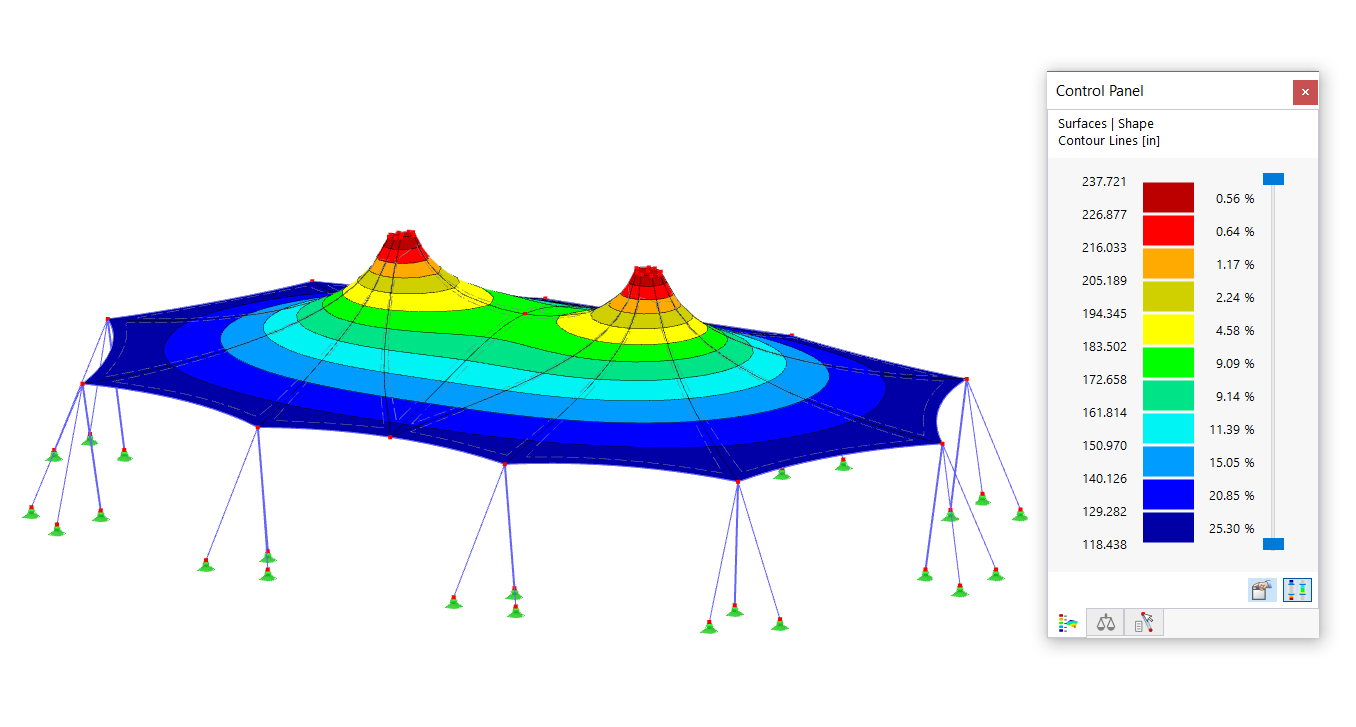
SHAPE-THIN determines the section properties and stresses of any open, closed, built-up, or non-connected cross-sections.
- Section Properties
- Cross-sectional area A
- Shear areas Ay, Az, Au, and Av
- Centroid position yS, zS
- moments of area 2 degrees Iy, Iz, Iyz, Iu, Iv, Ip, Ip,M
- Radii of gyration iy, iz, iyz, iu, iv, ip, ip,M
- Inclination of principal axes α
- Cross-section weight G
- Cross-section perimeter U
- torsional constants of area degrees IT, IT,St.Venant, IT,Bredt, IT,s
- Location of the shear center yM, zM
- Warping constants Iω,S, Iω,M or Iω,D for lateral restraint
- Max/min section moduli Sy, Sz, Su, Sv, Sω,M with locations
- Section ranges ru, rv, rM,u, rM,v
- Reduction factor λM
- Plastic Cross-Section Properties
- Axial force Npl,d
- Shear forces Vpl,y,d, Vpl,z,d, Vpl,u,d, Vpl,v,d
- Bending moments Mpl,y,d, Mpl,z,d, Mpl,u,d, Mpl,v,d
- Section moduli Zy, Zz, Zu, Zv
- Shear areas Apl,y, Apl,z, Apl,u, Apl,v
- Position of area bisecting axes fu, fv,
- Display of the inertia ellipse
- First moments of area Qu, Qv, Qy, Qz with location of maxima and specification of shear flow
- Warping coordinates ωM
- moments of area (warping areas) Sω,M
- Cell areas Am of closed cross-sections
- Normal stresses σx due to axial force, bending moments, and warping bimoment
- Shear stresses τ from shear forces as well as primary and secondary torsional moments
- Equivalent stresses σv with customizable factor for shear stresses
- Stress ratios, related to limit stresses
- Stresses for element edges or center lines
- Weld stresses in fillet welds
- Section properties of non-connected cross-sections (cores of high-rise buildings, composite sections)
- Shear wall shear forces due to bending and torsion
- Plastic capacity design with determination of the enlargement factor αpl
- Check of the c/t-ratios following the design methods el-el, el-pl or pl-pl according to DIN 18800

























![Basic Shapes of Membrane Structures [1]](/en/webimage/009595/2419502/01-en-png-png.png?mw=512&hash=6ca63b32e8ca5da057de21c4f204d41103e6fe20)