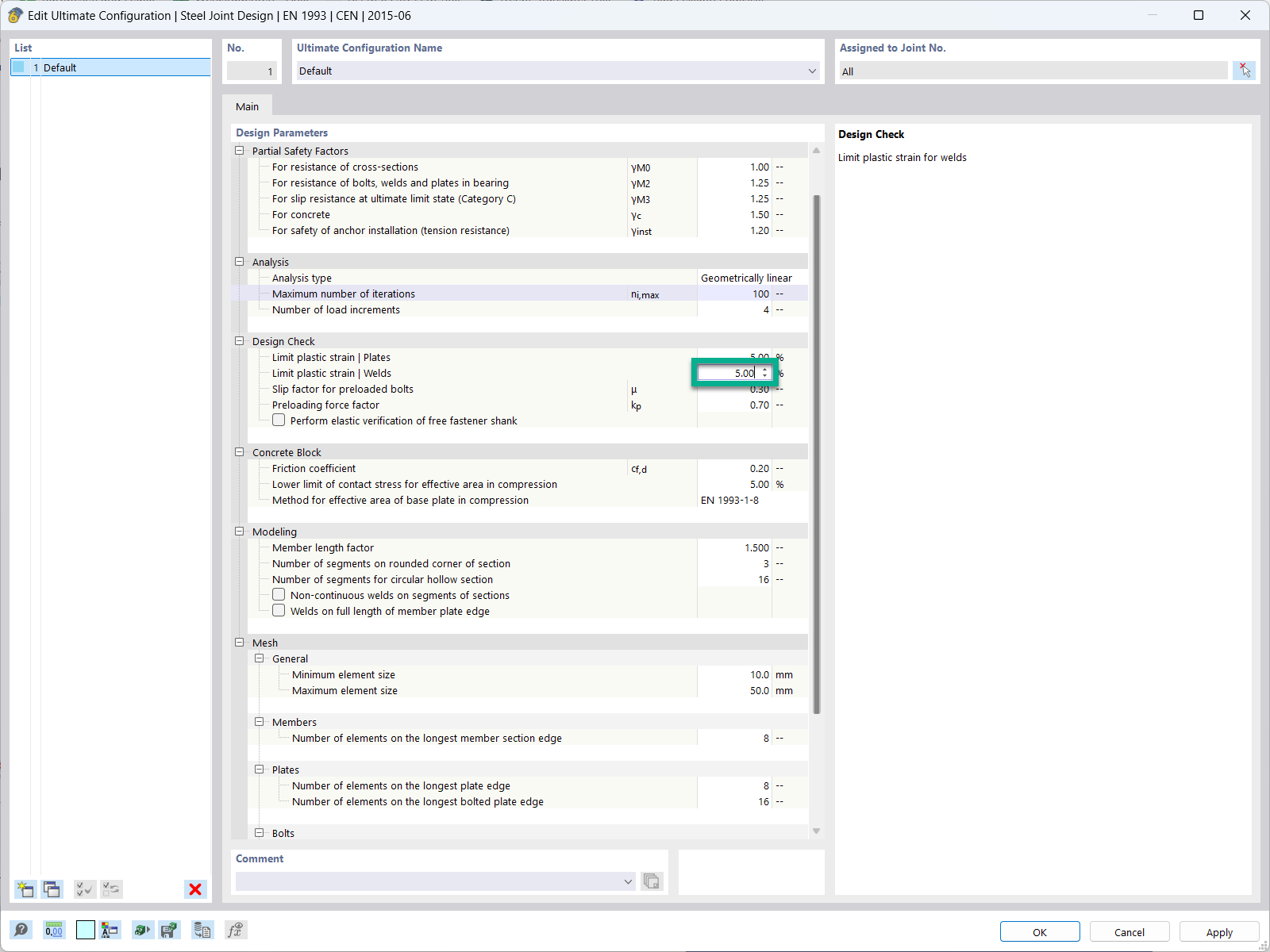
Currently, it is possible to apply three different fire situations to determine this temperature. In this case, the standard time-temperature curve is the most widely used fire curve, because most of the experimental studies on fire protection materials were performed according to this curve. Moreover, we have implemented the external fire curve as well as the hydrocarbon curve. Another option is to enter the component temperature directly, for example from experimental determination or other types of temperature field calculation.
