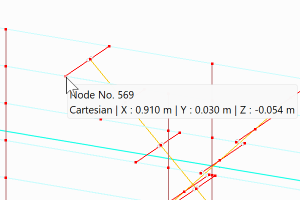
Yes, you can. Move your mouse pointer over the node and wait a moment. A bubble with the node coordinates will appear.
.png?mw=512&hash=4a84cbc5b1eacf1afb4217e8e43c5cb50ed8d827)
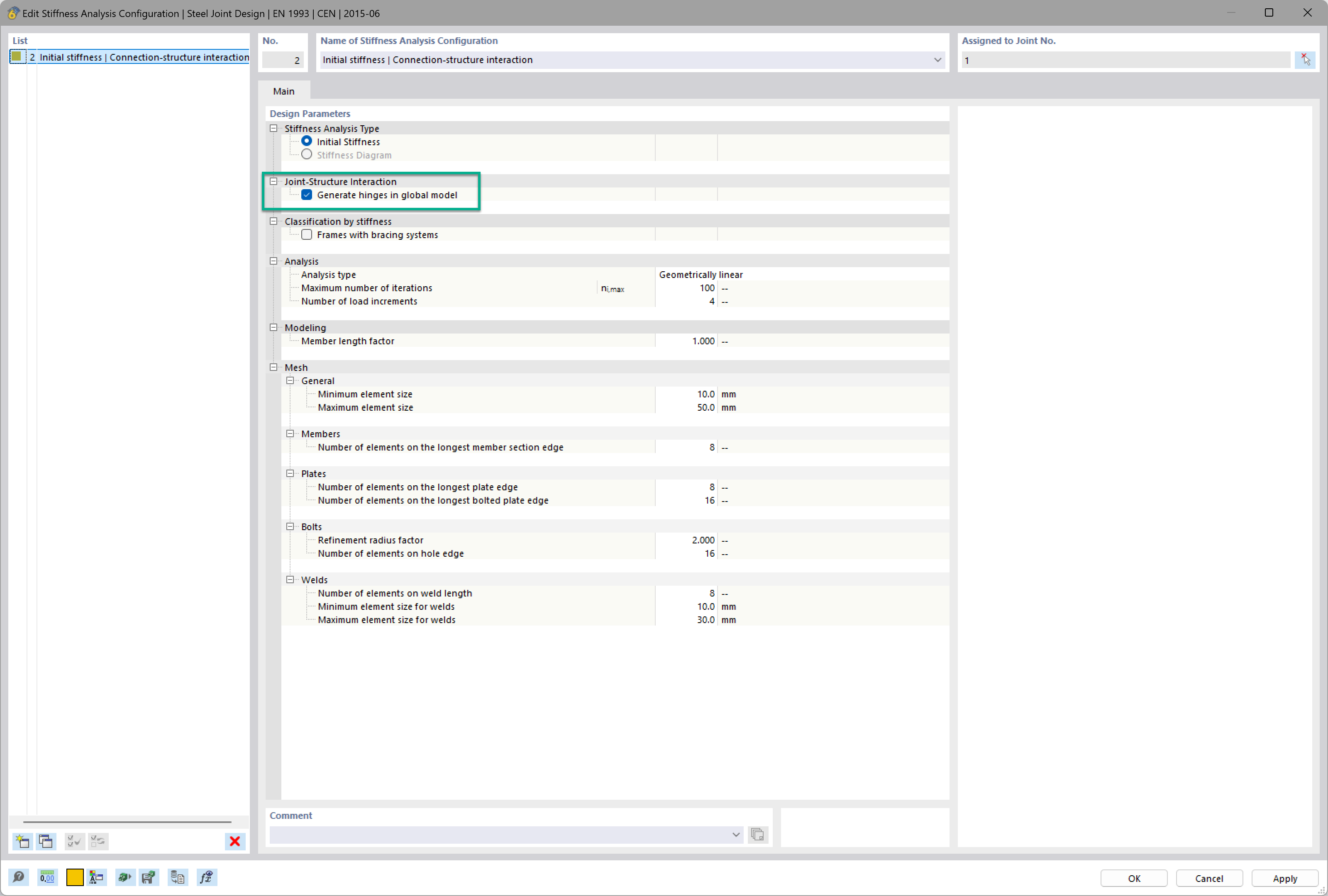
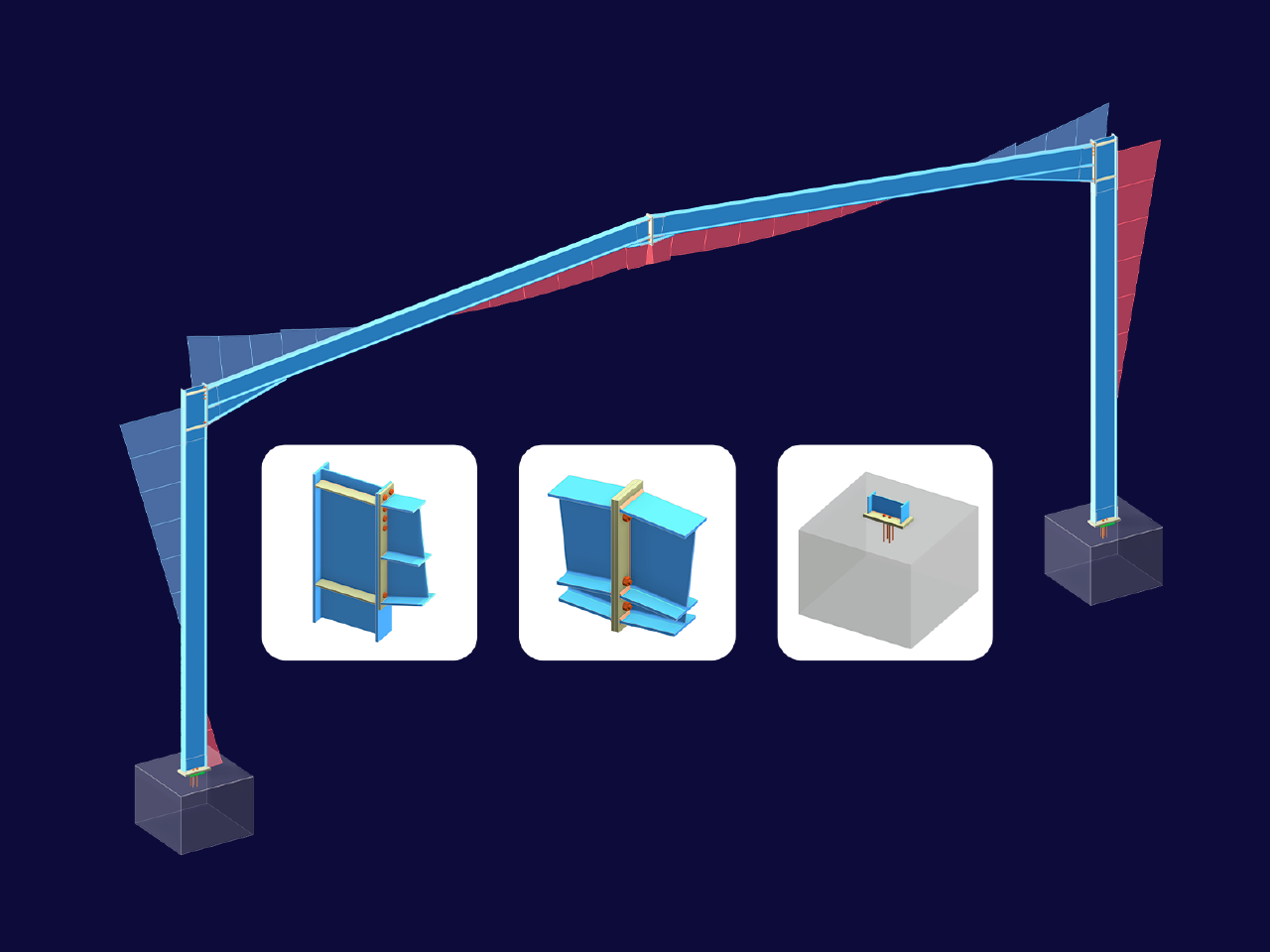
Want to automatically consider steel joint stiffness in your global RFEM model? Utilize the Steel Joints add-on!
