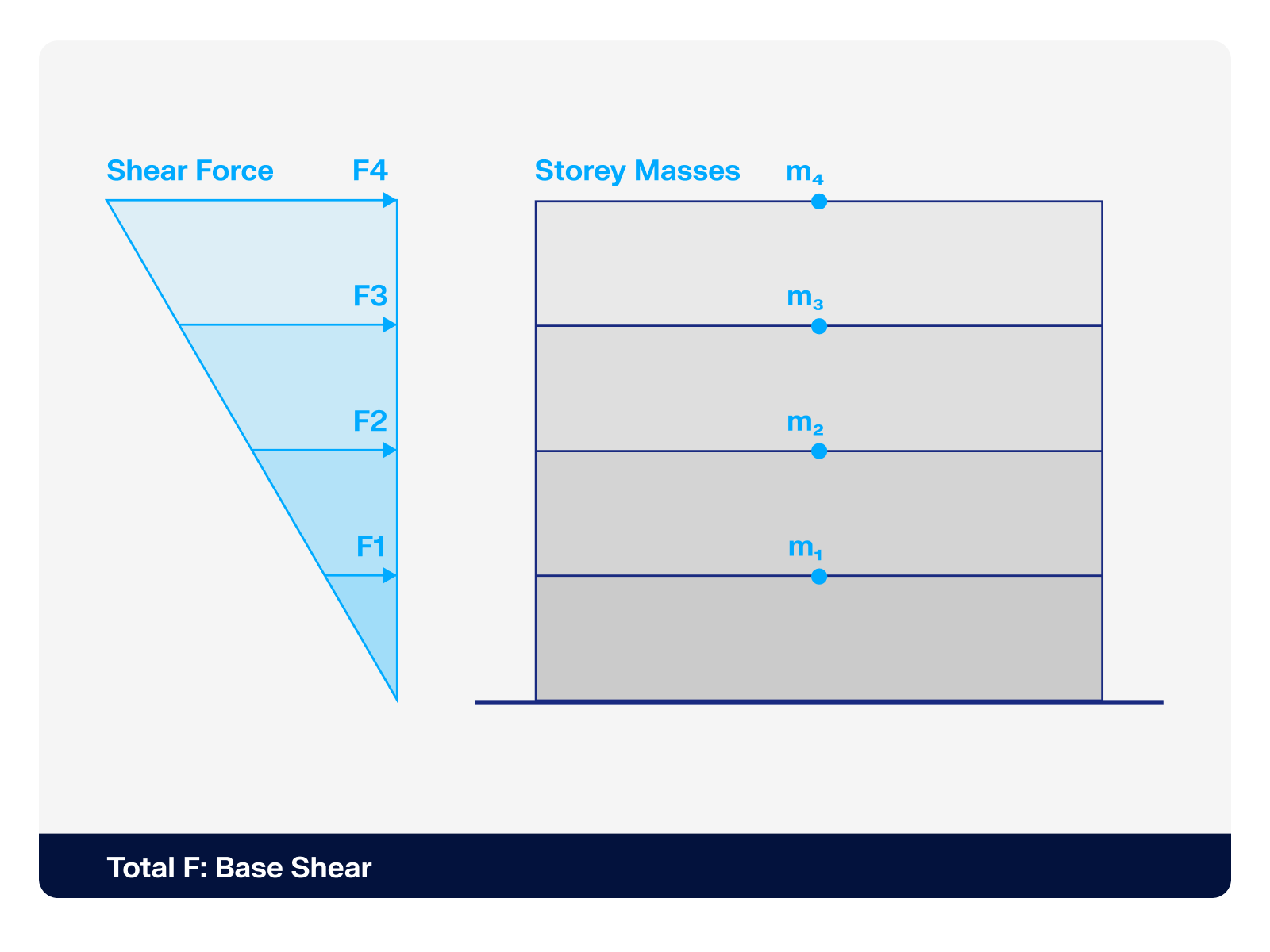
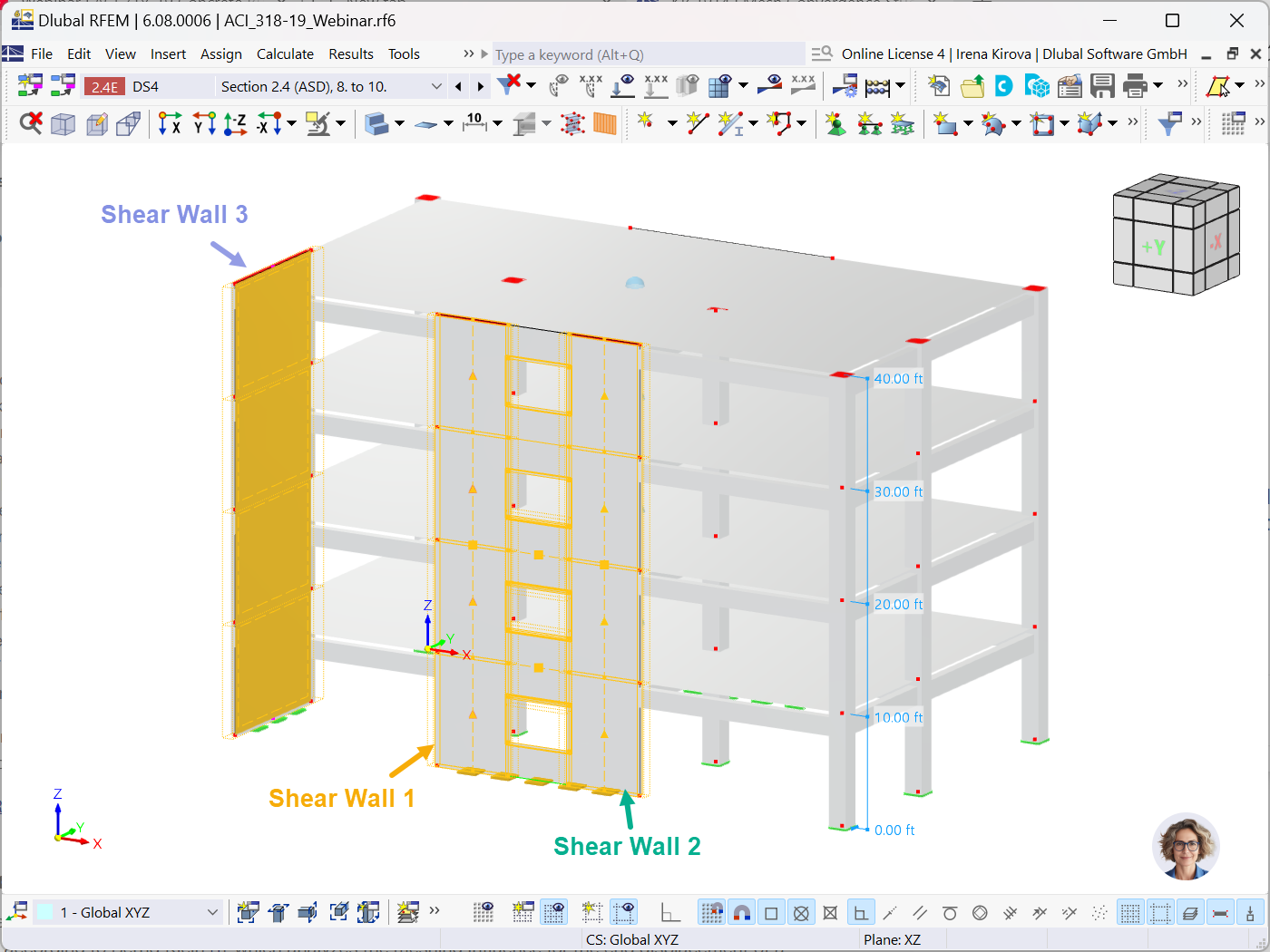
The aim of this technical article is to perform a design according to the general design method of Eurocode 2, using the example of a slender reinforced concrete column.

