
You can make various settings in order to achieve a clearly‑arranged display of the result values. For example, some users may not want the white background in text bubbles. You can adjust the background in "Display Properties" using the Transparent and Background color option.

For relatively large or relatively small surfaces, it can happen that the automatically created result values do not fit the model: In the case of large surfaces, there can be too many result values; in the case of small surfaces, too few.

Designing rigid end plate connections is difficult for four-row connection geometries and multi-axis bending stresses, because there are no official design methods.

The elastic deformations of a structural component due to a load are based on Hooke's law, which describes a linear stress-strain relation. They are reversible: After the relief, the component returns to its original shape. However, plastic deformations lead to irreversible deformations. The plastic strains are usually considerably larger than the elastic deformations. For plastic stresses of ductile materials such as steel, yielding effects occur where the increase in deformation is accompanied by hardening. They lead to permanent deformations - and in extreme cases to the destruction of the structural component.
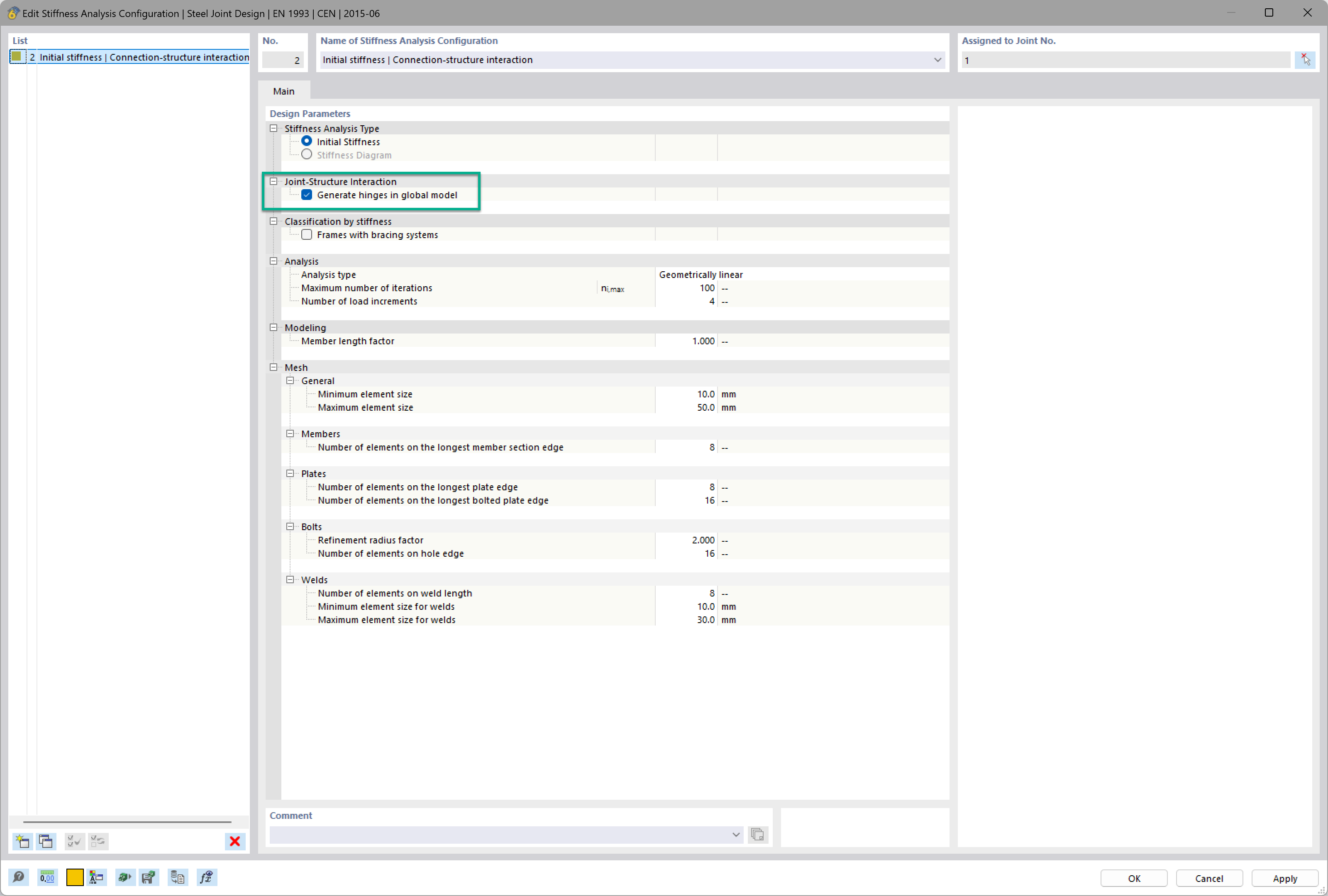
Want to automatically consider steel joint stiffness in your global RFEM model? Utilize the Steel Joints add-on!
