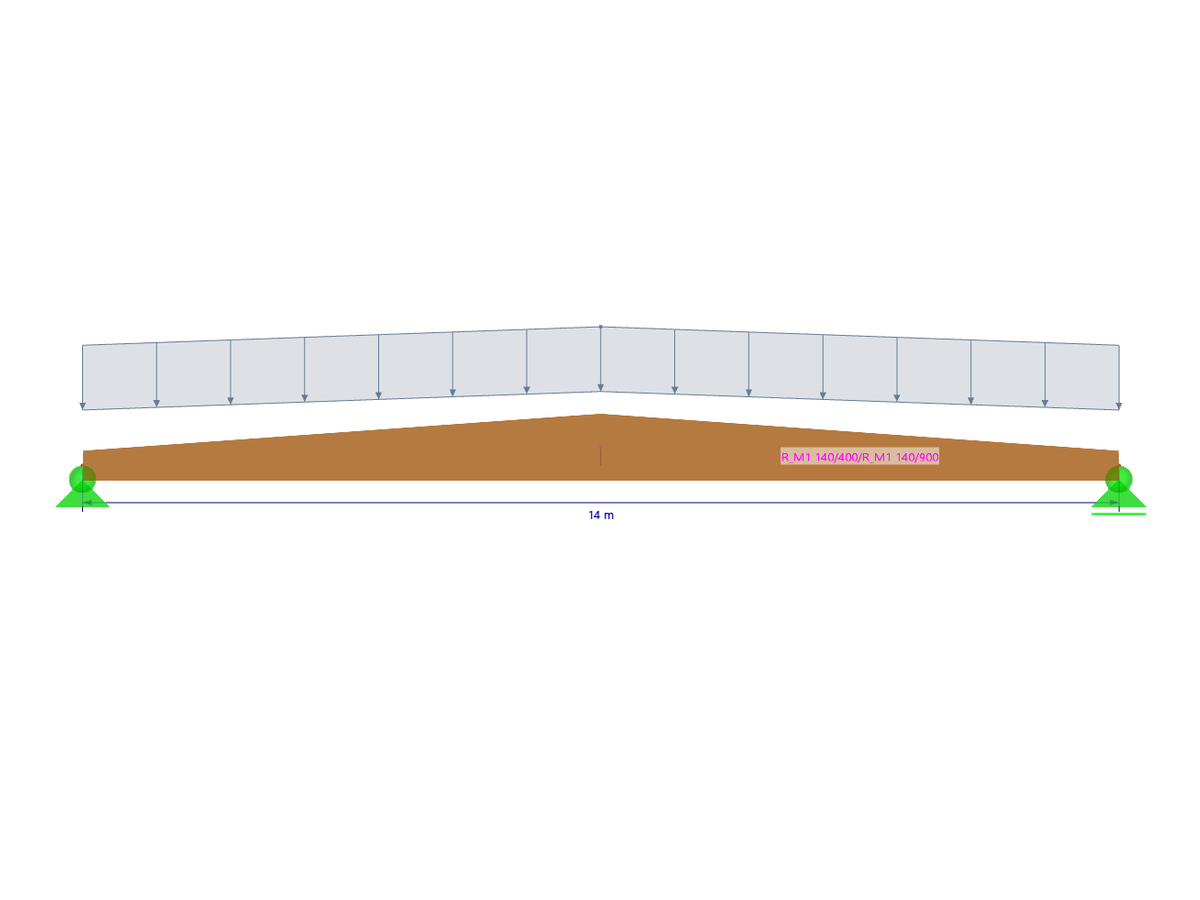
Load Ordinates

.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)


Did you know? In the Design Supports, you can now define fully threaded screws as transversal compression stiffening elements for the "Compression Perpendicular to Grain" design. In this case, the pressing-in and buckling of the bolts is analyzed.
Moreover, the design shear resistance is checked in the plane of the screw tip. The angle of dispersal can be considered as linear under 45° or nonlinear (according to Bejtka, I. (2005). Verstärkung von Bauteilen aus holz mit vollgewindeschrauben. KIT Scientific Publishing.).