.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)
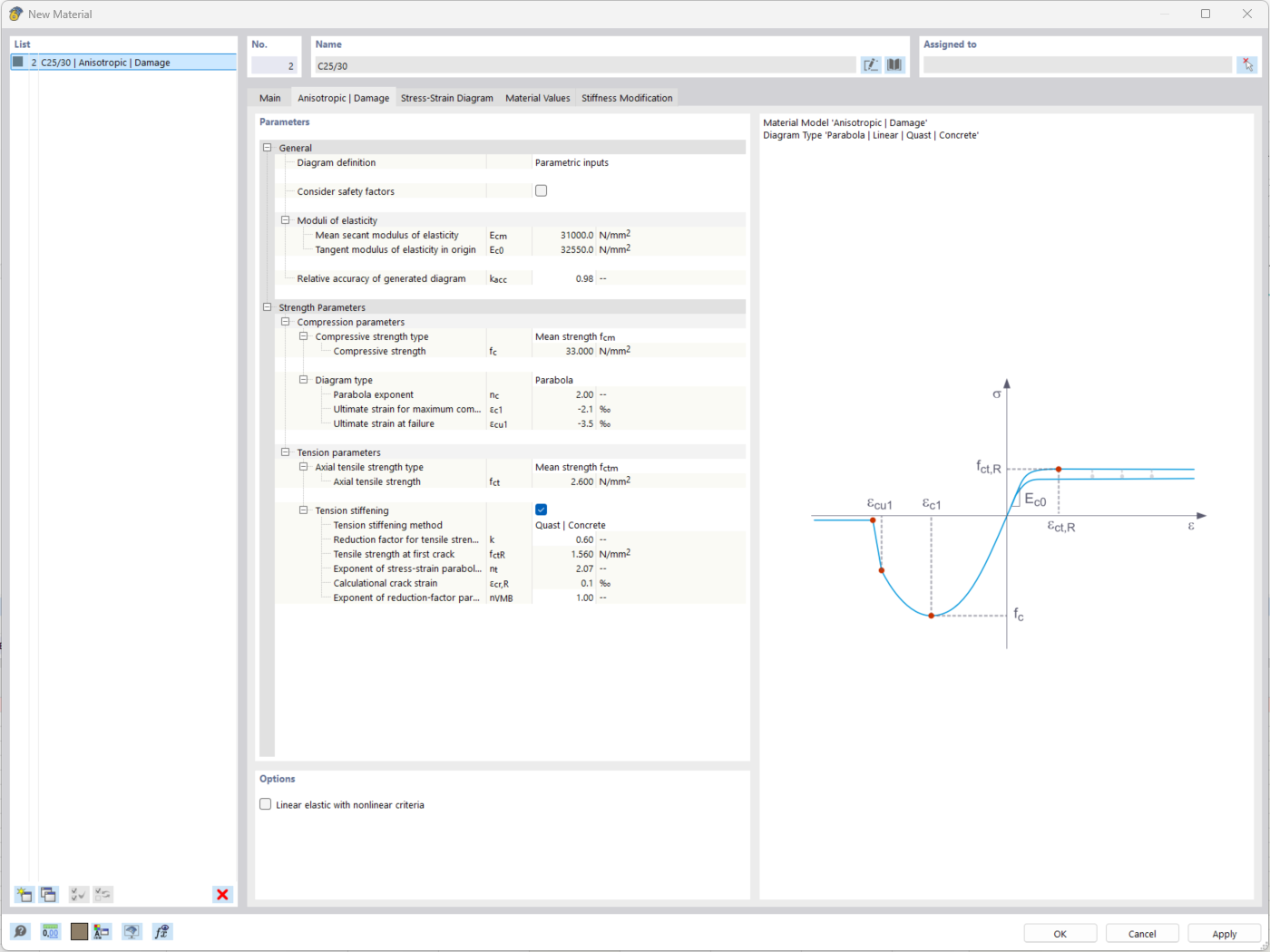
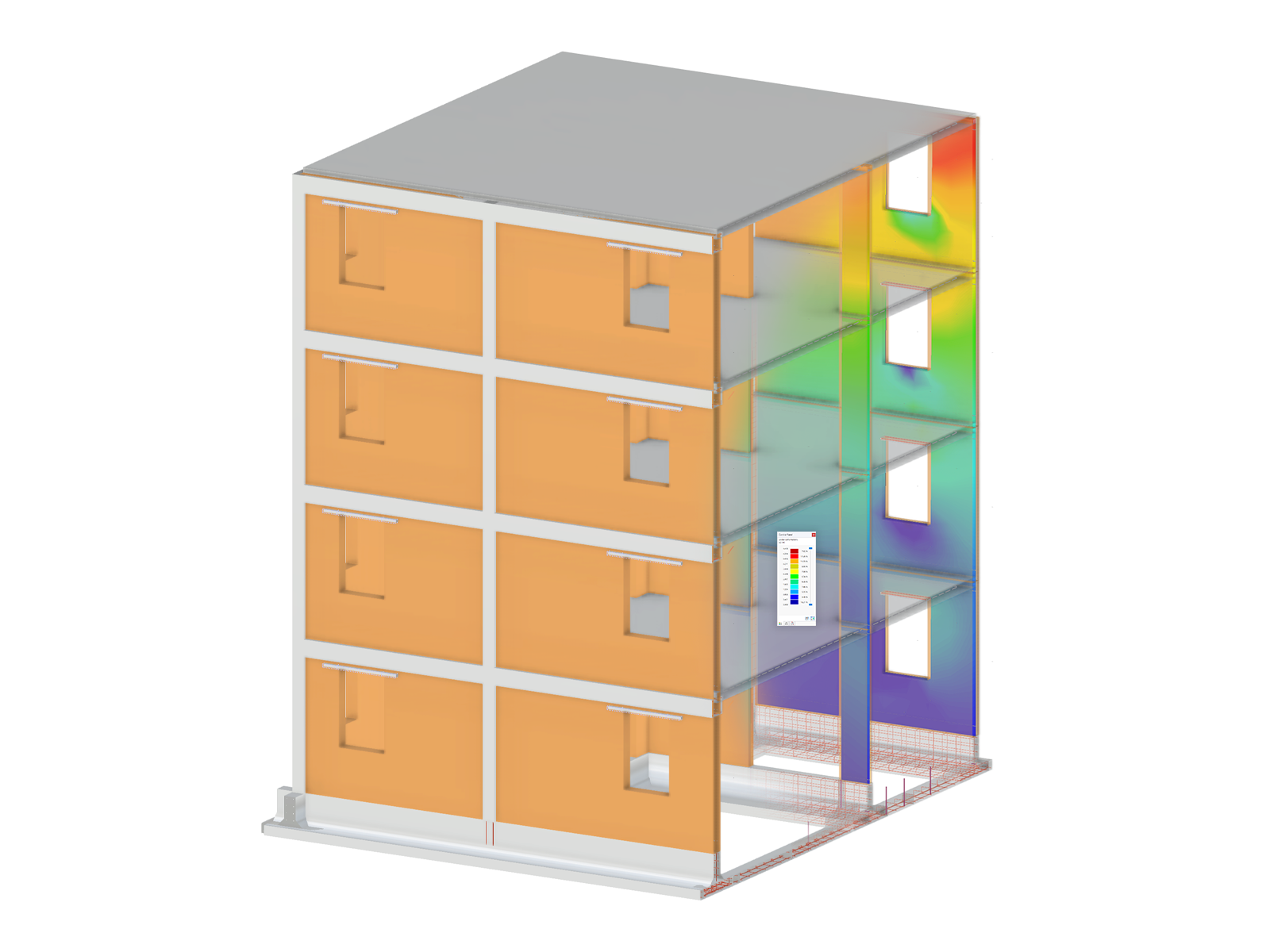
The "Nonlinear Material Behavior" add-on includes the Anistropic | Damage material model for concrete structural components. This material model allows you to consider concrete damage for members, surfaces, and solids.
You can define an individual stress-strain diagram via a table, use the parametric input to generate the stress-strain diagram, or use the predefined parameters from the standards. Furthermore, it is possible to consider the tension stiffening effect.
For the reinforcement, both nonlinear material models "Isotropic | Plastic (Members)" and "Isotropic | Nonlinear Elastic (Members)" are available.
It is possible to consider the long-term effects due to creep and shrinkage using the "Static Analysis | Creep & Shrinkage (Linear)" analysis type that has been recently released. Creep is taken into account by stretching the stress-strain diagram of the concrete using the factor (1+phi), and shrinkage is taken into account as the pre-strain of the concrete. More detailed time step analyses are possible using the "Time-Dependent Analysis (TDA)" add-on.