Activate joint-structure interaction in the stiffness analysis of your steel joints. Hinges with springs are then automatically generated in the global model and included in subsequent calculations.
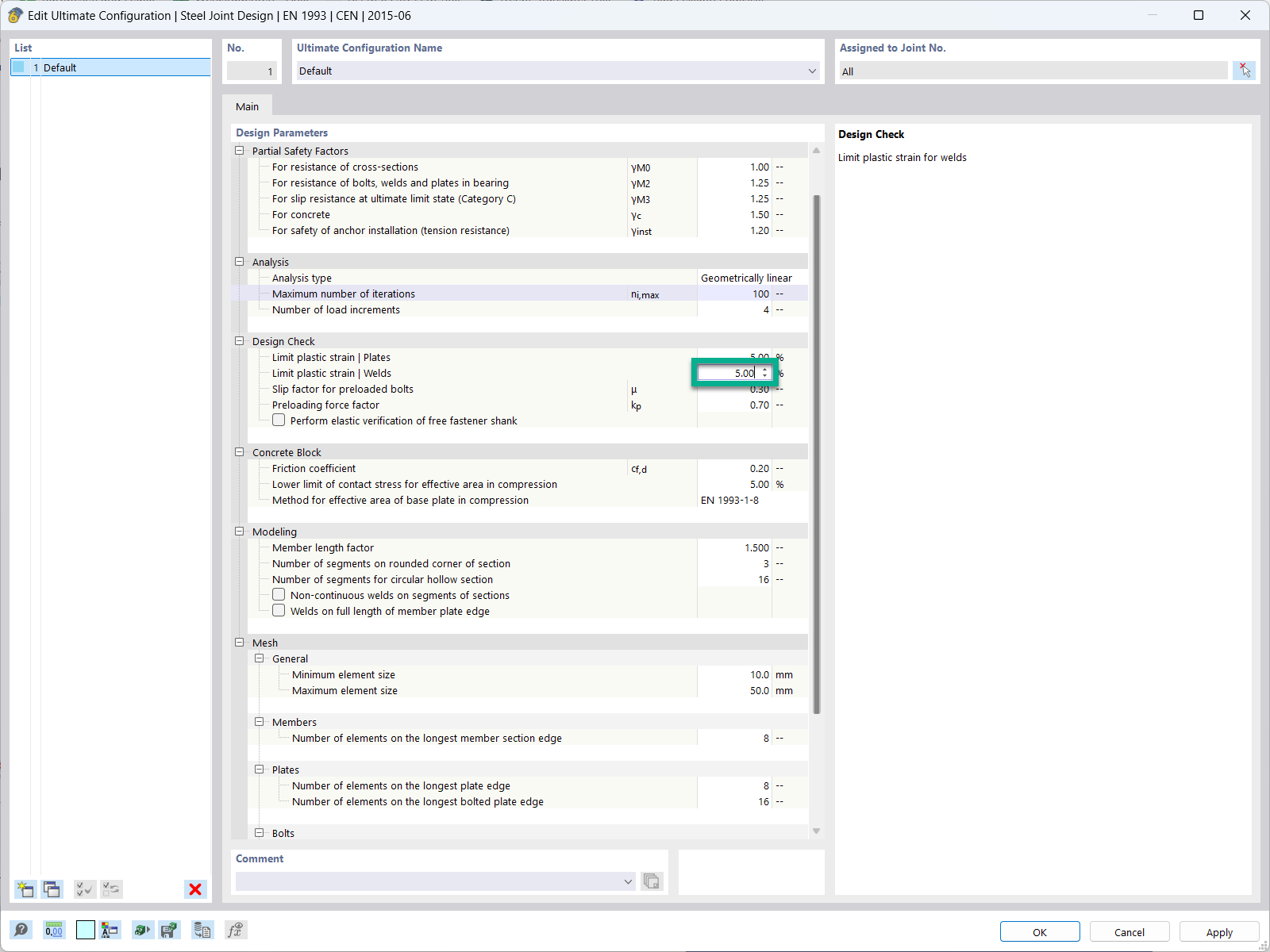
In the ultimate configuration of the steel joint design, you have the option to modify the limit plastic strain for welds.
