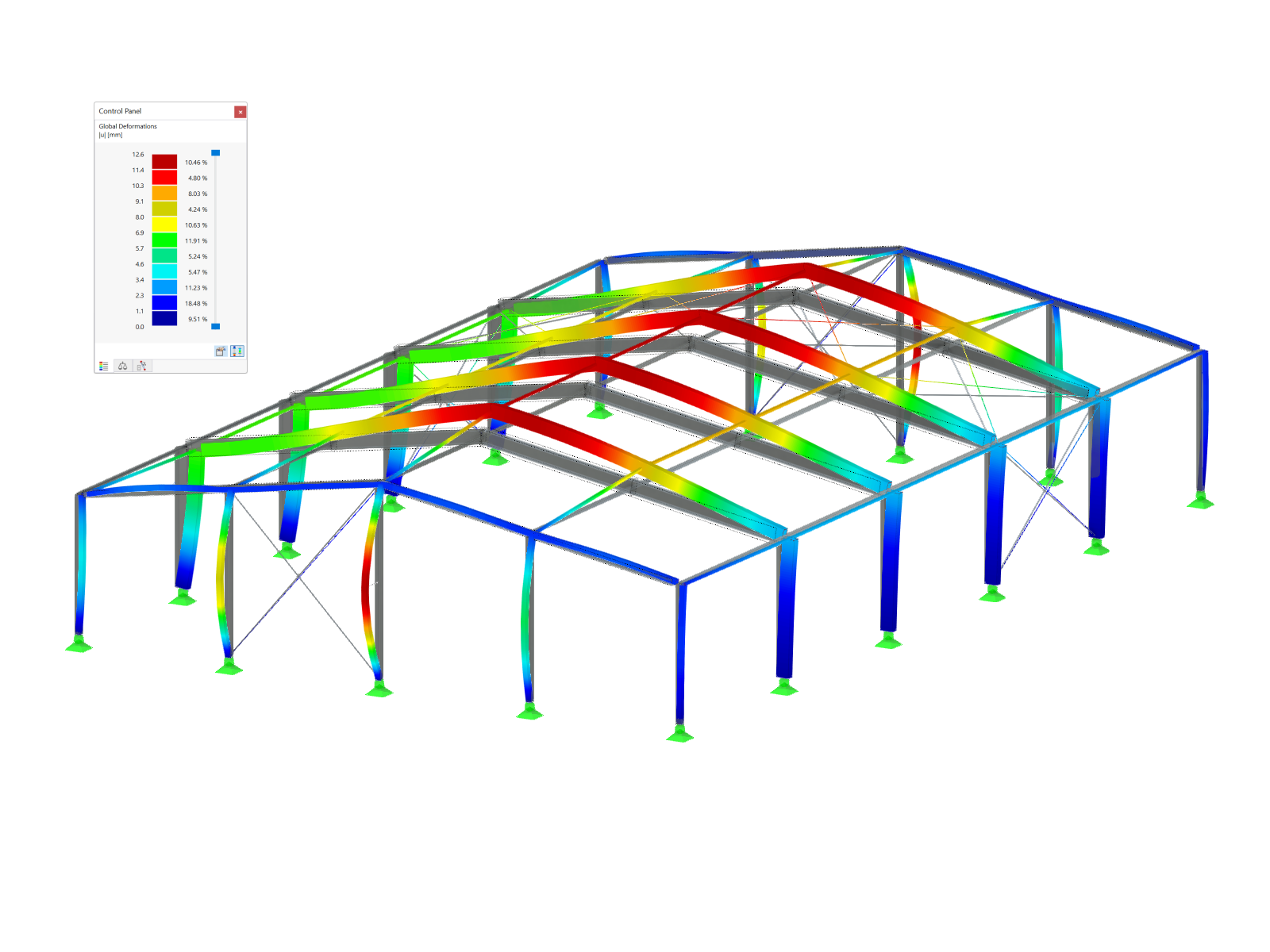
General
Slender truss structures made of closed cross-sections are popular in architecture. Due to computer-aided production of cuts and connection geometries, it is possible also to have complex spatial nodes. This technical article deals with the design of a K‑node. The node definition and the design, in particular, are described in detail.
