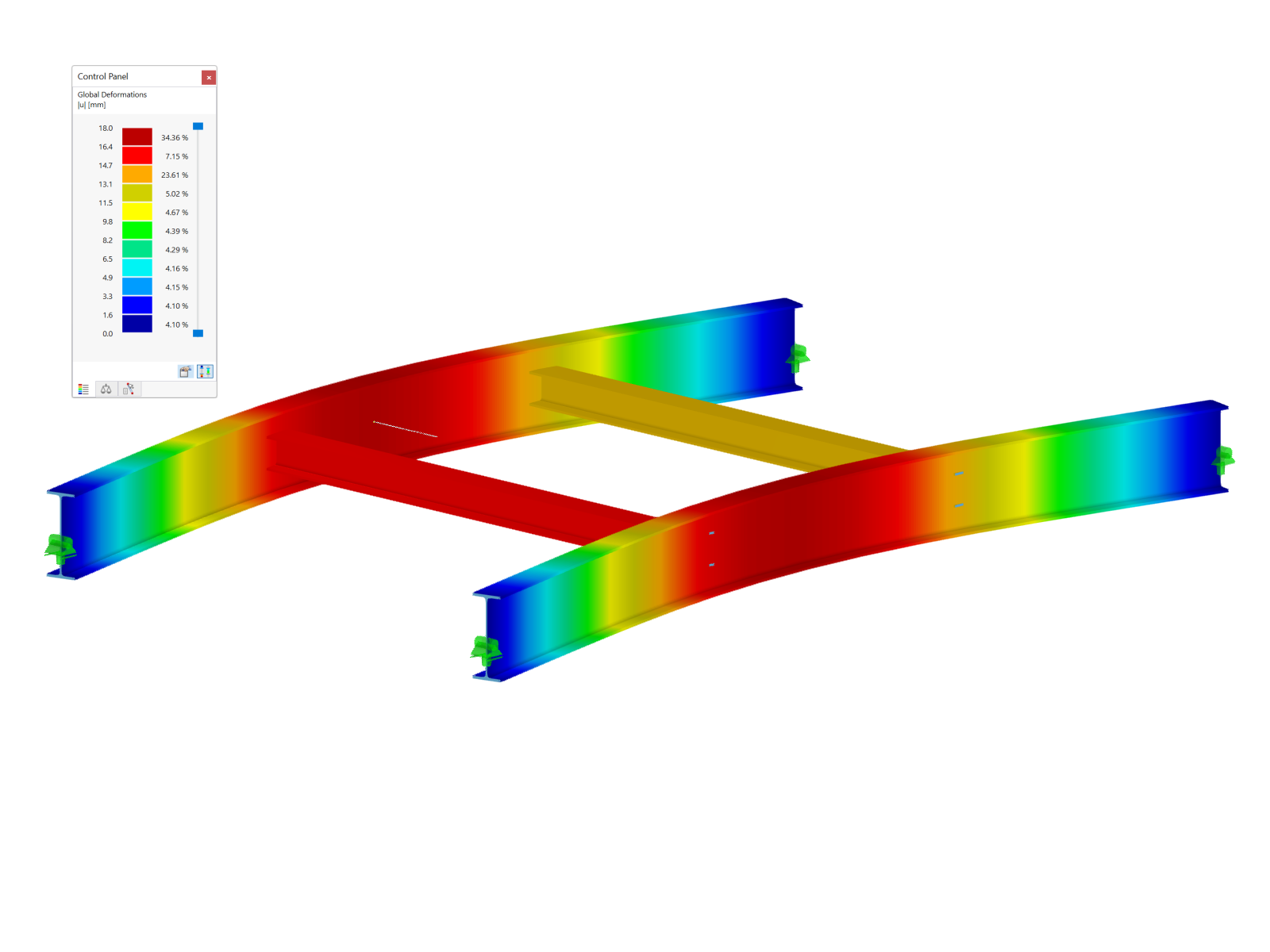
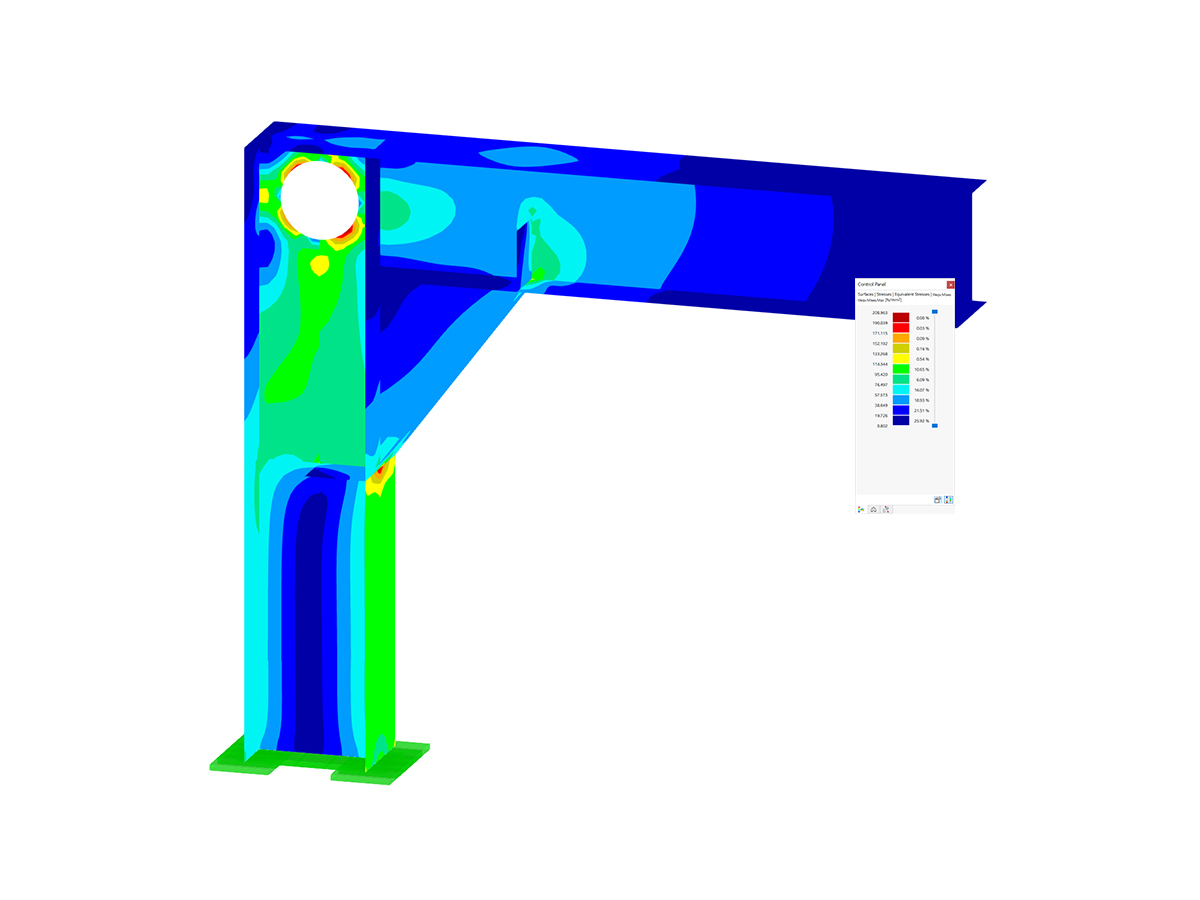
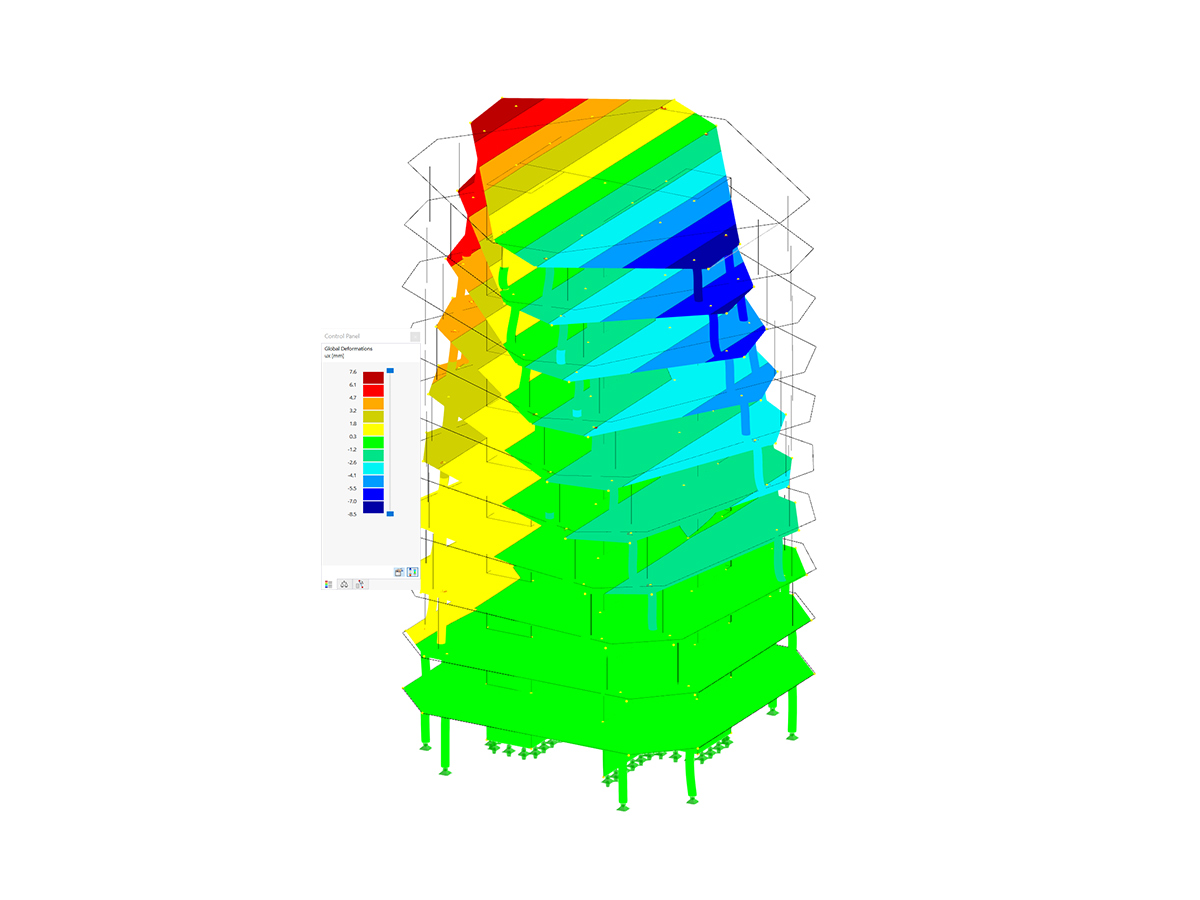
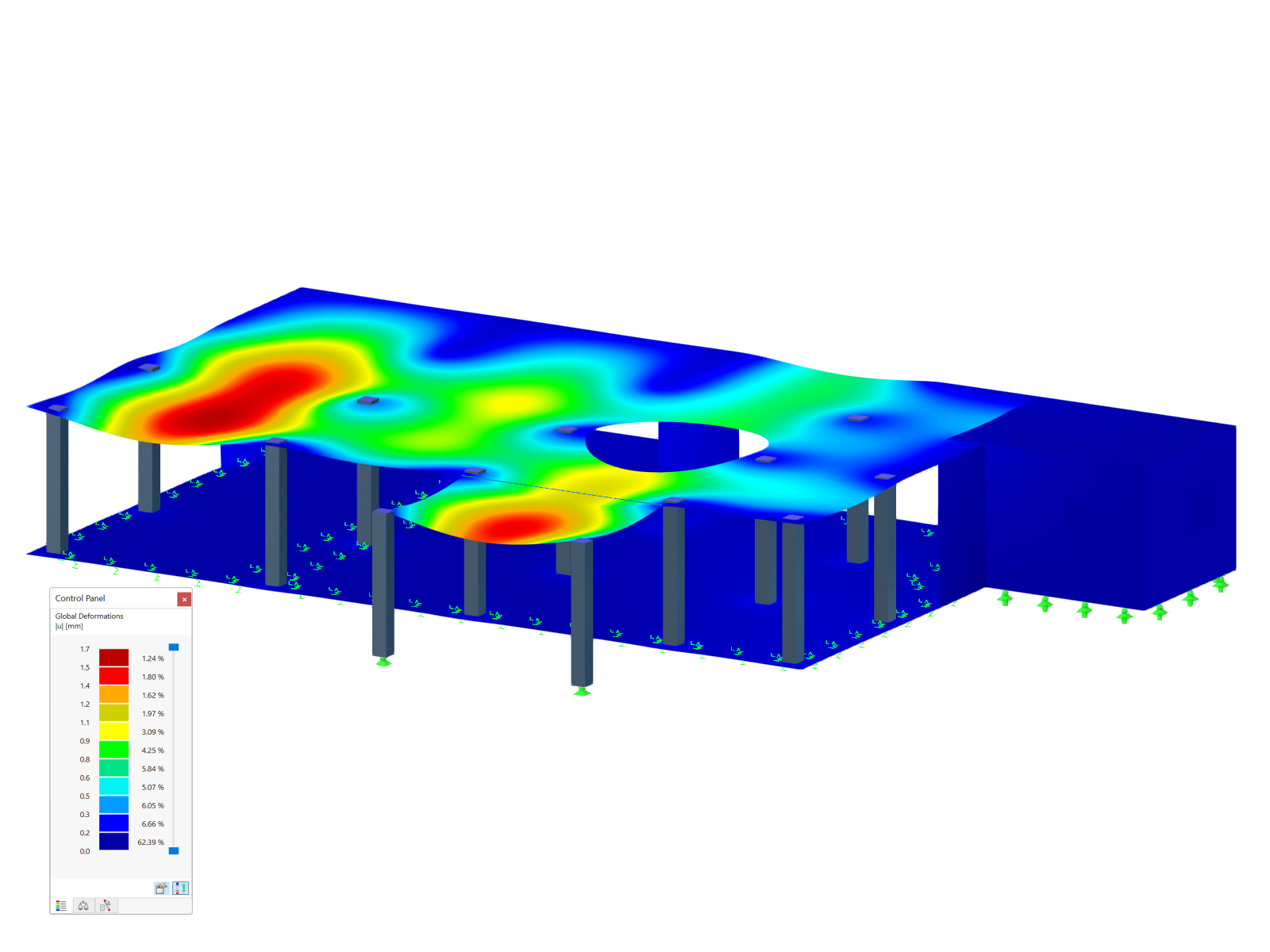
This model shows a lightweight timber building. The walls are designed to optimize the strength and structural stability of the building using modern timber construction methods. It is an illustrative example of the efficient use of renewable materials in architecture. The building is ideal for anyone interested in environmentally friendly and sustainable technologies.
| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Timber Frame Walls in Building
| Número de nudos | 560 |
| Número de líneas | 333 |
| Número de barras | 117 |
| Número de superficies | 22 |
| Número de sólidos | 0 |
| Número de casos de carga | 1 |
| Número de combinaciones de carga | 1 |
| Número de combinaciones de resultados | 0 |
| Peso completo | 6.651 t |
| Dimensiones (métricas) | 12,076 x 3,076 x 6,076 m |
| Dimensiones (imperiales) | 39.62 x 10.09 x 19.93 feet |
You can download this structural model to use it for training purposes or for your projects. However, we do not assume any guarantee or liability for the accuracy or completeness of the model.
![Basic Shapes of Membrane Structures [1]](/en/webimage/009595/2419502/01-en-png-png.png?mw=512&hash=6ca63b32e8ca5da057de21c4f204d41103e6fe20)

For design objects, you can optionally display sags or extreme results.