Activate joint-structure interaction in the stiffness analysis of your steel joints. Hinges with springs are then automatically generated in the global model and included in subsequent calculations.
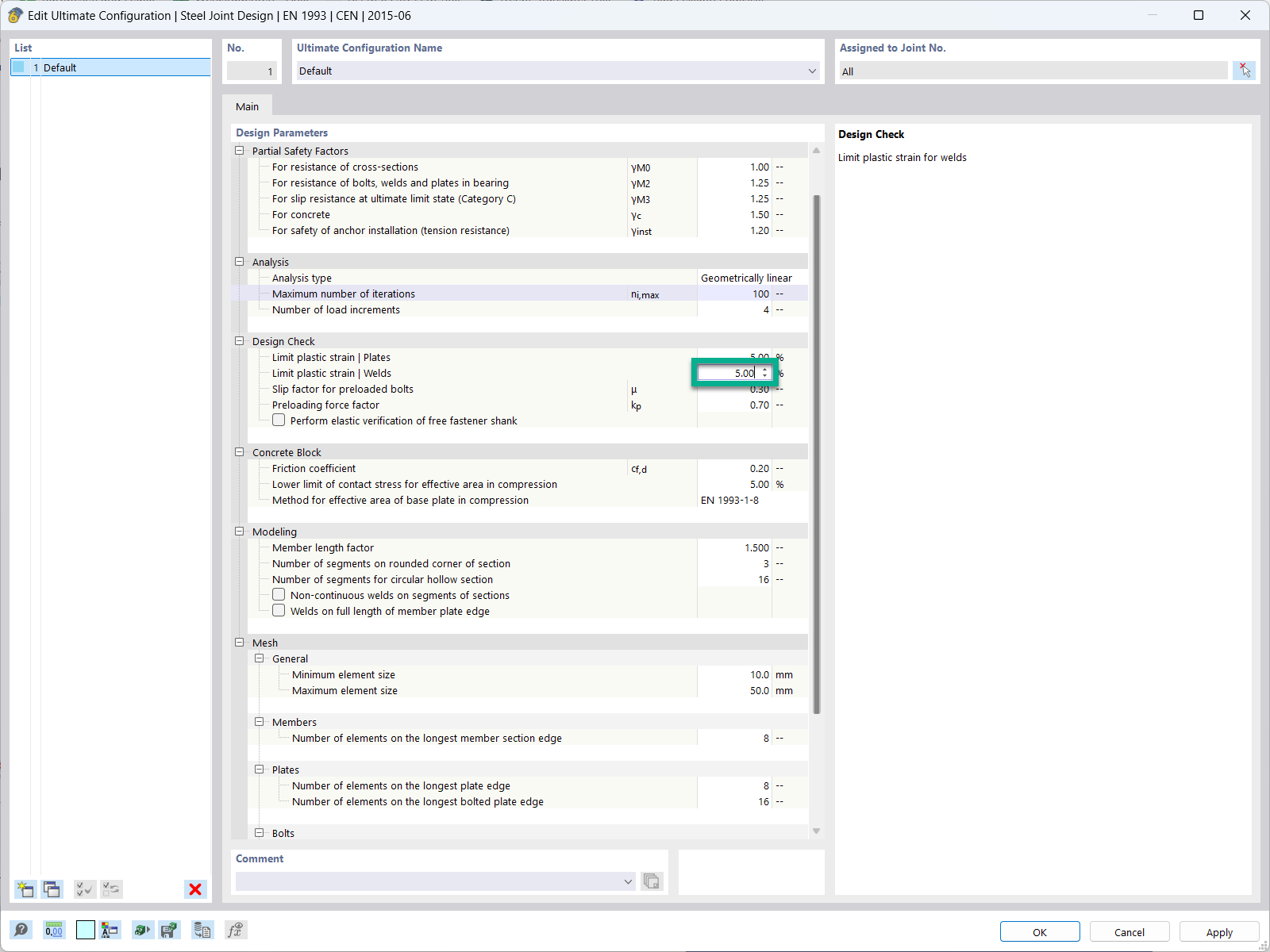
In the ultimate configuration of the steel joint design, you have the option to modify the limit plastic strain for welds.