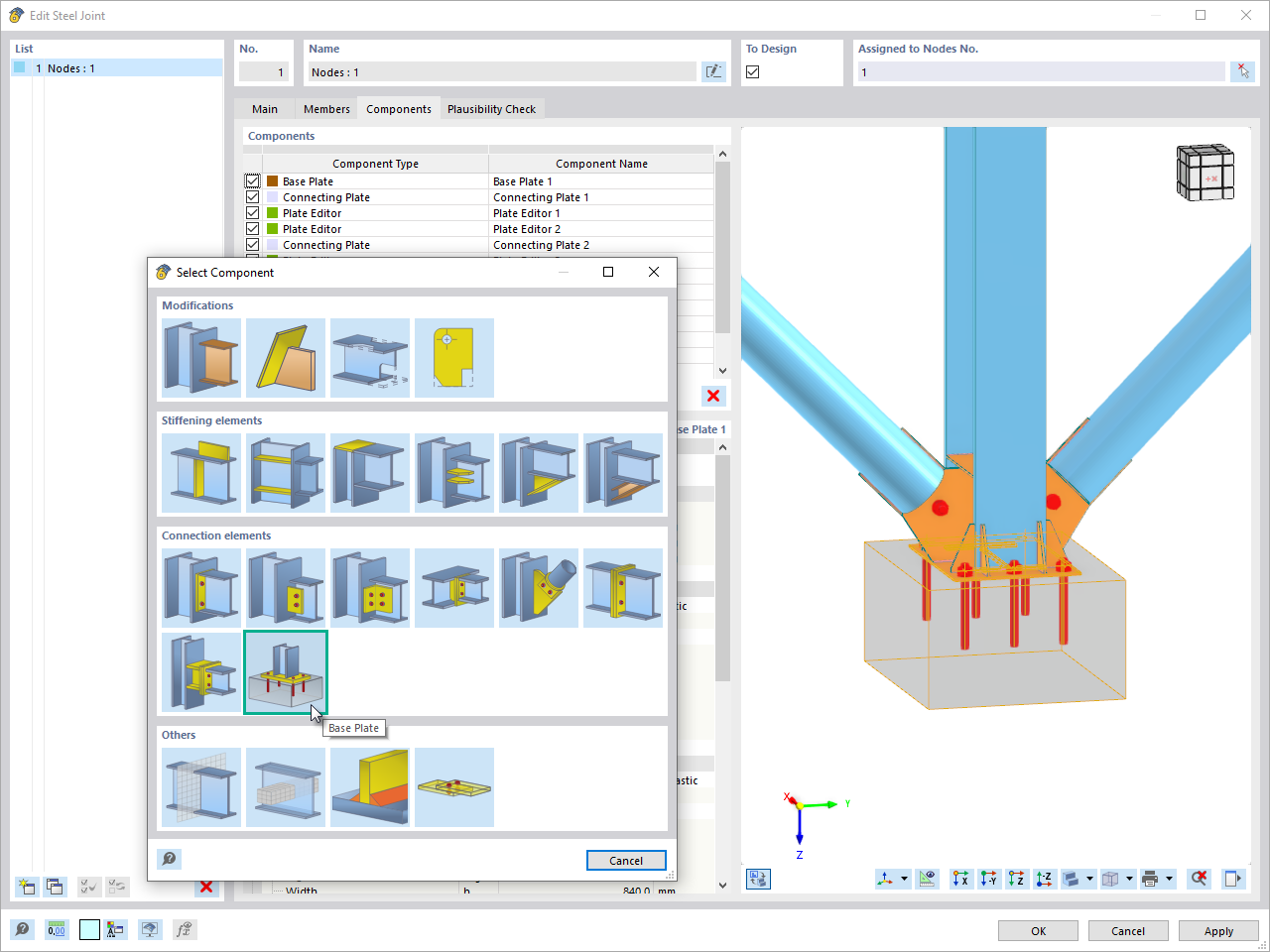
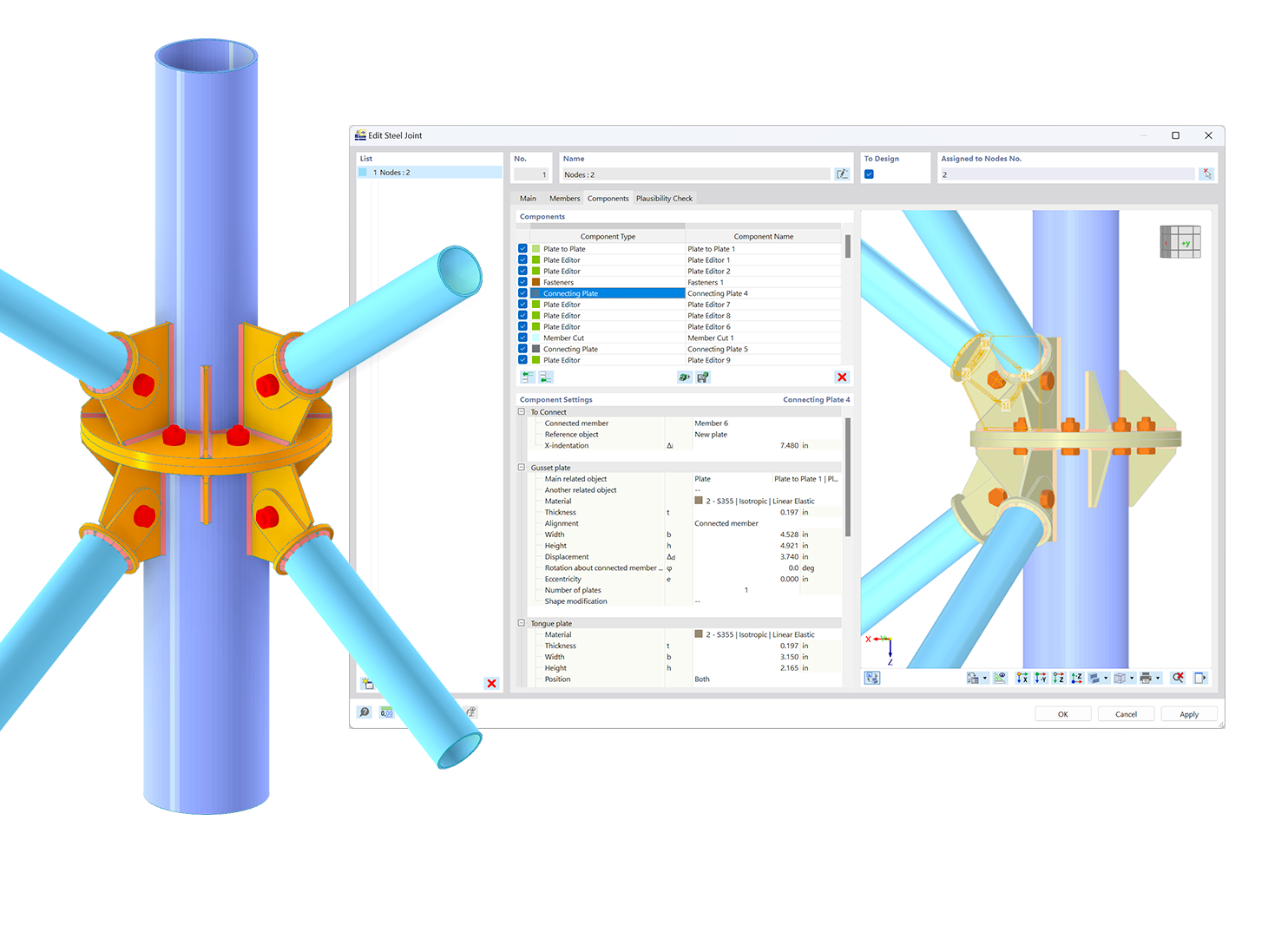
To protect structural components from the effects of fire, you can attach different types of encasements for fire protection to the components that you want to design. If you select a fire protection material, the relevant data will be calculated according to Section 4.5.2.2. According to DIN EN 1993‑1‑2, only panel materials or plasters are treated as fire protection materials. A design with this scheme is not allowed for coatings with an insulating effect or intumescent, as these claddings change their properties depending on the temperature.
