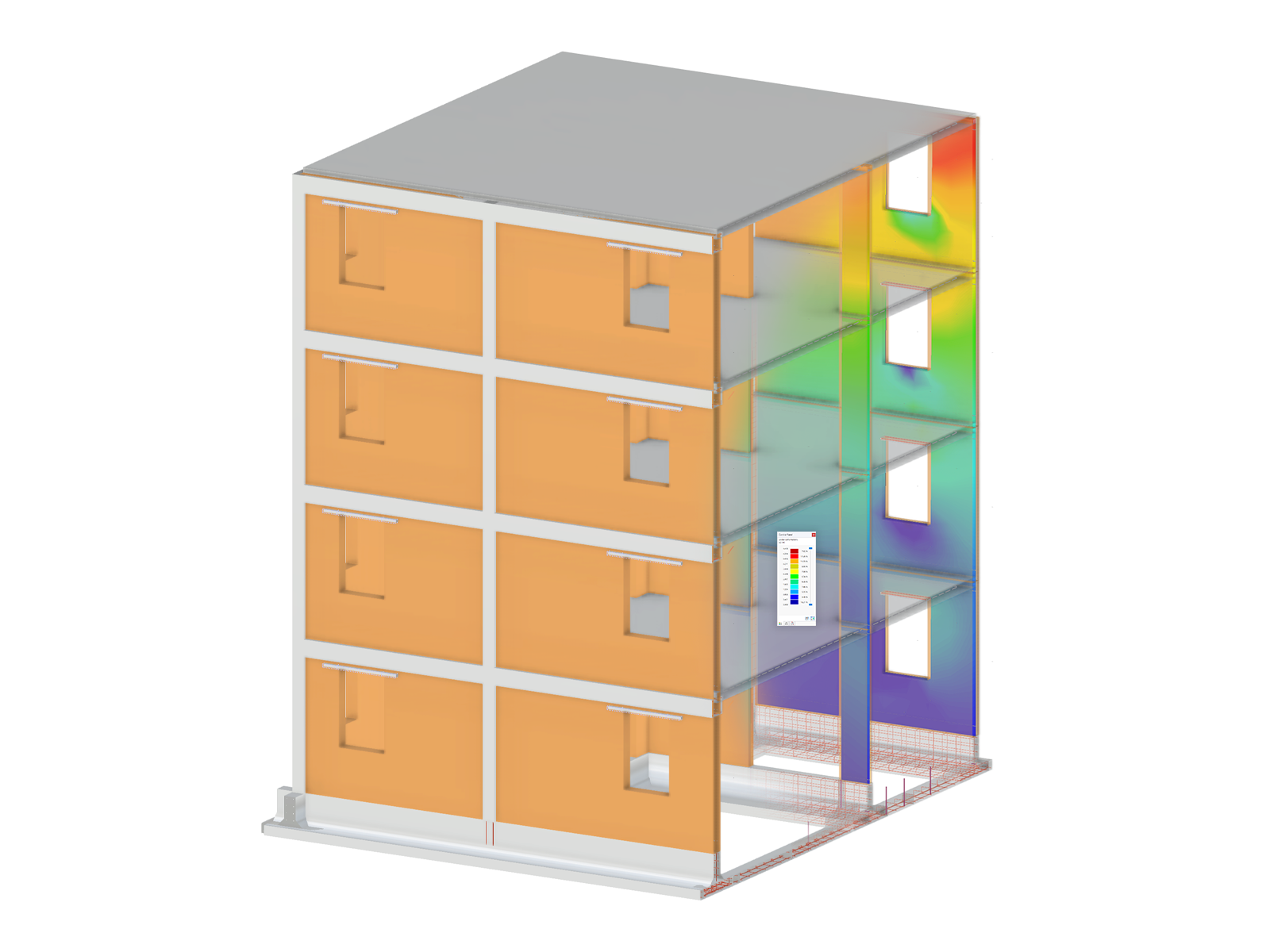
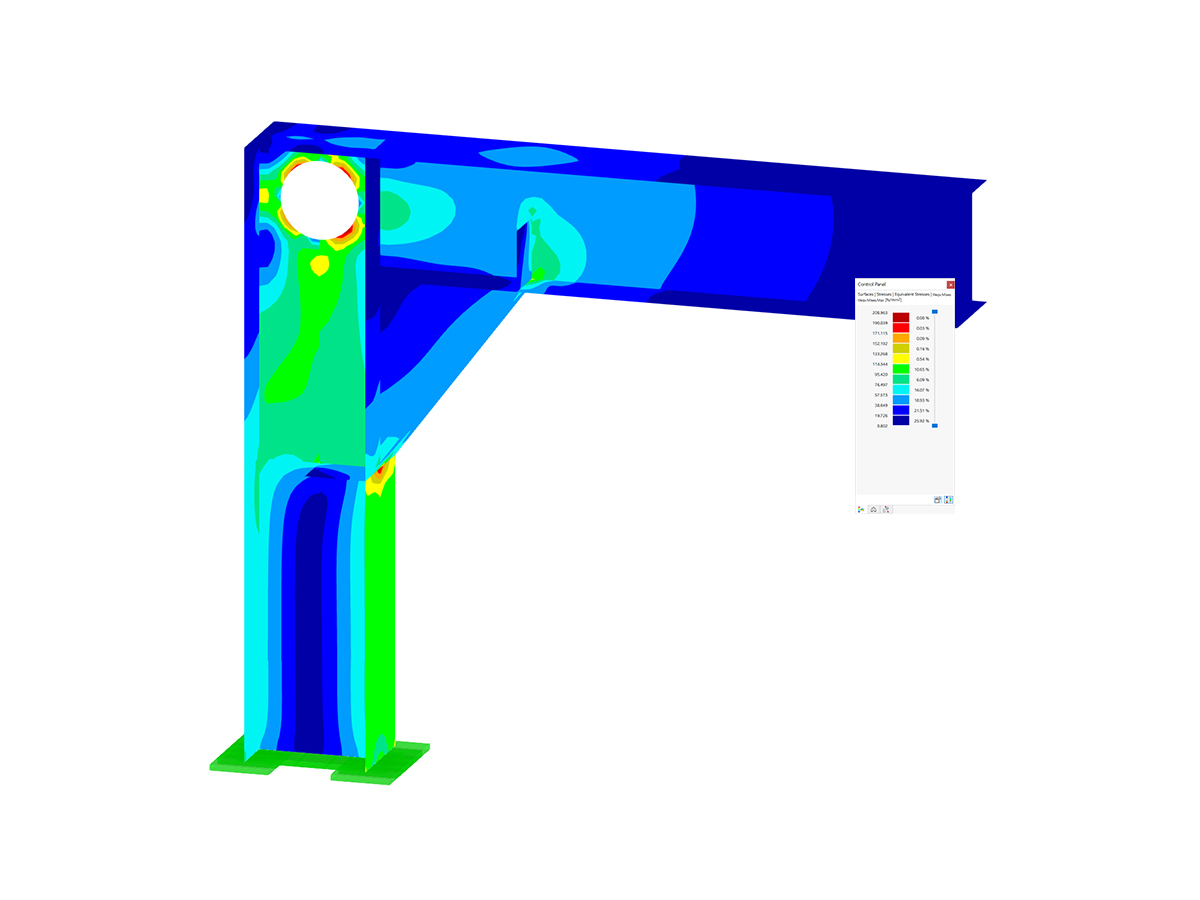
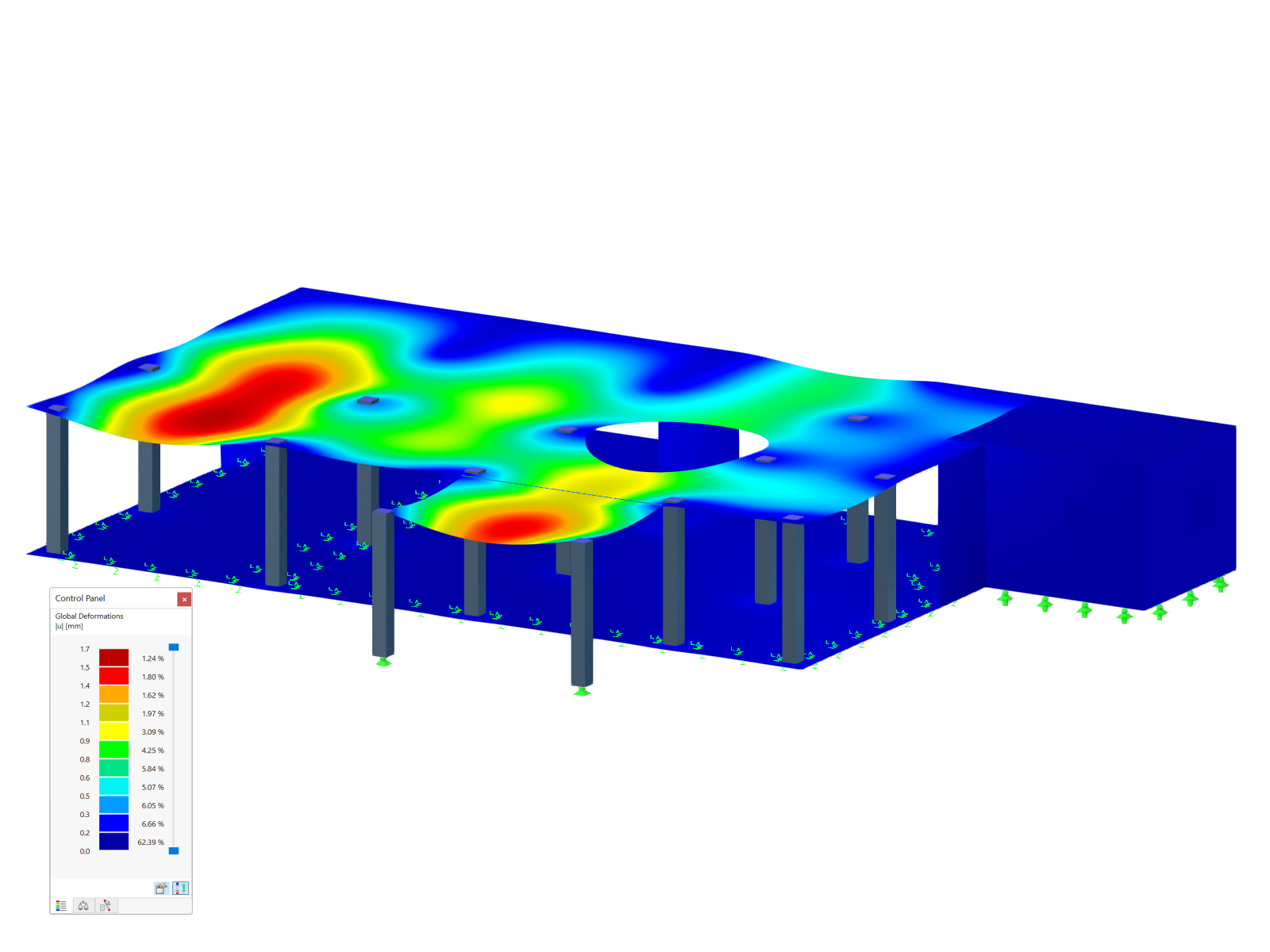
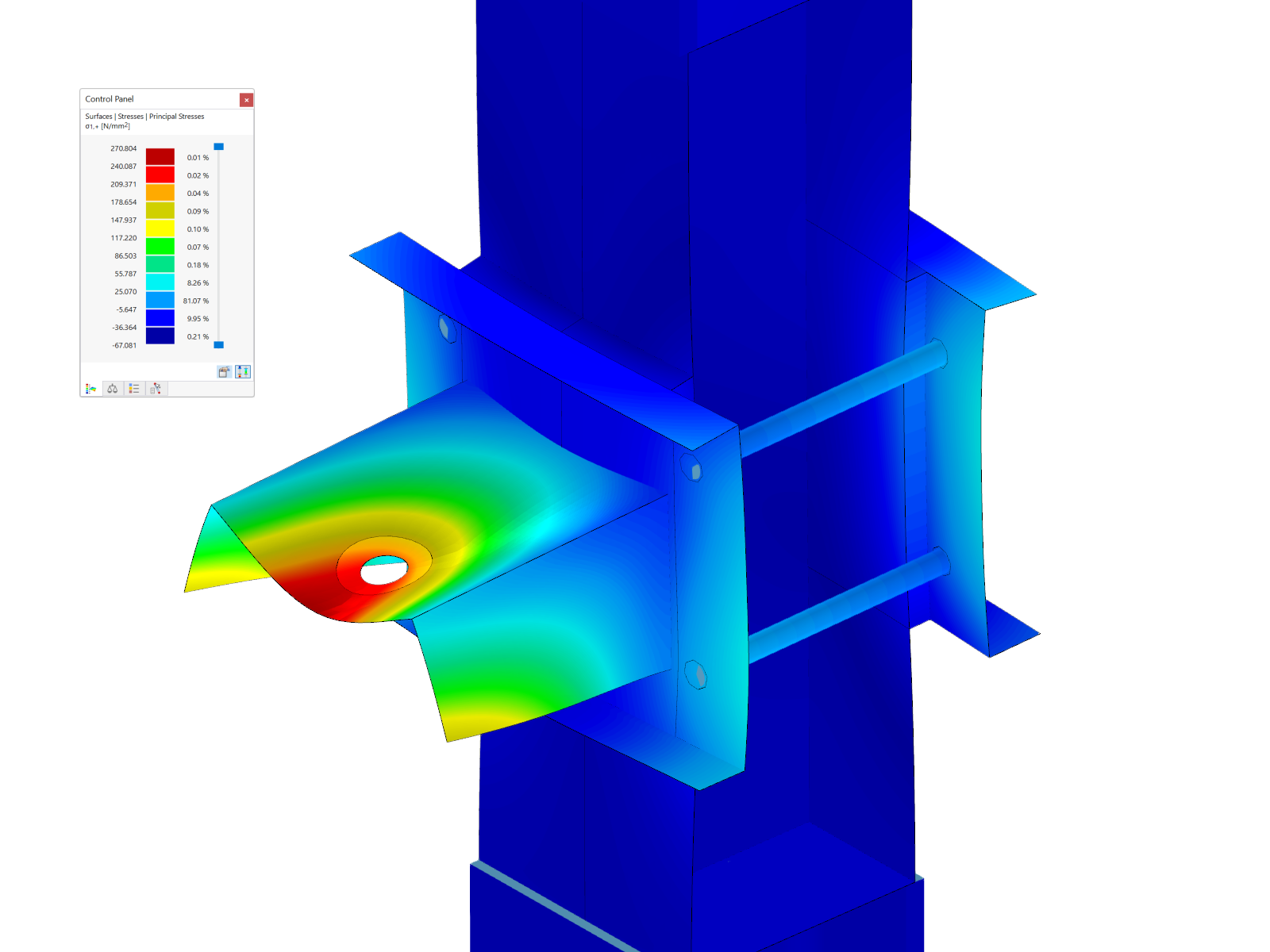
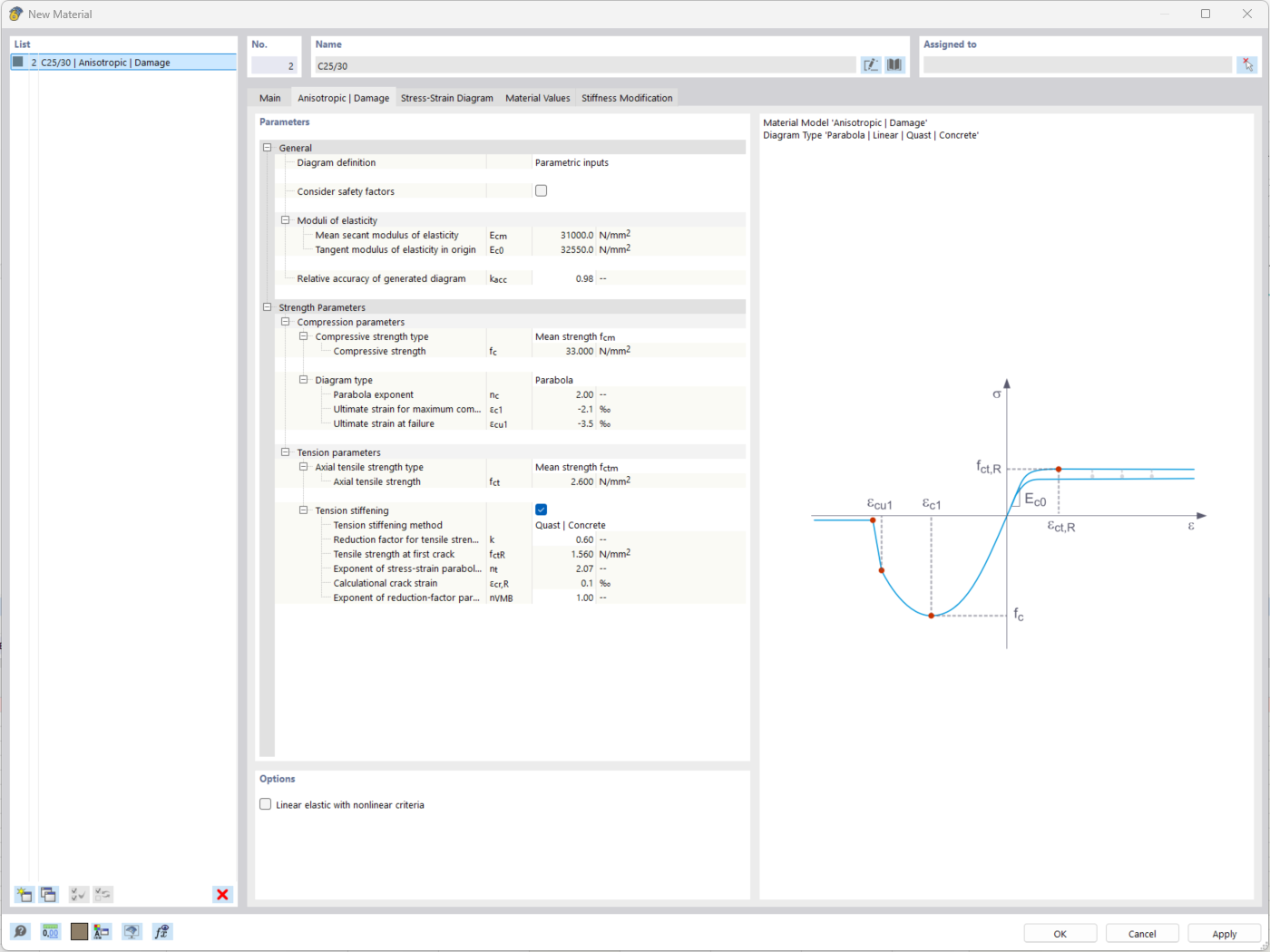
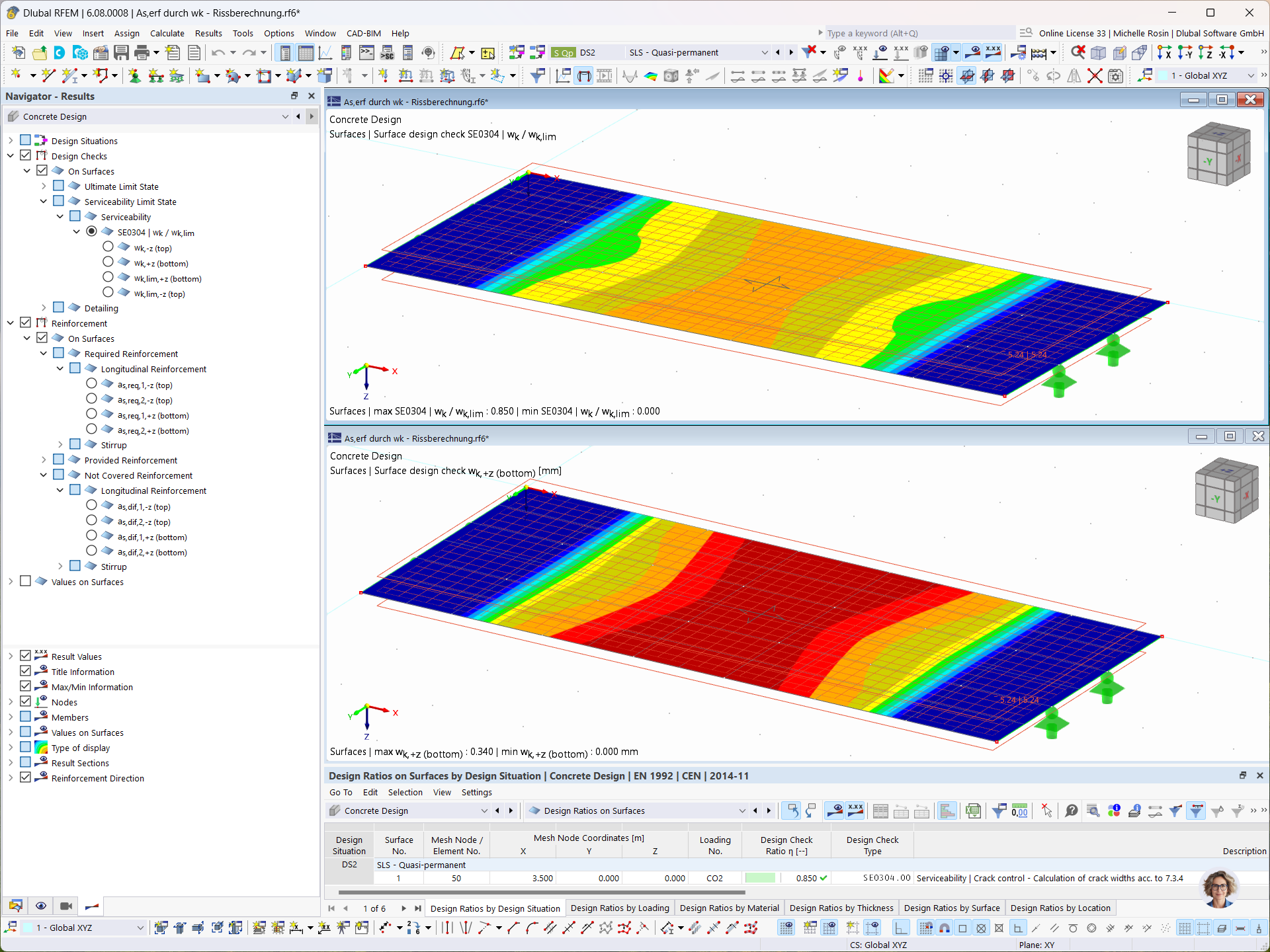
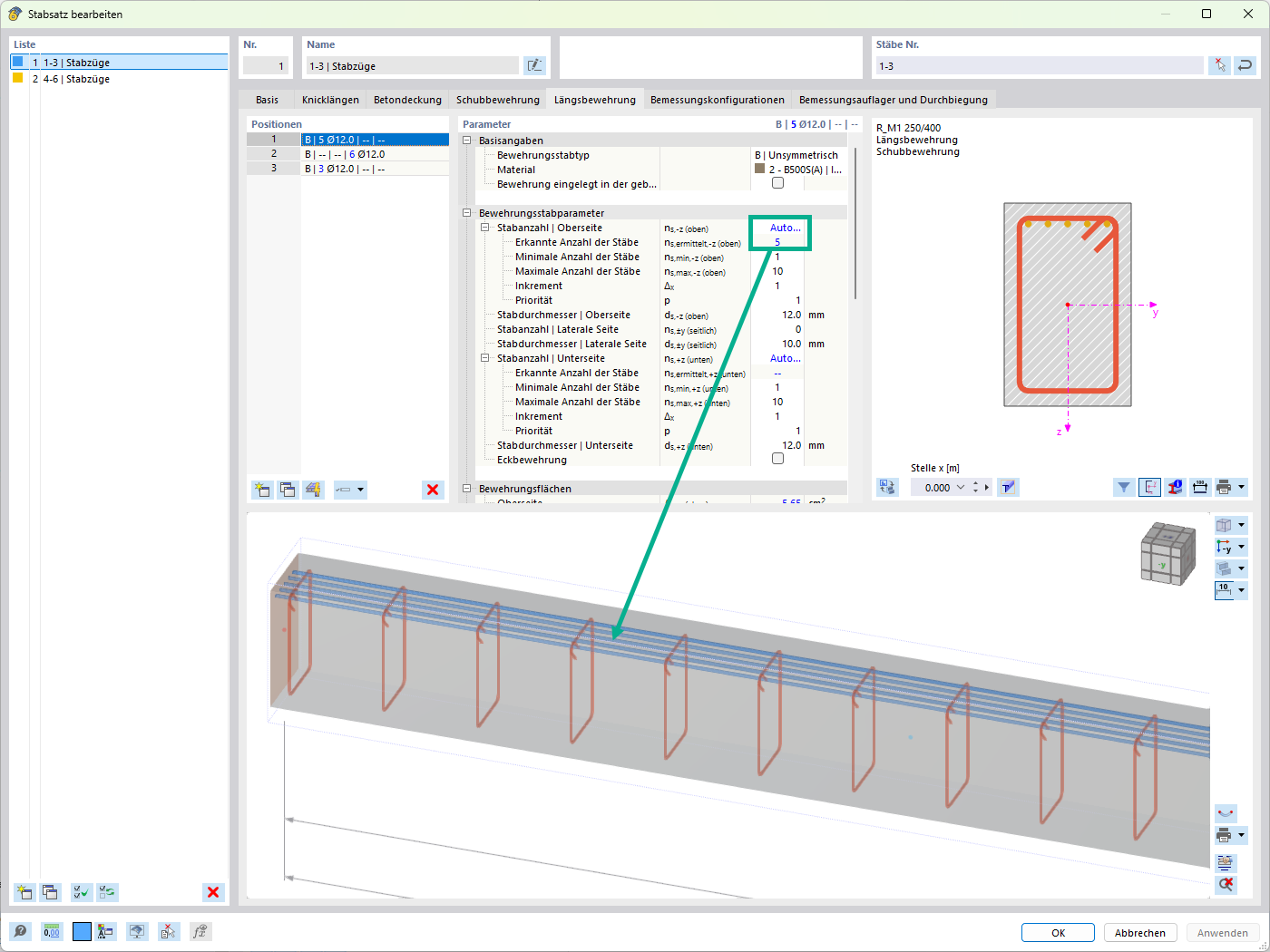