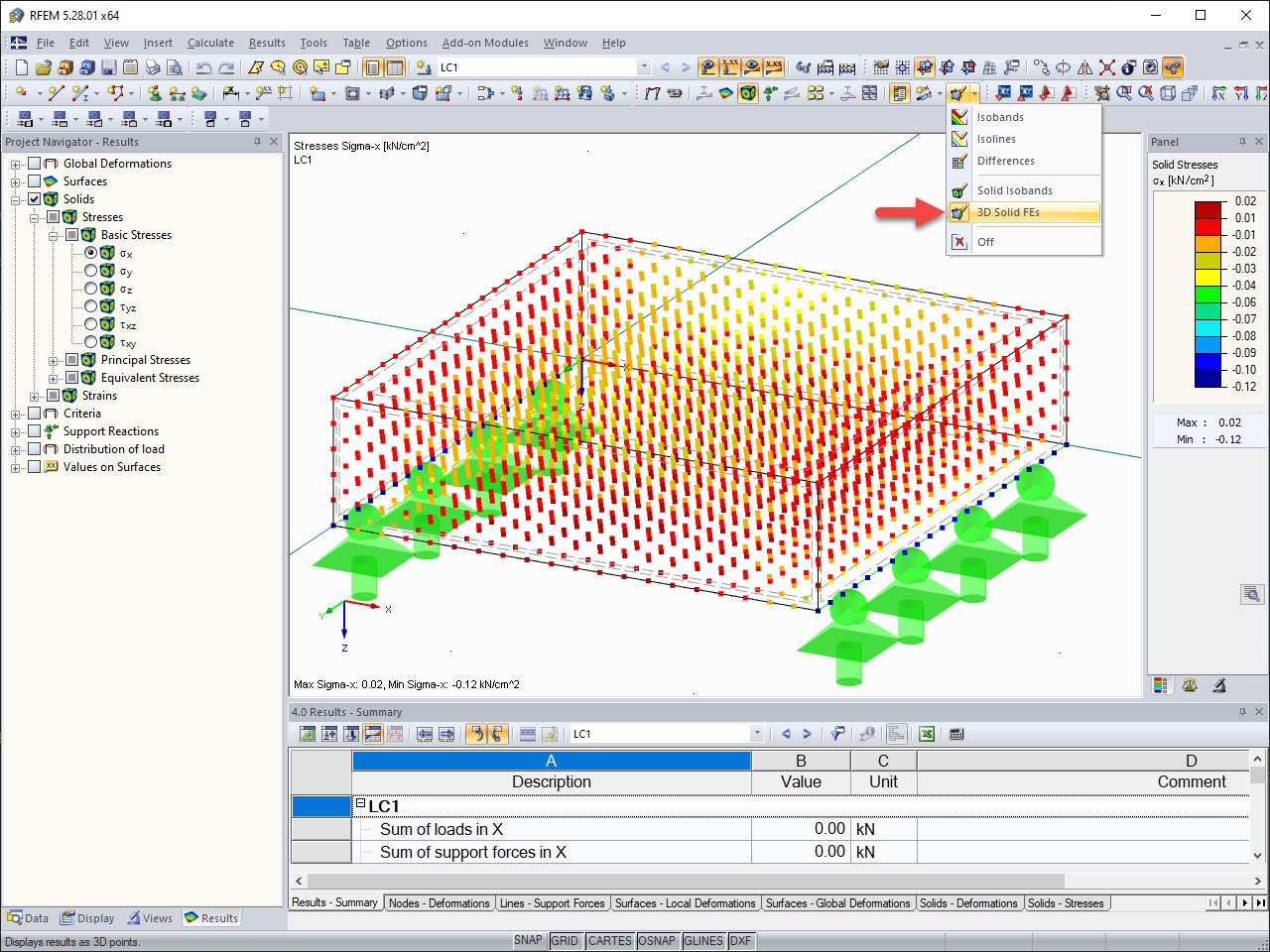
The results of solid stresses can be displayed as colored 3D points in the finite elements.
.png?mw=512&hash=ea9bf0ab53a4fb0da5c4ed81d32d53360ab2820c)
The number of degrees of freedom in a node is no longer a global calculation parameter in RFEM (6 degrees of freedom for each mesh node in 3D models, 7 degrees of freedom for the warping torsion analysis). Thus, each node is generally considered with a different number of degrees of freedom, which leads to a variable number of equations in the calculation.
This modification speeds up the calculation, especially for models where a significant reduction of the system could be achieved (for example, trusses and membrane structures).

Display extended strains of members, surfaces, and solids (for example, the important principal strains, equivalent total strains, and so on) in the Project Navigator - Results in RFEM as well as in Table 4.0.
For example, you can display governing plastic strains when performing the plastic design of connections with surface elements.
Where can I find the update reports for RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, SHAPE-THIN, SHAPE-MASSIVE, RX-TIMBER, CRANEWAY, PLATE-BUCKLING, COMPOSITE-BEAM?
For my NVIDIA graphics card, I need to select between a driver from the "Production Branch" and a "New Feature Branch." Which driver is best suited for RFEM/RSTAB?




.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)





















_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)










.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)