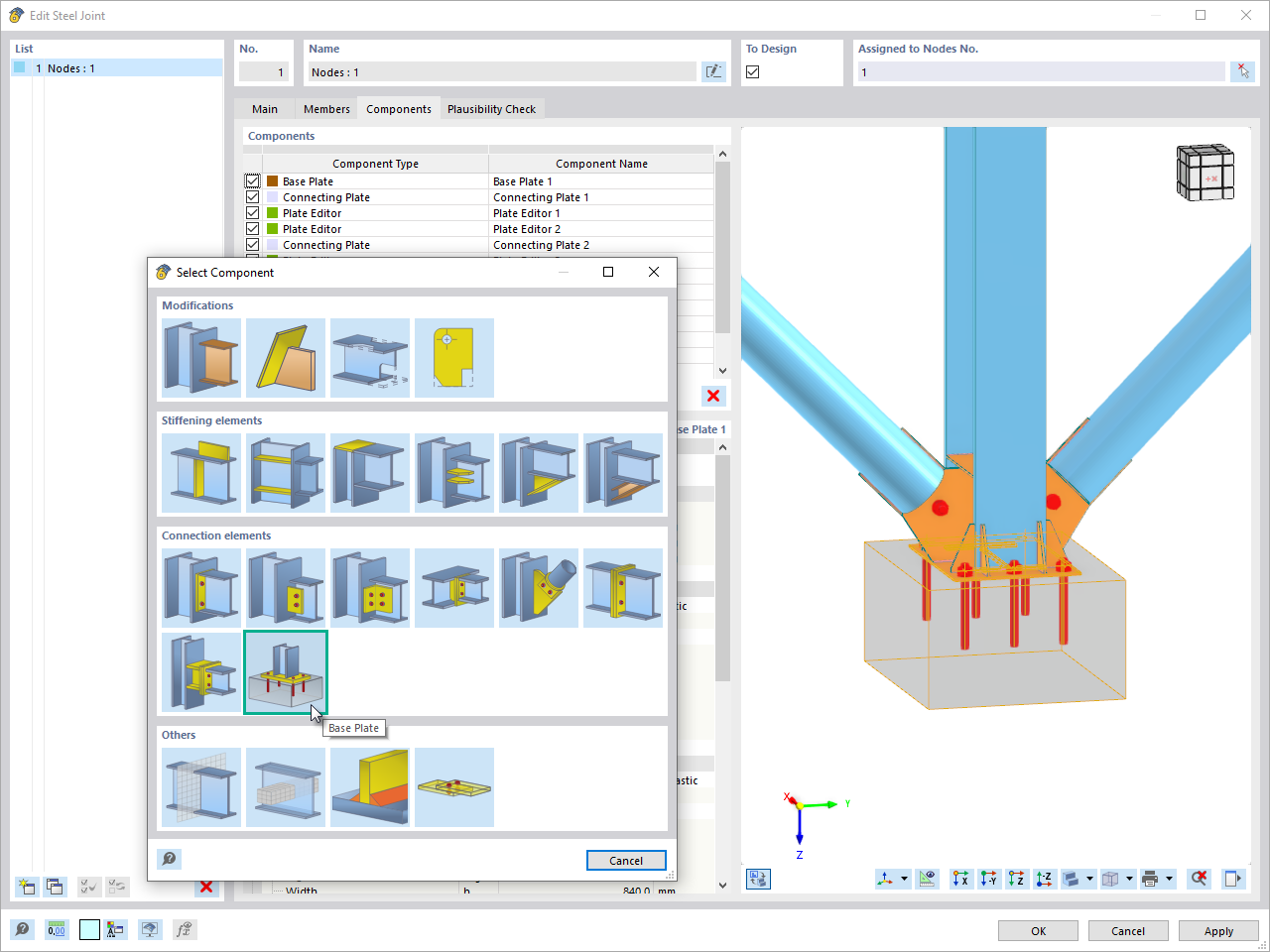
The "Base Plate" component allows you to design base plate connections with cast-in anchors. In this case, plates, welds, anchorages, and steel-concrete interaction are analyzed.