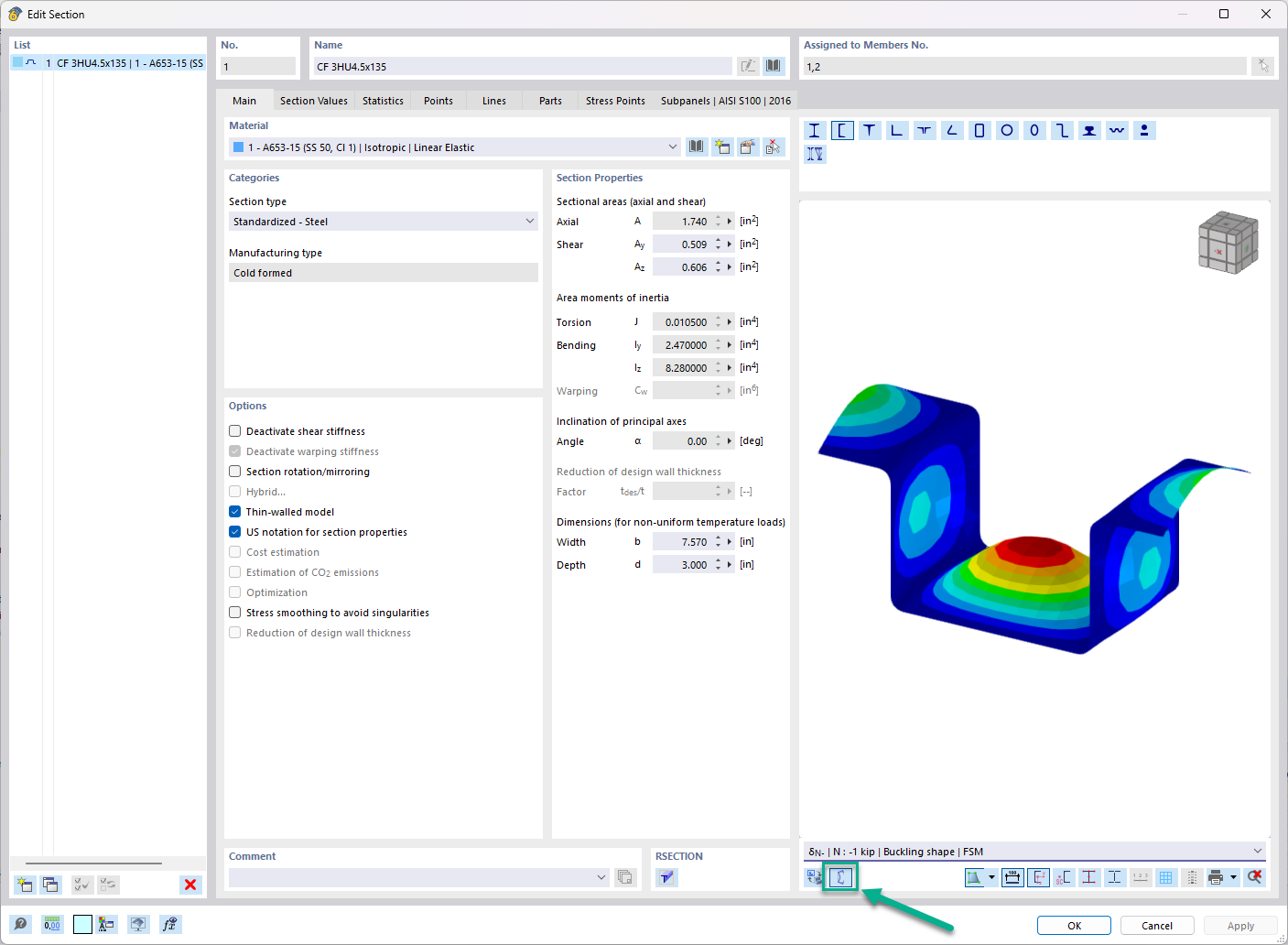
After the determination of steel temperatures, you design load-bearing capacity and stability once again, reducing the yield strength as well as the modulus of elasticity for the design due to the increased temperature available within the structural component. You can now consider cold and hot designs separately in the result windows.
In the result output, there is also the option to display the iteratively determined steel temperature in a diagram together with the selected fire curve.














































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)



-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)


.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)