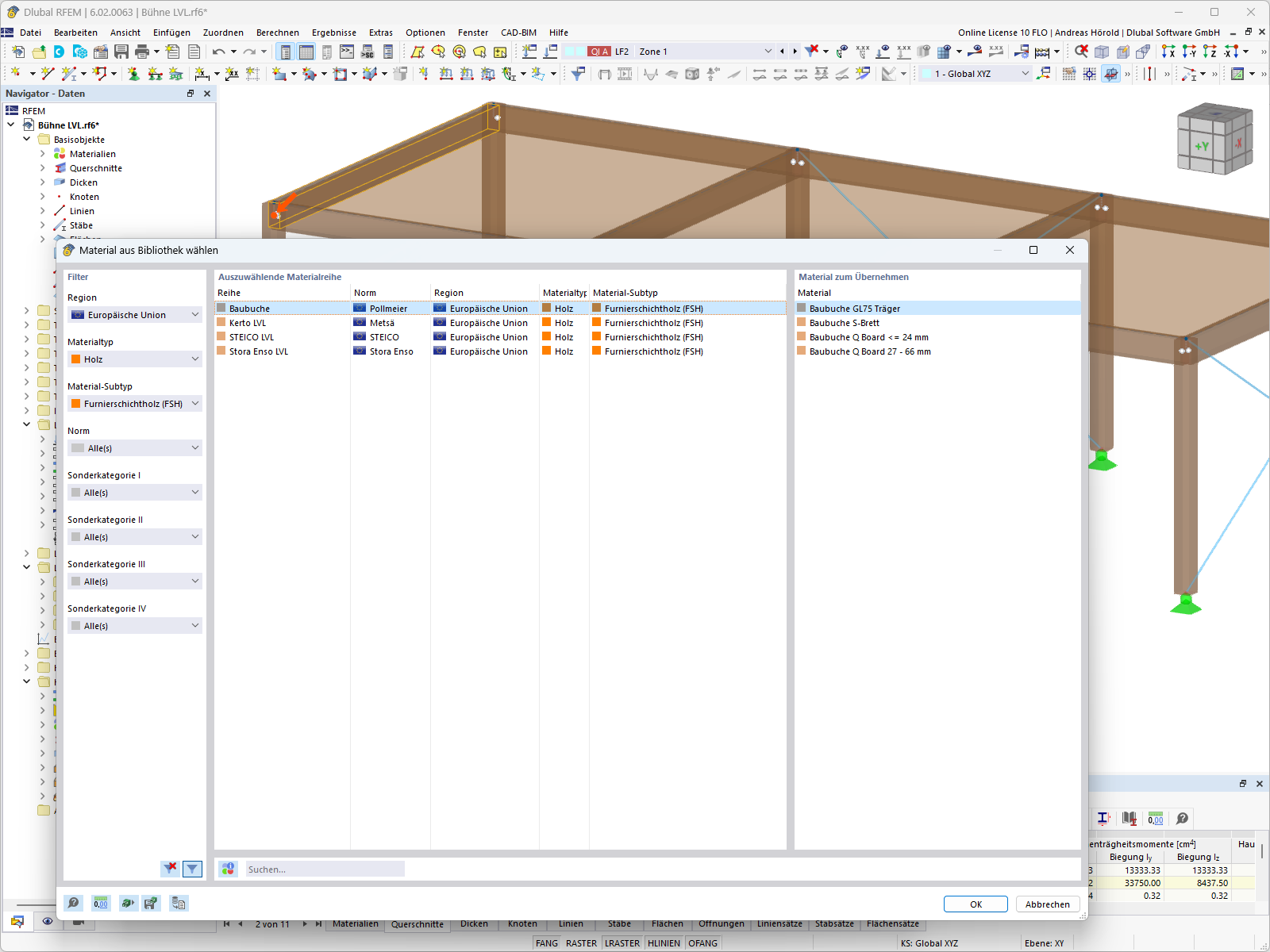
In RFEM and RSTAB, you can design members with the "Laminated Veneer Lumber" material type. The following manufacturers are available:
- Pollmeier (Baubuche)
- Metsä (Kerto LVL)
- STEICO
- Stora Enso
In the ultimate configuration, you can consider strength coefficients for increasing the strengths. The coefficients reducing the strengths are automatically taken into account regardless of this. Try it now!