Details of Model
- Material: S355
- Chord cross-section: RO 108x6.3 | DIN 2448, DIN 2458
- Strut cross-section: RO 60.3x4 | DIN 2448, DIN 2458
- Dimensions: see the graphic
Assigning Node to Joint Type
The connection type for a hollow section node is not only defined by the geometry, but also by the orientation of the axial forces in the struts. In our example, there is a tensile force in Member 35 (Strut 1) and a compression force in Member 36 (Strut 2) on Node 28 to be designed. Given this distribution of internal forces and moments, the joint type is a K‑node. If there was compression or tension in both struts, the connection type would be a Y‑node.
Checking Validity Limits
Compliance with the validity limits is crucial for any design. The ratio of the diameters of struts and chords is important. If it is not in the range of 0.2 ≤ di / do ≤ 1.0, it is impossible to perform the design. The diameter ratio di / do is also referred to as β. The European standard EN 1993-1-8 [1] specifies in Table 7.1 the validity limits for struts and chord members, as well as a limitation of the struts' overlap. If you want to have a gap between the struts, a minimum dimension of g ≥ t1 + t2 must be observed, too. t is the respective wall thickness of the struts. Structural components subjected to compression also need to be classified into cross-section classes 1 or 2. A corresponding check is carried out according to EN 1993-1-1 [2], Chapter 5.5.
Design
In our example, the connection meets the validity limits according to Table 7.1. Therefore, it is sufficient according to EN 1993-1-8, Section 7.4.1 (2), to analyze the chord member for flange failure and punching shear.
Flange Failure of Chord Member due to Axial Force According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.2, Row 3.2
Determination of Diameter-Wall Ratio γ
|
γ |
Verhältnis der Breite oder des Durchmessers des Gurtstabes zum zweifachen seiner Wanddicke |
|
d0 |
Gesamtdurchmesser Gurtstab |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
γ = 8.57
Determination of Factor kg
|
kg |
Beiwert bei Knotenanschlüssen mit Spalt g |
|
γ |
Verhältnis der Breite oder des Durchmessers des Gurtstabes zum zweifachen seiner Wanddicke |
|
e |
Eulersche Zahl |
|
g |
Spaltweite zwischen den Streben eines K- oder N-Anschlusses |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
kg = 1.72
Determination of Chord Tension Coefficient kp
|
kp |
Gurtvorspannungsbeiwert |
|
np |
Verhältniswert |
|
fp |
Wert der einwirkenden Druckspannung im Gurtstab ohne die Spannungen infolge der Komponenten der Strebenkräfte am Anschluss parallel zum Gurt |
|
fy |
Streckgrenze |
|
Np |
Anlaufende Normaldruckkraft im Gurt |
|
A0 |
Querschnittsfläche Gurtstab |
|
M0 |
Sekundäres Moment aus Exzentrizität |
|
W0 |
Elastisches Widerstandsmoment des Gurtquerschnitts |
fp is the chord tension from the axial force Np and the additional moment from eccentricity. Since there is compression and tension in the chors, it is assumed that Np = 0. Furthermore, the eccentricity of the joint is so small that an additional moment from any eccentric connection of the struts does not have to be considered. The auxiliary coefficient is thus zero. The sign convention for compression and tension forces in RFEM and RSTAB differs from those of the European standard EN 1993-1-8. Therefore, the formula is adjusted to kp.
kp = 1.0
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force NRd
|
N1,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Normalkrafttragfähigkeit des Anschlusses für Strebe 1 |
|
kg |
Beiwert bei Knotenanschlüssen mit Spalt g |
|
kp |
Gurtvorspannungsbeiwert |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
θ1 |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe 1 und Gurtstab |
|
d1 |
Gesamtdurchmesser Strebe 1 |
|
d0 |
Gesamtdurchmesser Gurtstab |
|
yM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
|
N2,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Normalkrafttragfähigkeit des Anschlusses für Strebe 2 |
|
θ2 |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe 2 und Gurtstab |
N1,Rd = N2,Rd = 257.36 kN
N1,Ed / N1,Rd = 197.56 / 257.36 = 0.77 < 1.0
N2,Ed / N2,Rd = 186.89 / 257.36 = 0.73 < 1.0
Punching of Chord Member due to Axial Force According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.2, Row 4
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force NRd
|
Ni,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Normalkrafttragfähigkeit des Anschlusses für das Bauteil i |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
π |
Kreiszahl |
|
di |
Gesamtdurchmesser bei KHP-Bauteilen i |
|
θi |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe i und Gurtstab |
|
γM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
N1,Rd = N2,Rd = 417.58 kN
N1,Ed / N1,Rd = 197.56 / 417.58 = 0.47 < 1.0
N2,Ed / N2,Rd = 186.89 / 417.58 = 0.45 < 1.0
Flange Failure of Chord Member due to Moment Mop According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.5, Row 2
This design is only relevant for 3D structures where moments may also occur from the truss plane.