Geometry, material, cross-section, action, and imperfection data are entered in clearly arranged input windows:
Geometry
- Quick and convenient data input
- Definition of support conditions based on various support types (hinged, hinged movable, rigid, and user-defined, as well as lateral on upper or bottom flange)
- Optional specification of warping restraint
- Variable arrangement of rigid and deformable support stiffeners
- Possibility to insert hinges
CRANEWAY Cross-Sections
- I-shaped rolled cross-sections (I, IPE, IPEa, IPEo, IPEv, HE-B, HE-A, HE-AA, HL, HE-M, HE, HD, HP, IPB-S, IPB-SB, W, UB, UC, and other cross-sections according to AISC, ARBED, British Steel, Gost, TU, JIS, YB, GB, and others) combinable with section stiffener on the upper flange (angles or channels) as well as rail (SA, SF) or splice with user-defined dimensions
- Unsymmetrical I-sections (type IU) also combinable with stiffeners on the upper flange as well as with rail or splice
Actions
It is possible to consider the actions of up to three simultaneously operated cranes. You can simply select a standard crane from the library. You can also enter data manually:
- Number of cranes and crane axles (maximum of 20 axles per crane), center distances, position of crane buffers
- Classification in damage classes with editable dynamic factors according to EN 1993-6, and in lifting classes and exposure categories according to DIN 4132
- Vertical and horizontal wheel loads from self-weight, hoist load, mass forces from drive, as well as loads from skewing
- Axial loading in driving direction as well as buffer forces with user-defined eccentricities