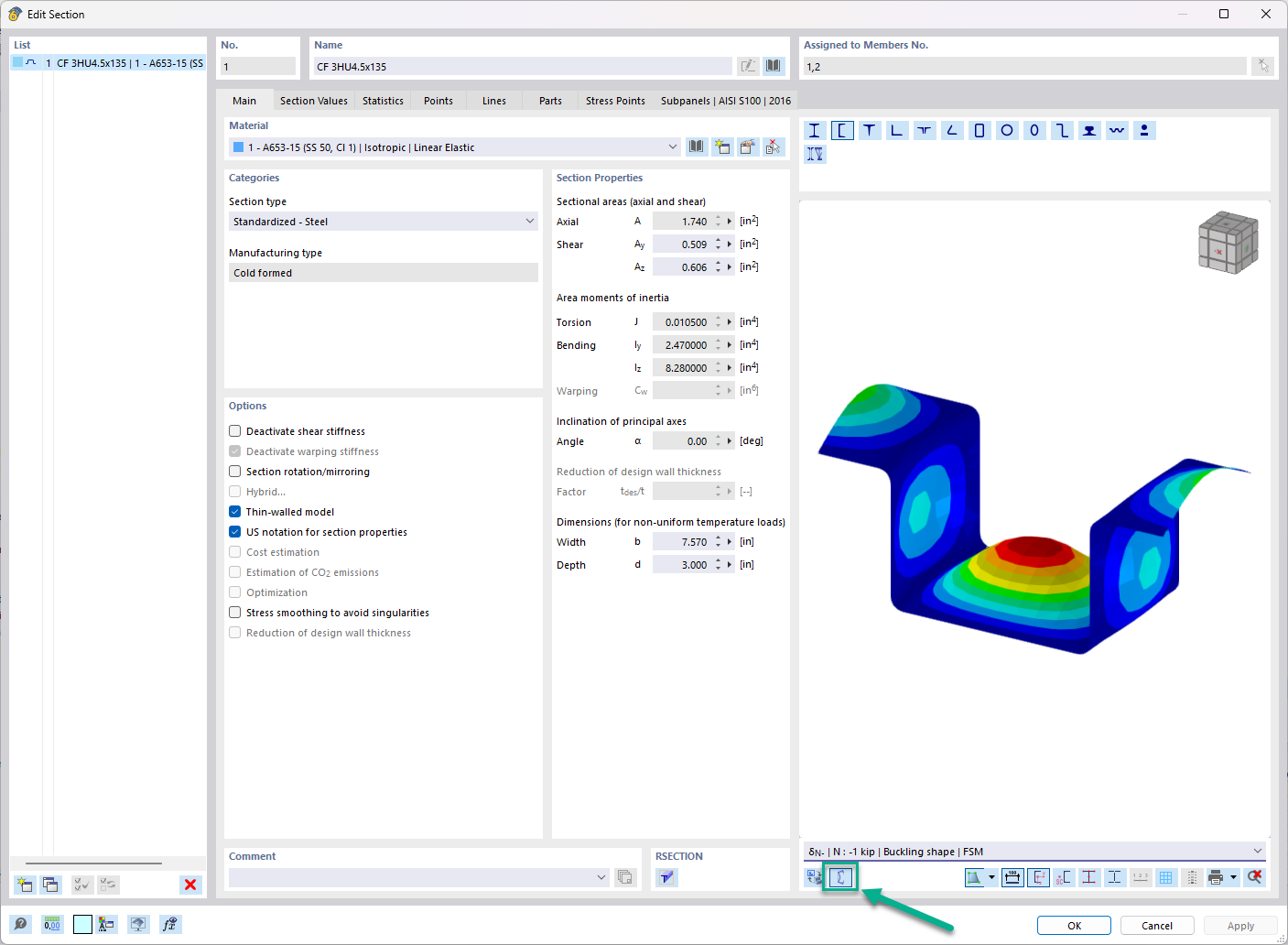
In the "Edit Section" dialog box, you can display the buckling shapes of the Finite Strip Method (FSM) as a 3D graphic.