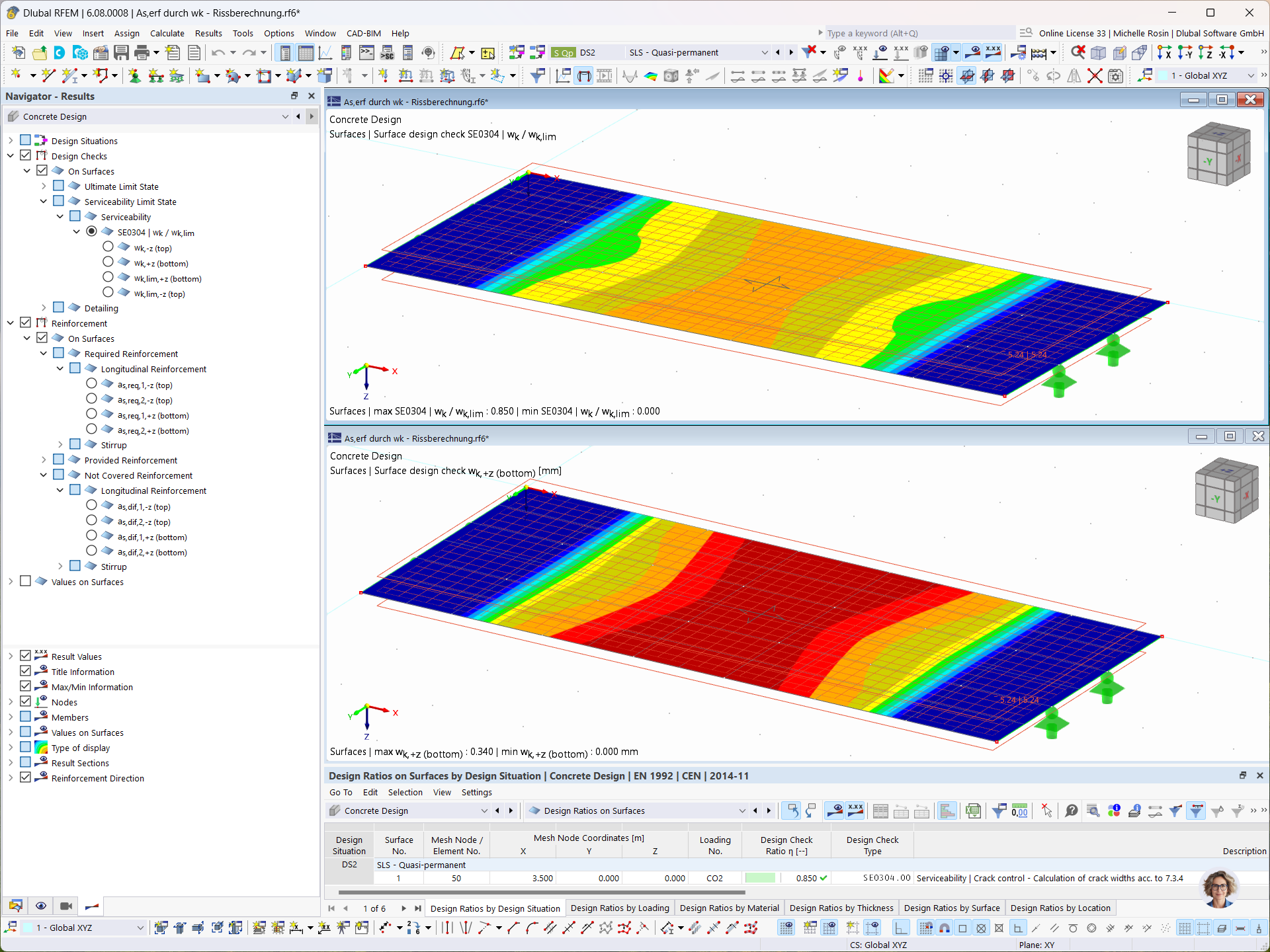
In the Concrete Design add-on, you can determine the required longitudinal reinforcement for the direct crack width analysis (w k).
