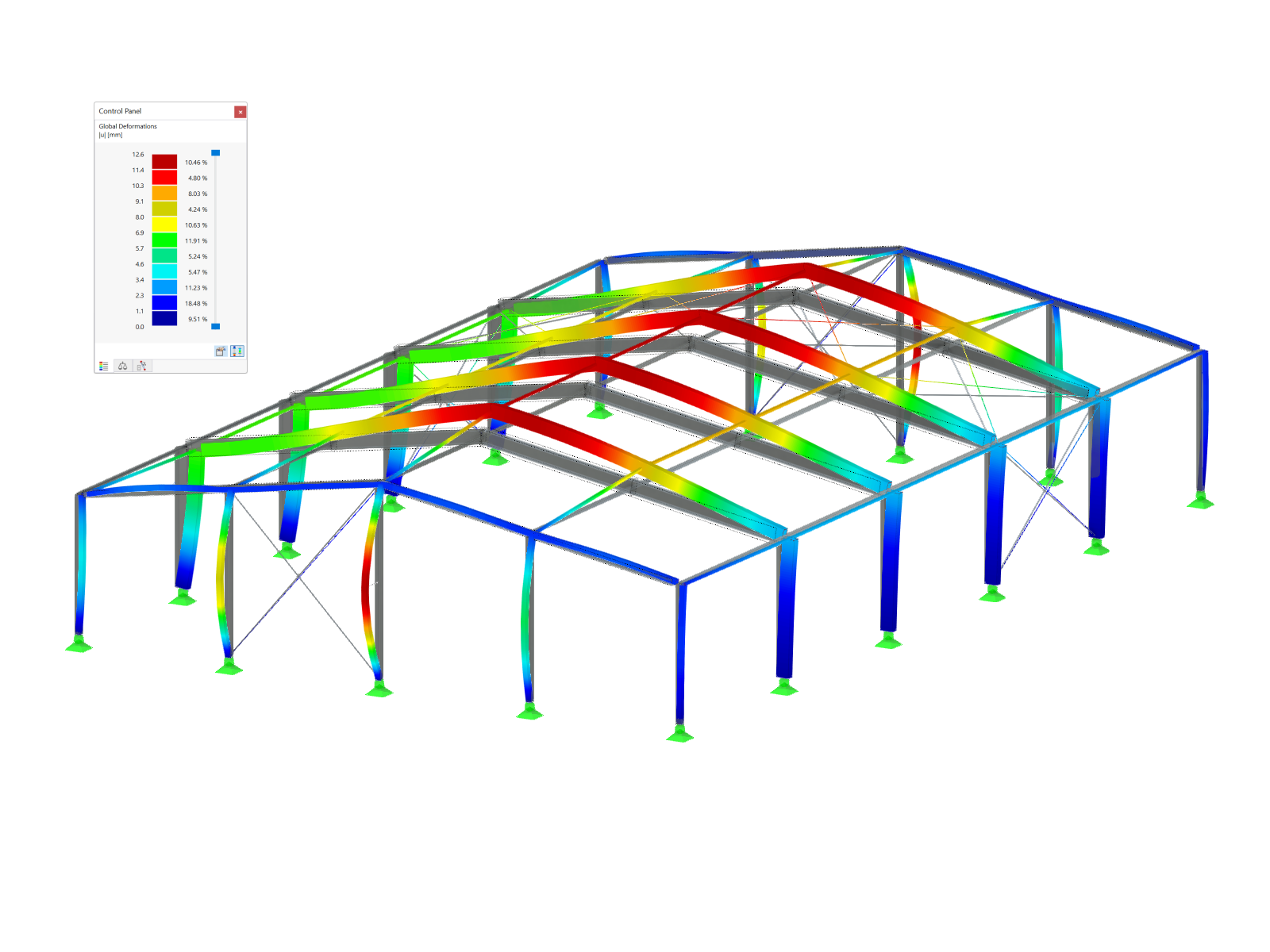
The combination of actions should aim to find the most unfavorable load combination for the design for each location of the structure. Each additional load case with a changing effect increases the possible combinations, and thus increases the number of load combinations to be analyzed.
Since the calculation effort increases with the number of load combinations, it is always important to keep the number of load combinations low. For example, by examining the results of all involved load cases, you can exclude the effectless load cases and thus finally reduce the number of load combinations to be analyzed.
For example, a symmetrical two-hinged frame has the following principal load cases:
| Load case | Description | Acting | Axial Force Left Column | Axial Force Right Column |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Self-weight | permanent | - 3.38 kN | - 3.38 kN |
| 2 | Wind to the right | variable | + 2.00 kN | - 2.00 kN |
| 3 | Wind lifting | variable | + 4.00 kN | + 4.00 kN |
| 4 | Snow | variable | - 4.00 kN | -4.00 kN |
Because LC1 is always acting and the other three load cases can occur alternatively, the following eight mathematically possible combinations result:
CO1 = LC1 + LC2 + LC3 + LC4
LC2 = LC1
LC3 = LC1 + LC2
CO4 = LC1 + LC3
LC5 = LC1 + LC4
CO6 = LC1 + LC2 + LC3
CO7 = LC1 + LC3 + LC4
CO8 = LC1 + LC2 + LC4
This selection can be reduced, for example, by using the load case participations to achieve extreme normal force results from a linear result combination. To do this, the available load case results are to be superimposed linearly at each point of the model according to the selected superposition standard, and the load case participations are to be used to achieve extreme combination results to reduce the number of analyzed load combinations.
For the two-hinged frame, this linear result combination would look like this:
RC = LC1/permanent + LC2 + LC4
Considering the axial forces of the columns, the superposition yields the following resulting extreme values:
| Extreme Situation | Axial Force | Load Case Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum N - Left Column | + 2.62 kN | LC1, LC2, LC3 |
| Minimum N - Left Column | - 7.38 kN | LC1, LC4 |
| Maximum N - Right Column | + 0.62 kN | LC1, LC3 |
| Minimum N - Right Column | - 9.38 kN | LC1, LC2, LC4 |
By considering the determined load cases, you can reduce the original eight load combinations to four load combinations:
CO1 = LC1 + LC2 + LC3
LC2 = LC1 + LC4
LC3 = LC1 + LC3
CO4 = LC1 + LC2 + LC4
In RFEM 5 and RSTAB 8, you can implement this type of reduction in the "Edit Load Cases and Combinations" menu under the "Combination Rules" tab with the "Examine Results …" option.
To do this, activate the result combination to be analyzed for a specific result criterion with a certain element selection in the "Reduce - Examine results" sub-tab.
The program then takes this information into account for the automatic determination of the required combinations.






.png?mw=600&hash=49b6a289915d28aa461360f7308b092631b1446e)