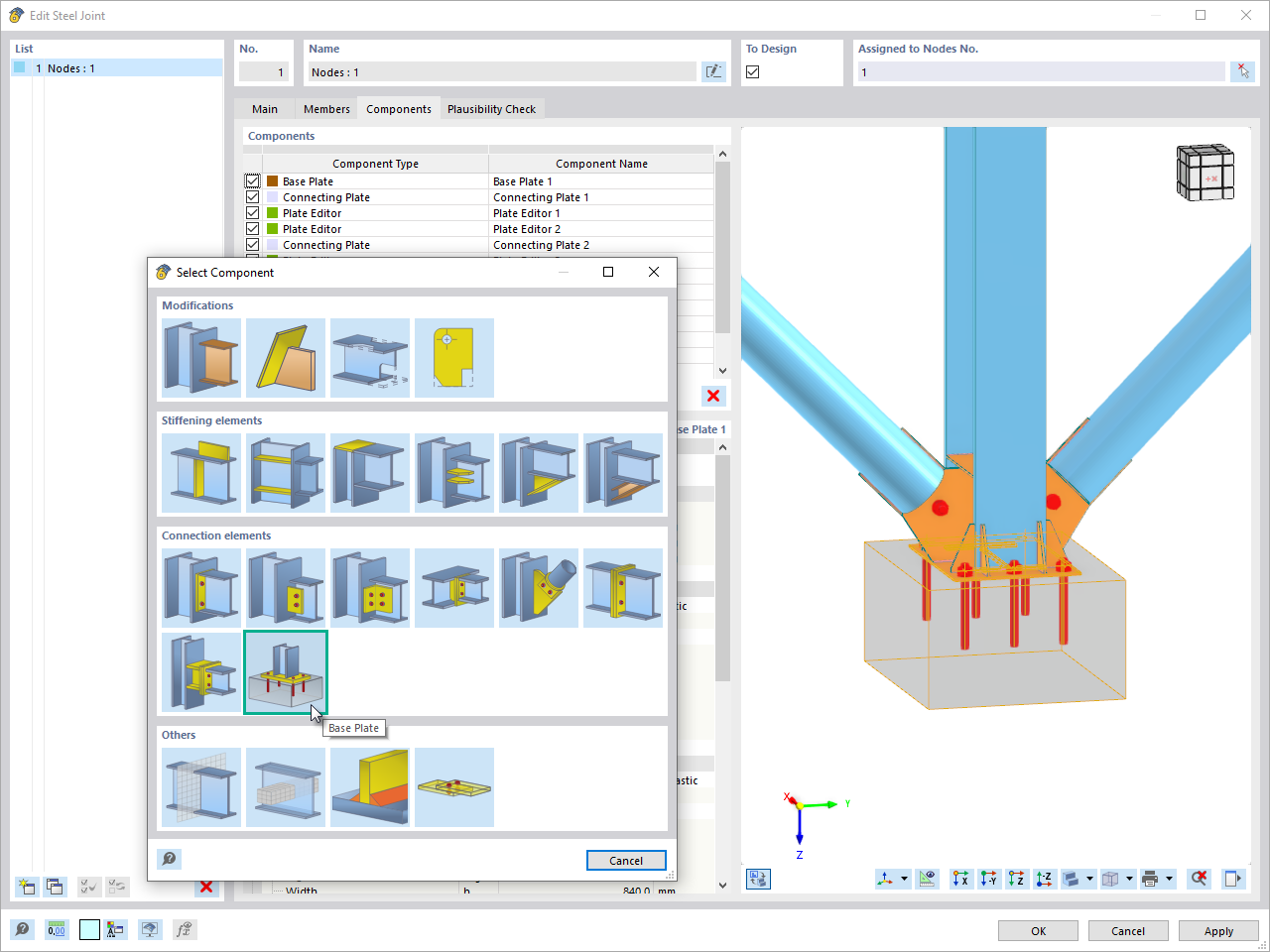
The "Base Plate" component allows you to design base plate connections with cast-in anchors. In this case, plates, welds, anchorages, and steel-concrete interaction are analyzed.