- Permanent and variable secondary loads with user-defined eccentricities
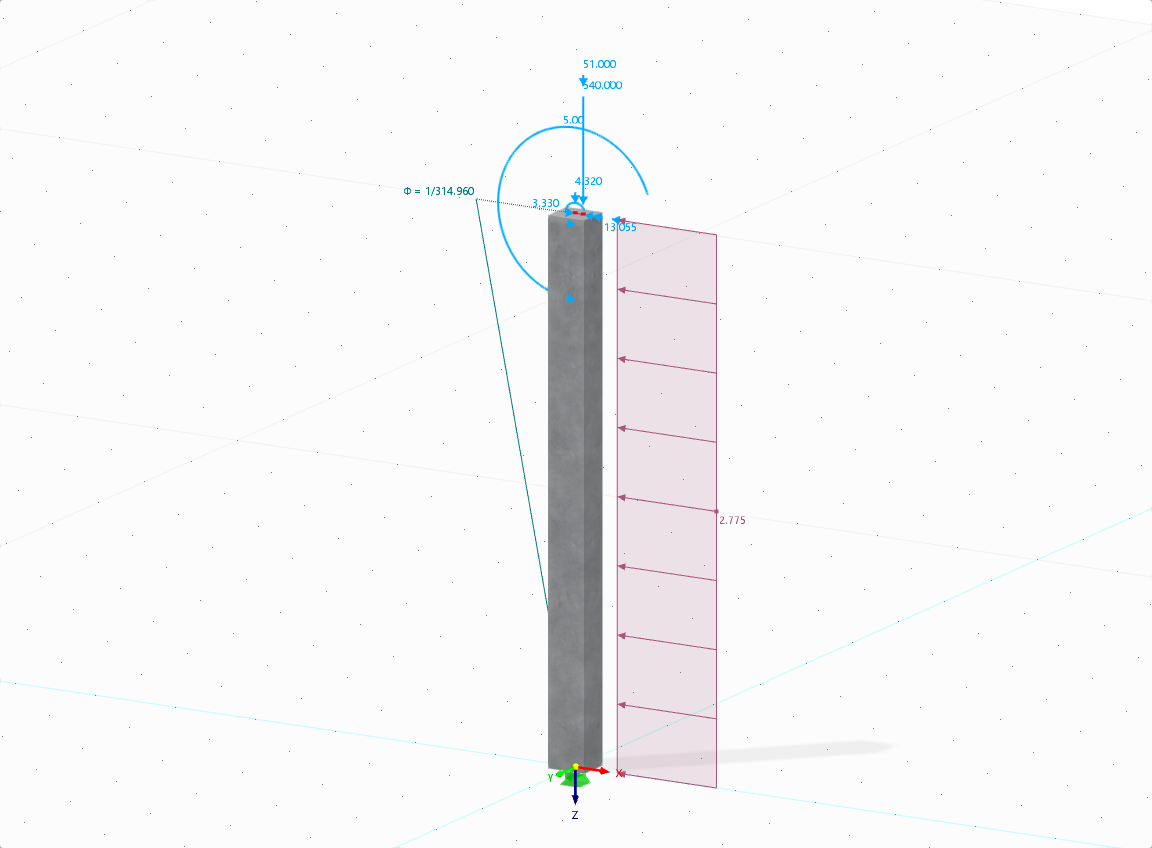
Imperfections
- The imperfection load applies in compliance with the first natural vibration mode - either identically for all load combinations to be designed, or individually for each load combination, as mode shapes may vary depending on the load.
- Convenient tools available for scaling the mode shapes (rise determination of inclination and precamber).







































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)

-querkraft-hertha-hurnaus.jpg?mw=350&hash=3306957537863c7a7dc17160e2ced5806b35a7fb)