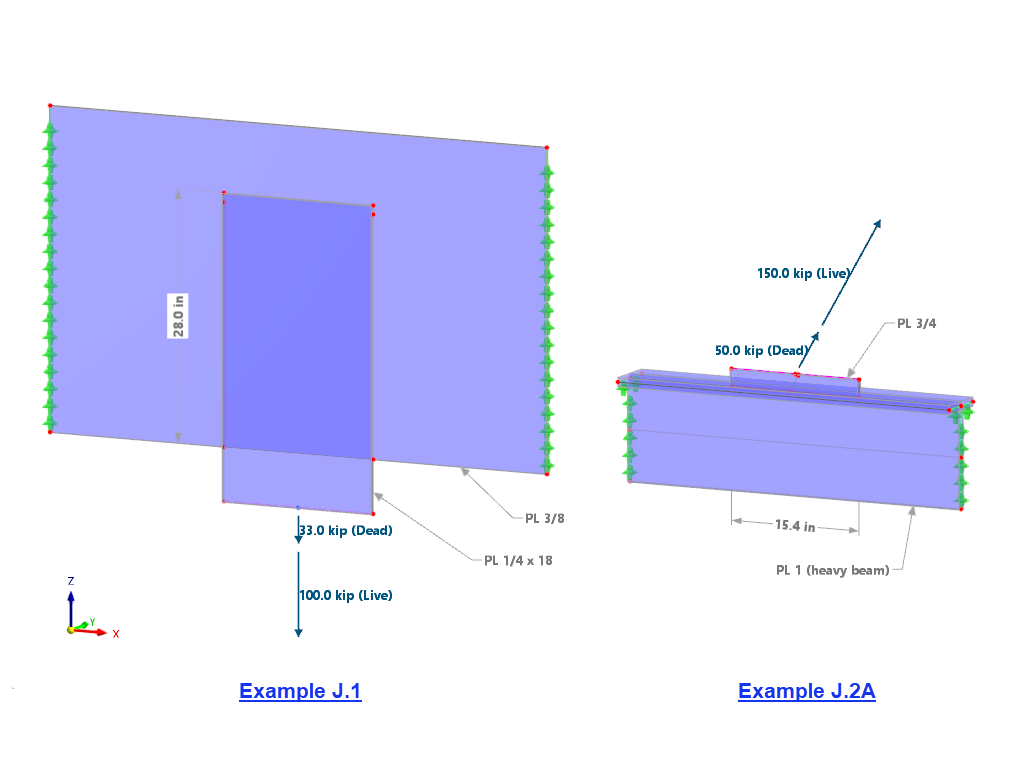
In the Steel Joints add-on, I get high utilization ratios for preloaded bolts in the tension design. Where do these high utilization ratios come from and how can I evaluate the load-bearing reserves of the bolt?