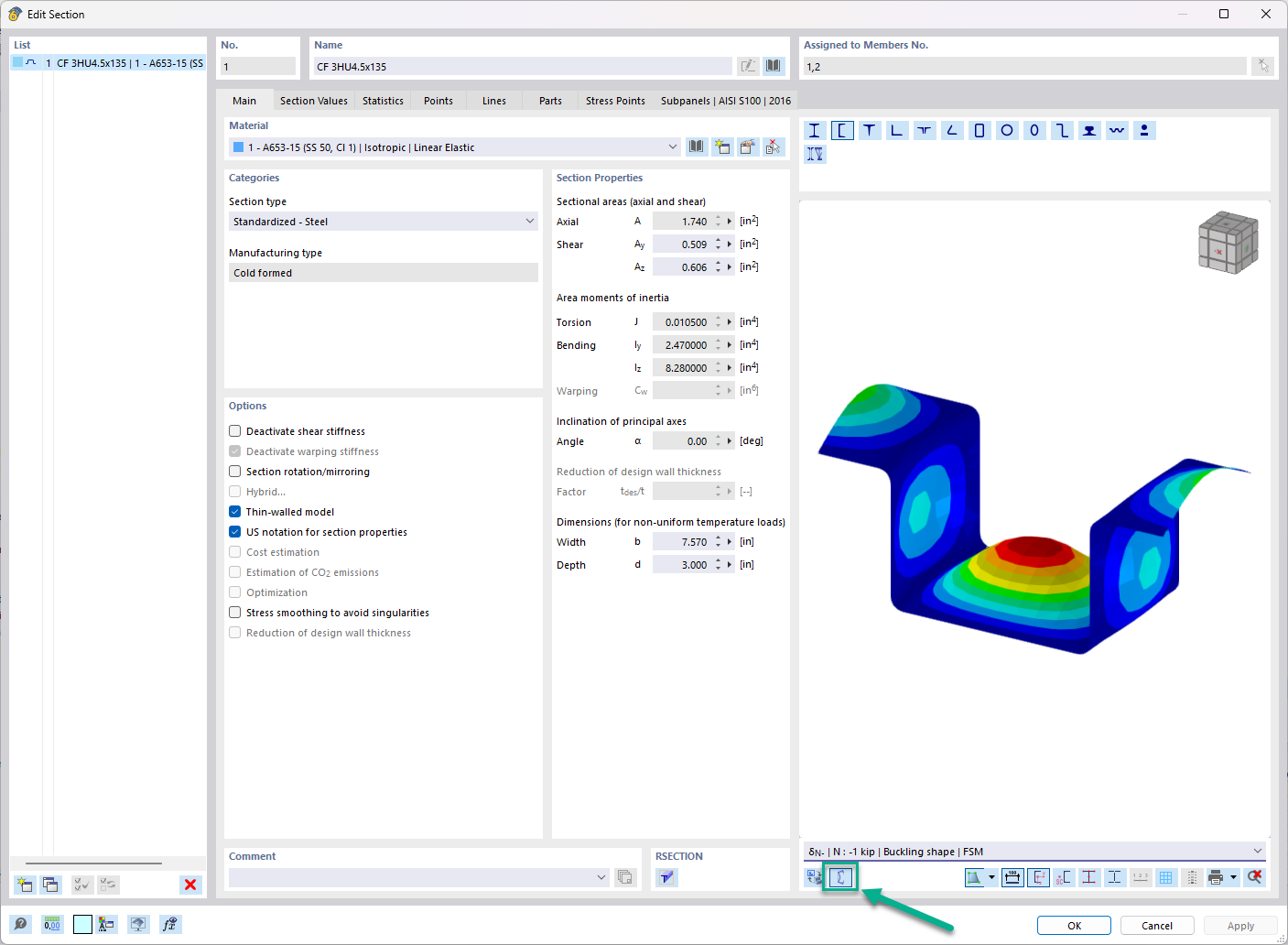
In the "Edit Section" dialog box, you can display the buckling shapes of the Finite Strip Method (FSM) as a 3D graphic.
Are the models and presentations from Info Day 2018 freely available, and can you send them to me?
How can I display membrane stresses in the results of RF‑STEEL Surfaces?
How are the signs for the release results of a line release and line hinges interpreted?
Are the models and presentations from Info Day 2020 freely available, and can you send them to me?
How can I perform a stability/buckling analysis on a plate structure?
I have to dimension a wall bracket as a steel brackets that I have modeled as surface components in RFEM 5. Which add-on module can I use to design it?

































Dlubal_KohlA_]_LI.jpg?mw=350&hash=21d94ec9a723c608496e9e95a21bb1309ab5067a)












_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)