Go to Explanatory Video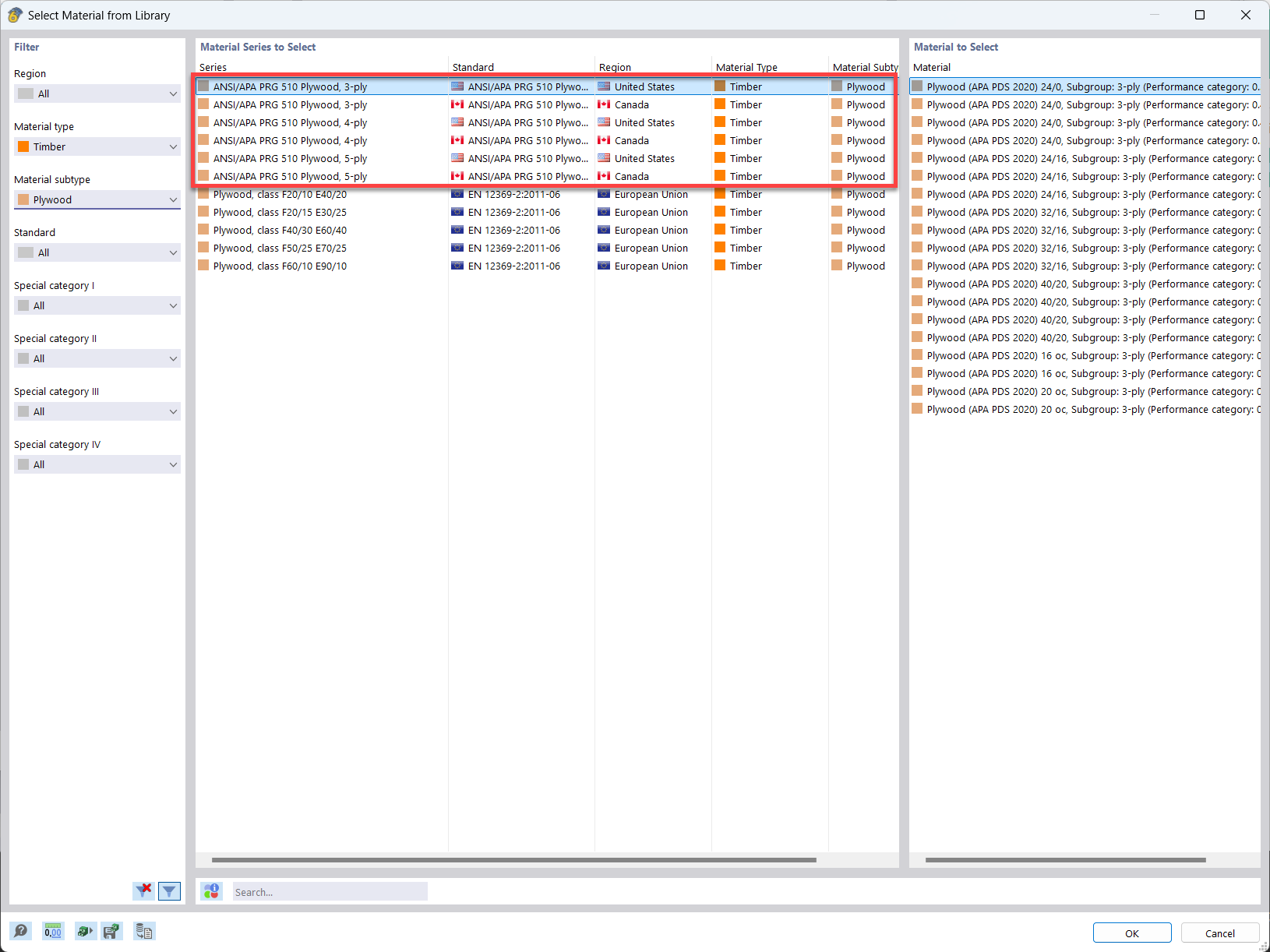
In the material library of RFEM, you can find plywood materials according to the US and Canadian standards ANSI/APA PRG 510 Plywood (USA/CAN).
