| 5 star | ||
| 4 star | ||
| 3 star | ||
| 2 star | ||
| 1 star |
Graduation Thesis 000517 | Methodological Approaches to Calculating Wind Loads...
| Number of Nodes | 1040 |
| Number of Lines | 1298 |
| Number of Members | 360 |
| Number of Surfaces | 399 |
| Number of Solids | 0 |
| Number of Load Cases | 8 |
| Number of Load Combinations | 74 |
| Number of Result Combinations | 0 |
| Total Weight | 9902.520 tons |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 37,200 x 62,800 x 19,830 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 122.05 x 206.04 x 65.06 feet |
You can download this structural model to use it for training purposes or for your projects. However, we do not assume any guarantee or liability for the accuracy or completeness of the model.



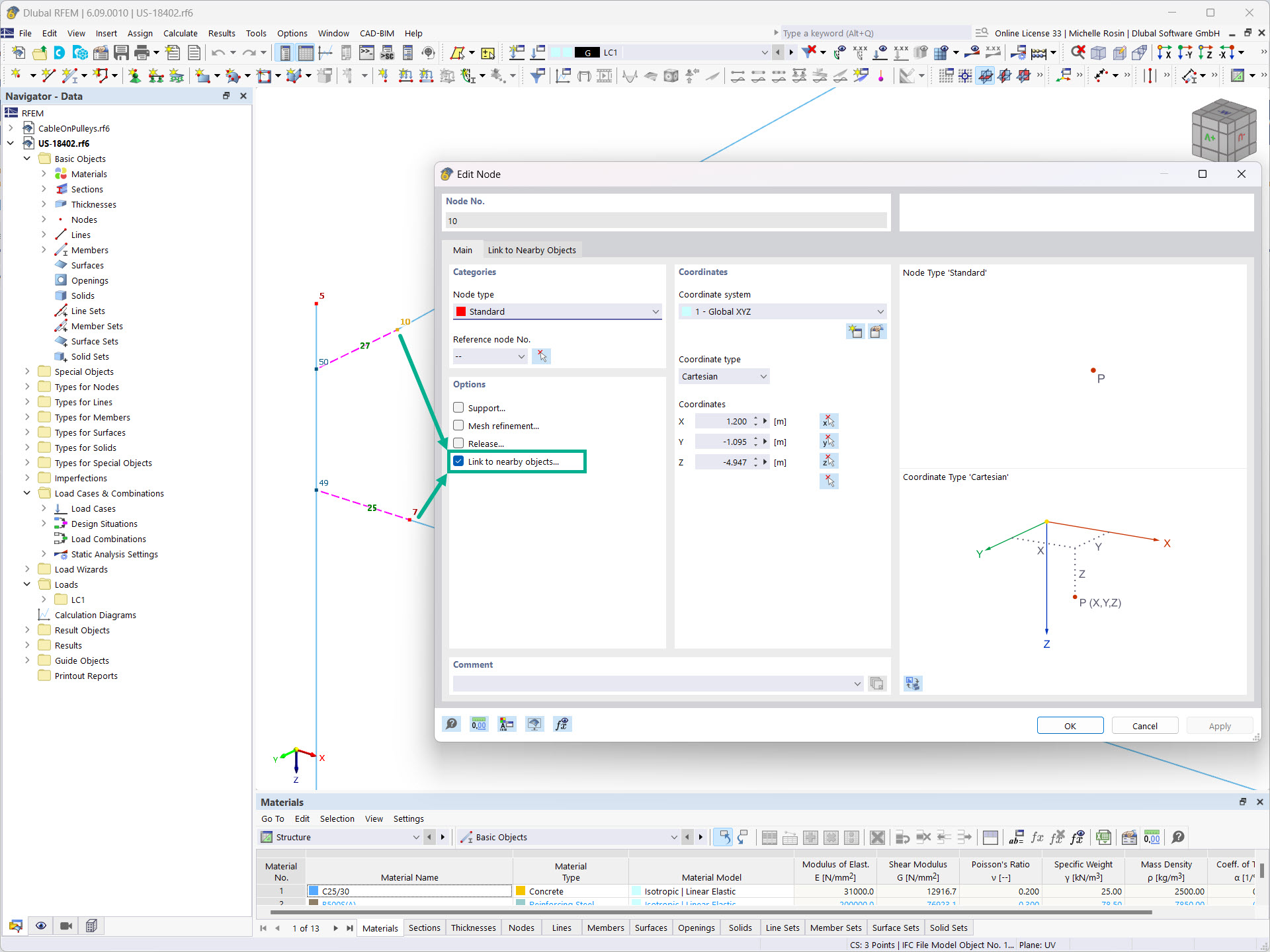
If you activate the "Link to Nearby Objects…" option for nodes, RFEM or RSTAB automatically searches for neighboring objects. A link in the form of a rigid member is then created for these members, nodes, or surfaces.
You can specify various settings for searching for nearby objects. Including search area, object types to be searched for, and objects to be excluded. Furthermore, you can specify member hinges for the created connecting member.
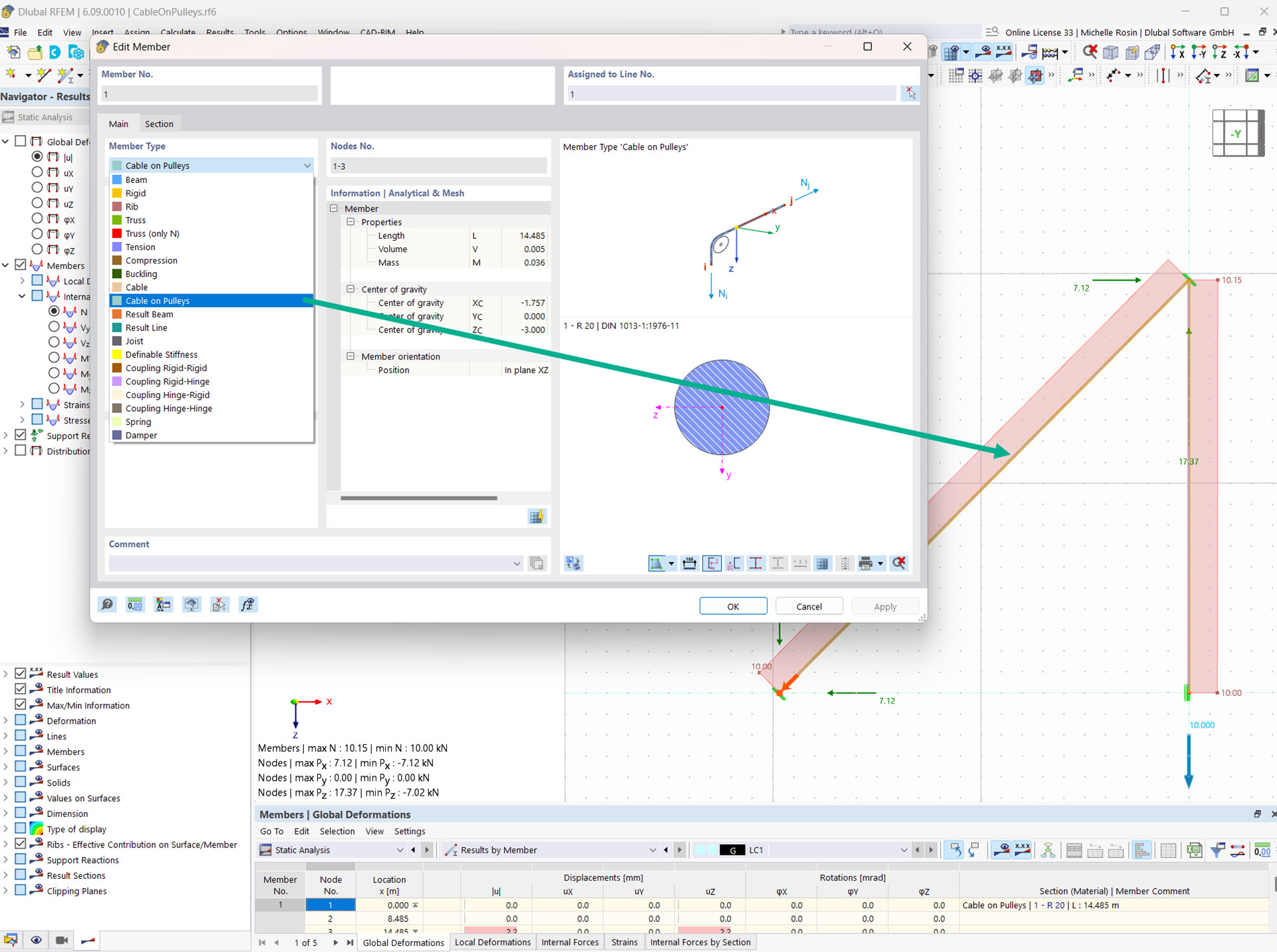
The "Cable on Pulleys" member type allows you to simulate a cable system deflected by pulleys.
This member type only absorbs tensile forces and can only be displaced in the longitudinal direction. It is suitable for flexible tension elements whose longitudinal forces are transferred through the model via deflection points (e.g. pulley).

The gRPC-based Dlubal API gives you access to almost all modeling and calculation functions, allowing you to create, modify, and analyze models programmatically. The ability to extract results is not yet implemented, but will be added in a future update.
The API is based on Python and is the technological successor to the previous Webservice with Python. While most modeling functions are already available, work is ongoing to complete the implementation.
Further information can be found on the following website:

In addition to the program login using your Dlubal account, you can optionally log in with your Microsoft account.
Can I optimize parametric cross-sections?
How can I define RSECTION cross-sections in Grasshopper?
How can I fix the error warning “10060 - The structure is unstable” for modal analysis instability?
Is it always necessary to consider tension member nonlinearities in response spectrum analysis?
How can I convert a member set or several members into a single member again?
Is it possible to use both the convenient automatic generation and to subsequently customize the structure?



















.png?mw=350&hash=c6c25b135ffd26af9cd48d77813d2ba5853f936c)






















-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)