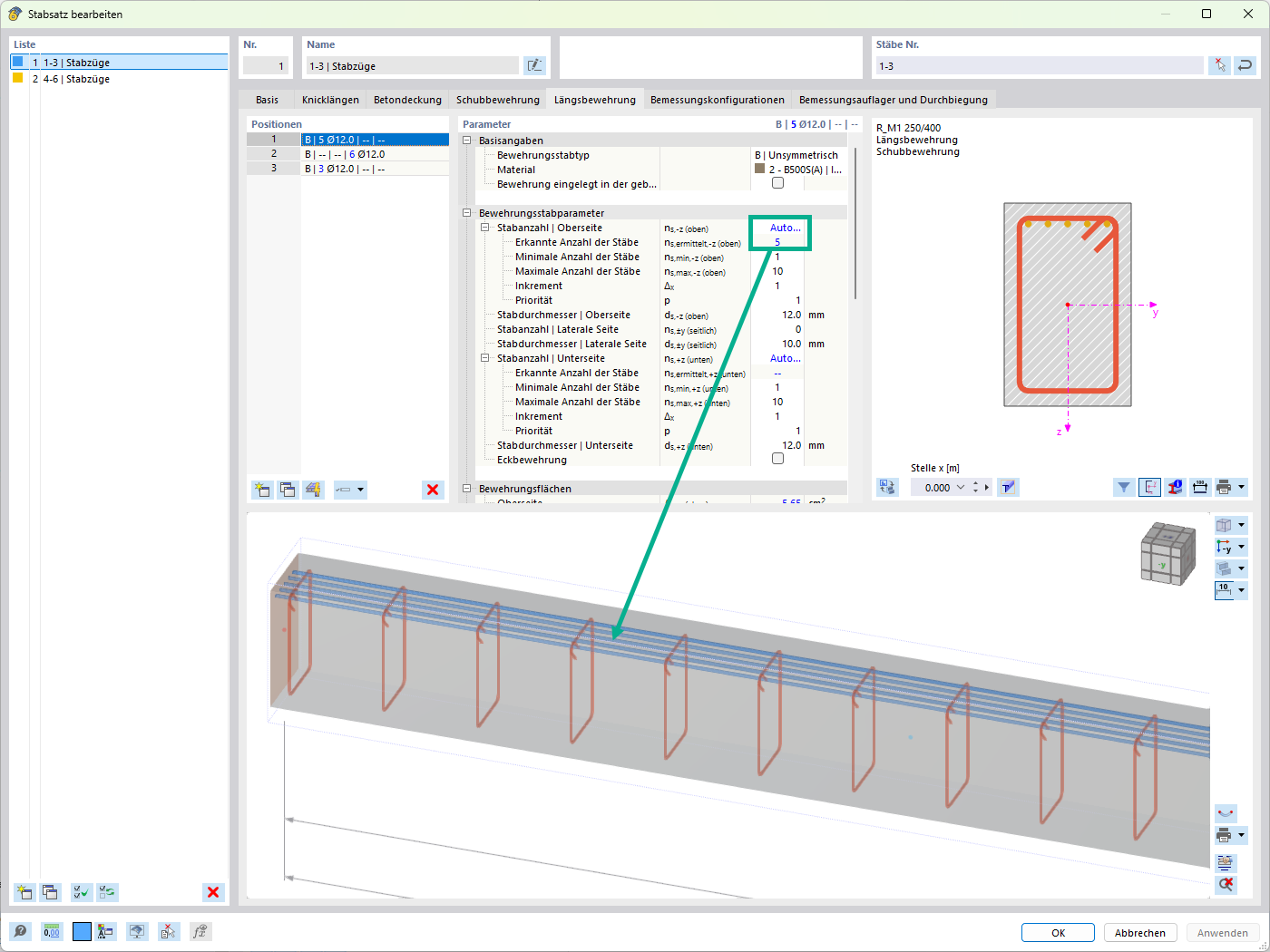
For the design of reinforced concrete members, there is the option to automatically determine the number or diameter of rebars.
