The most common causes of unstable models are failing member nonlinearities such as tension members.
As the simplest example, there is a frame with supports on the column footing and moment hinges on the column head. This unstable system is stabilized by a cross bracing of tension members. In the case of load combinations with horizontal loads, the system remains stable. However, if it is loaded vertically, both tension members fail and the system becomes unstable, which causes a calculation error.
You can avoid such an error by selecting the exceptional handling of failing members under "Calculate" → "Calculation Parameters" → "Global Calculation Parameters".
KB 000982 | Unstable Model
- Useful Tools for Fast Generation of Structures in RFEM
- Useful Tools for Fast Generation of Structures in RSTAB




The stiffness of gas given by the ideal gas law pV = nRT can be considered in the nonlinear dynamic analysis.
The calculation of gas is available for accelerograms and time diagrams for both the explicit analysis and the nonlinear implicit Newmark analysis. To determine the gas behavior correctly, at least two FE layers for gas solids should be defined.
- Automatic consideration of masses from self-weight
- Direct import of masses from load cases or load combinations
- Optional definition of additional masses (nodal, linear, surface masses, as well as inertia masses)
- Combination of masses in different mass cases and mass combinations
- Preset combination coefficients according to EC 8
- Optional import of normal force distributions (in order to consider prestress, for example)
- Stiffness modification (for example, deactivated members or stiffnesses can be imported from RF-/CONCRETE)
- Consideration of failed supports or members
- Definition of several natural vibration cases (for example, to analyze different masses or stiffness modifications)
- Results of eigenvalue, angular frequency, natural frequency, and period
- Determination of mode shapes and masses in nodes or FE mesh points
- Results of modal masses, effective modal masses, and modal mass factors
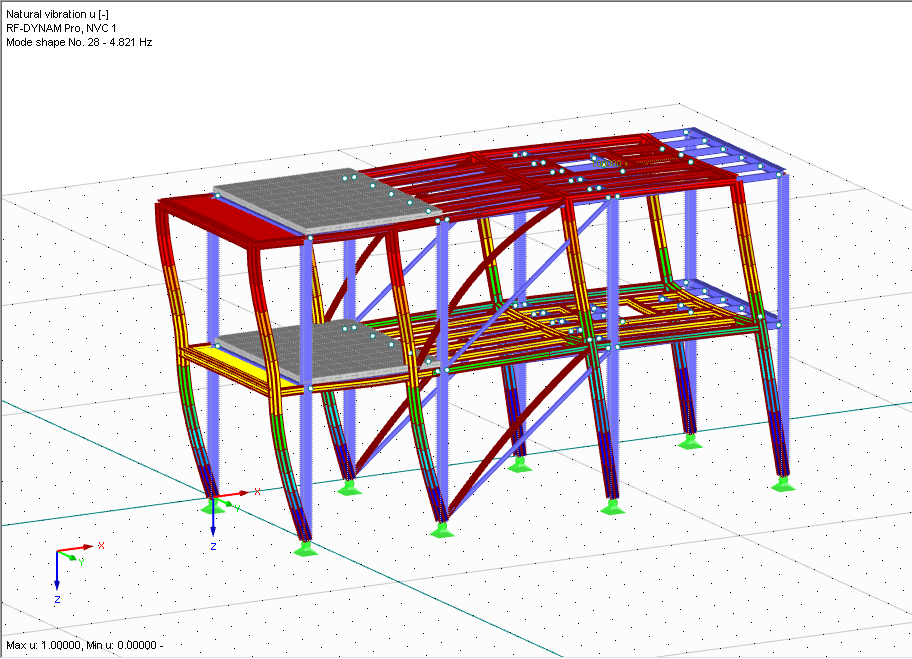
- Visualization and animation of mode shapes
- Various scaling options for mode shapes
- Documentation of numerical and graphical results in the printout report

After the calculation, the eigenvalues, natural frequencies, and natural periods are listed. These result windows are integrated in the main program RFEM/RSTAB. The mode shapes of the structure are included in tables and can be displayed graphically or as an animation.
All result tables and graphics are part of the RFEM/RSTAB printout report. This way, clearly arranged documentation is ensured. Furthermore, it is possible to export the tables to MS Excel.

The RF-DYNAM Pro - Natural Vibrations module of RFEM provides four powerful eigenvalue solvers:*Root of characteristic polynomial
- Method by Lanczos
- Subspace Iteration
- ICG iteration method (Incomplete Conjugate Gradient)
The DYNAM Pro - Natural Vibrations module for RSTAB provides two eigenvalue solvers:
- Subspace Iteration
- Shifted inverse power method
The selection of the eigenvalue solver depends primarily on the size of the model.





































.jpg.jpg?mw=350&hash=95cdc2da78debd6bc1f523f80e935deb0e31dfe4)






.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)