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force Mop,Rd
|
Mop,i,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Momententragfähigkeit des Anschlusses bei Biegung aus der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
di |
Gesamtdurchmesser bei KHP-Bauteilen i |
|
θi |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe i und Gurtstab |
|
β |
Verhältnis der mittleren Durchmesser oder mittleren Breiten von Strebe und Gurtstab |
|
kp |
Gurtvorspannungsbeiwert |
|
yM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
Mop,1,Rd = Mop,2,Rd = 5.92 kNm
Mop,1,Ed / Mop,1,Rd = 0.08 / 5.92 = 0.01 < 1.0
Mop,2,Ed / Mop,2,Rd = 0.01 / 5.92 = 0.00 < 1.0
Flange Failure of Chord Member due to Moment Mip According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.5, Row 1
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force Mip,Rd
|
Mip,i,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Momententragfähigkeit des Anschlusses bei Biegung in der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
di |
Gesamtdurchmesser bei KHP-Bauteilen i |
|
θi |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe i und Gurtstab |
|
γ |
Verhältnis der Breite oder des Durchmessers des Gurtstabes zum zweifachen seiner Wanddicke |
|
β |
Verhältnis der mittleren Durchmesser oder mittleren Breiten von Strebe und Gurtstab |
|
kp |
Gurtvorspannungsbeiwert |
|
γM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
Mip,1,Rd = Mip,2,Rd = 9.53 kNm
Mip,1,Ed / Mip,1,Rd = 0.37 / 9.53 = 0.04 < 1.0
Mip,2,Ed / Mip,2,Rd = 0.14 / 9.53 = 0.01 < 1.0
Punching of Chord Member due to Moment Mop According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.5, Row 3.2
This design is only relevant for 3D structures where moments may also occur from the truss plane.
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force Mop,Rd
|
Mop,i,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Momententragfähigkeit des Anschlusses bei Biegung aus der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
di |
Gesamtdurchmesser bei KHP-Bauteilen i |
|
θi |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe i und Gurtstab |
|
yM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
Mop,1,Rd = Mop,2,Rd = 8.70 kNm
Mop,1,Ed / Mop,1,Rd = 0.08 / 8.70 = 0.01 < 1.0
Mop,2,Ed / Mop,2,Rd = 0.01 / 8.70 = 0.00 < 1.0
Punching of Chord Member due to Moment Mip According to EN 1993-1-8, Table 7.5, Row 3.1
Determination of Allowable Limit Internal Force Mip,Rd
|
Mip,i,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Momententragfähigkeit des Anschlusses bei Biegung in der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
fy0 |
Streckgrenze des Werkstoffs eines Gurtstabes |
|
t0 |
Wanddicke des Gurtstabquerschnitts |
|
di |
Gesamtdurchmesser bei KHP-Bauteilen i |
|
θi |
Eingeschlossener Winkel zwischen Strebe i und Gurtstab |
|
yM5 |
Teilsicherheitsbeiwert |
Mip,1,Rd = Mip,2,Rd = 7.33 kNm
Mip,1,Ed / Mip,1,Rd = 0.37 / 7.33 = 0.05 < 1.0
Mip,2,Ed / Mip,2,Rd = 0.14 / 7.33 = 0.02 < 1.0
Interaction Conditions According to EN 1993-1-8, Chapter 7.4.2, Equation 7.3
In this design step, the struts are designed for the shared loading from axial force and bending. Currently, only bending perpendicular to the truss plane is considered here.