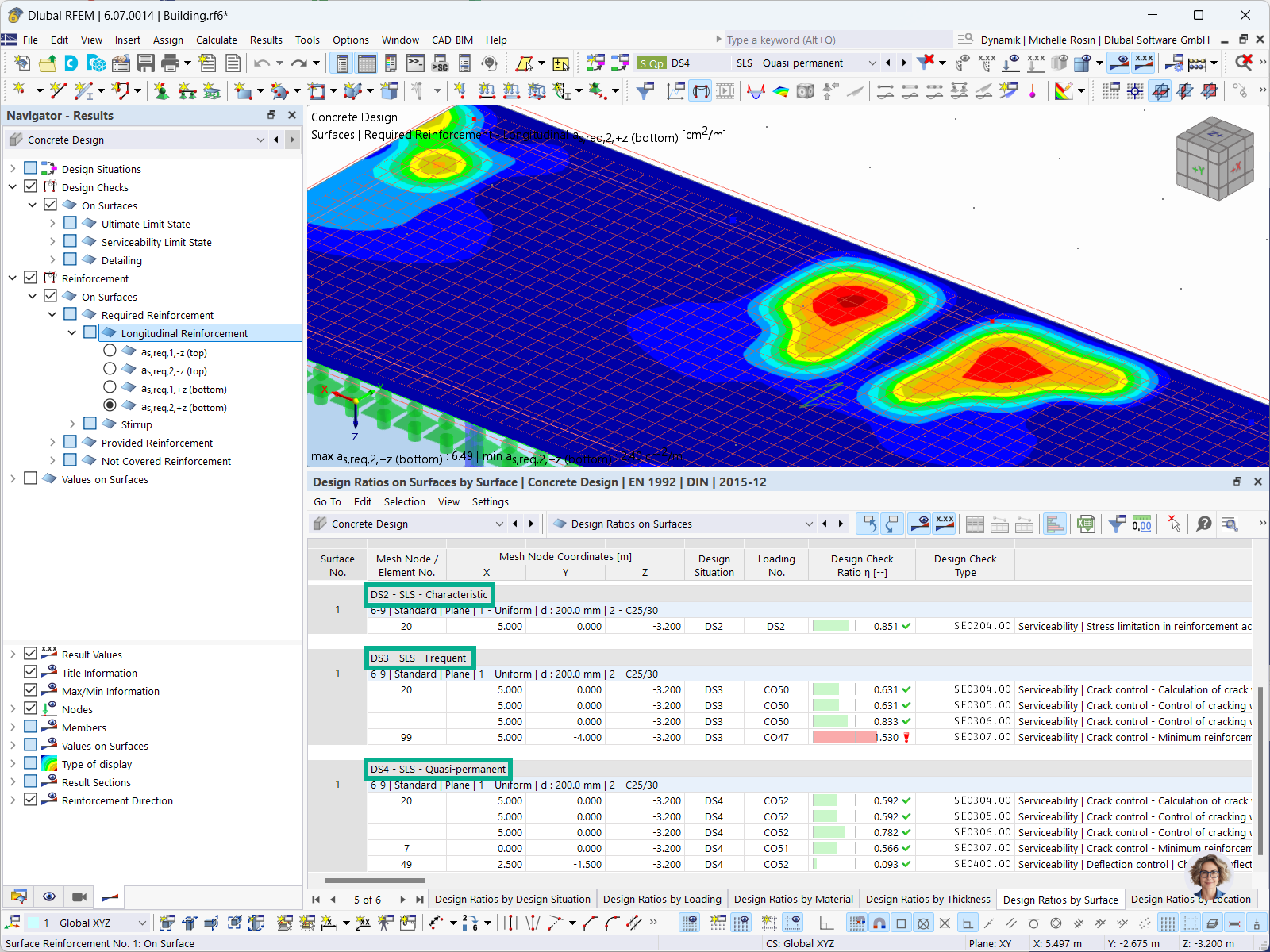
For concrete design, you can display the reinforcement results in tables separately by design situation.
Why is the effective depth different with the effective depth used in shear checks?
How can I check the determination of the required reinforcement?
IB_Wagner,_Gangkofen.png?mw=926&hash=061a9b9f10c37a9d12fee0b56a34dc2fcea6678c)






























_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)

-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)