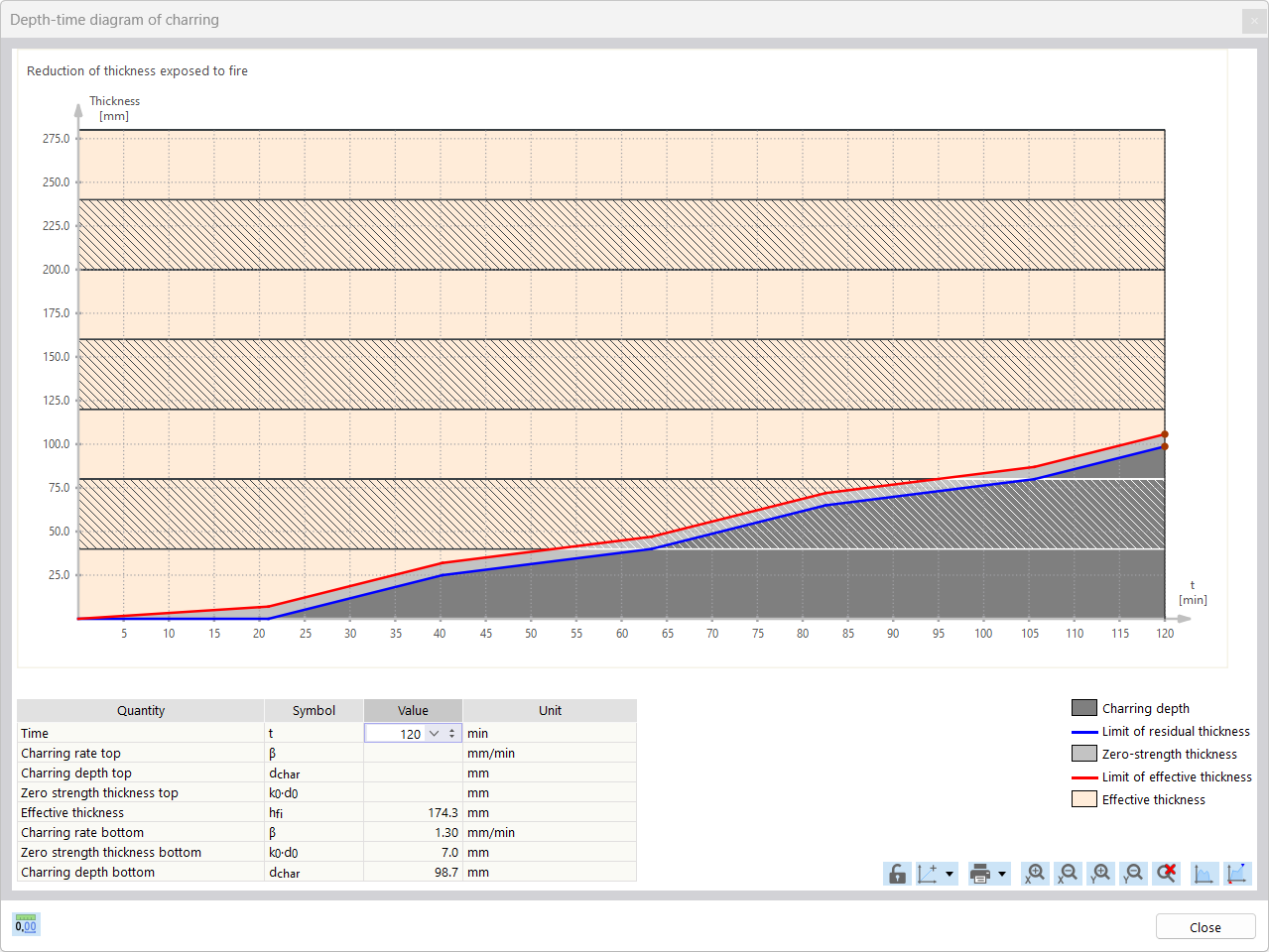
For the fire resistance design of timber surfaces, you can display a charring diagram depending on the time of fire exposure.
It is also possible to print this charring diagram into the printout report.
Do I need to add a line hinge/line release for the CLT wall-to-floor connection in the Building Model add-on?



















