|
Ni,Ed |
Bemessungswert der einwirkenden Normalkraft für das Bauteil i |
|
Ni,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Normalkrafttragfähigkeit des Anschlusses für das Bauteil i |
|
Mop,i,Ed |
Bemessungswert des einwirkenden Momentes aus der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
Mop,i,Rd |
Bemessungswert der Momententragfähigkeit des Anschlusses bei Biegung aus der Tragwerksebene für das Bauteil i |
|
S1 |
Strebe 1 |
|
S2 |
Strebe 2 |
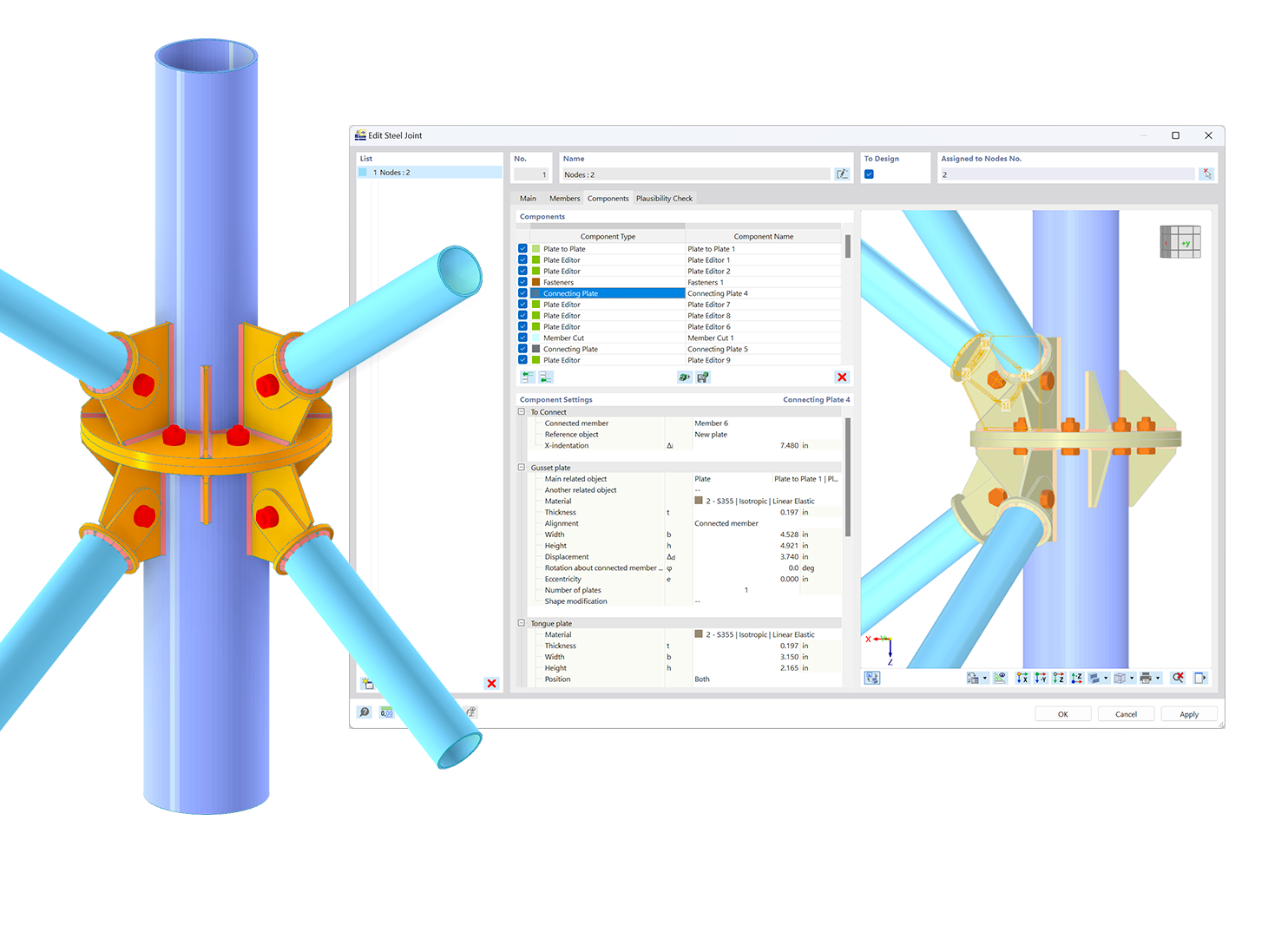
Conclusion
The technical article shows that the design for a K-node is not trivial. With the RF-/HSS add-on module, Dlubal offers a tool for designing all nodal types defined in the European standard, for CHS as well as SHS and RHS sections.













.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)