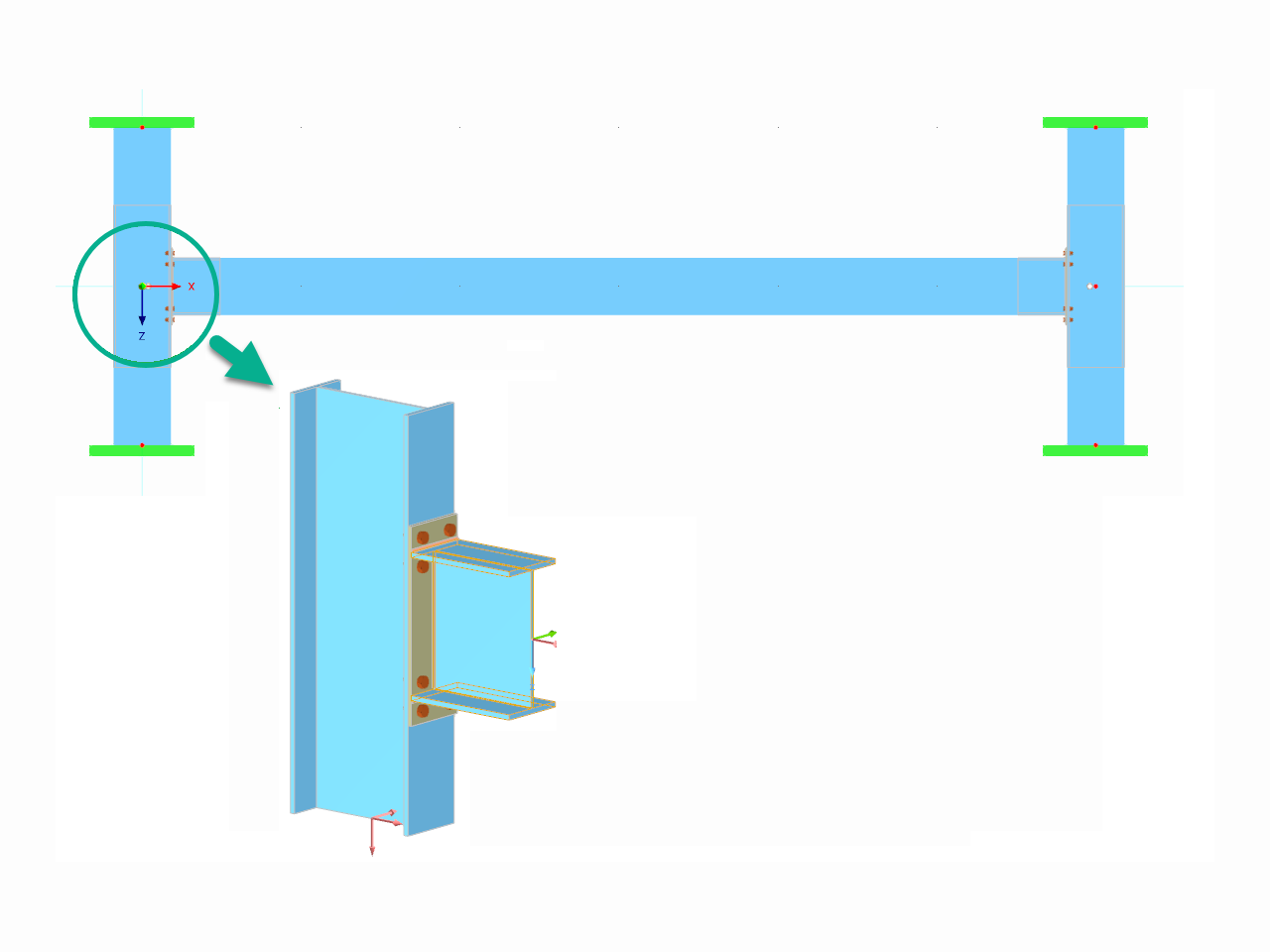
How can treating a connection as fully rigid result in an uneconomical design?
Is it possible to consider shear panels and rotational restraints in the global calculation?
I am calculating a support that is clamped at the base, held in the X direction at the head, and can buckle in the Y direction. I have set the bar shear lengths using node carriers. In the verification, the buckling length values for the calculation are the same, L_(cr,z) = L_(cr,y) = 2.41 m. What am I doing wrong?



















.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)




























_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)



