Slope coefficients for drained conditions for the ground failure resistance
Slope Coefficients

According to AISC Design Guide 9 Section 4.1 [1], the following torsional stresses must be considered for open cross-sections subjected to warping:

Utilizing the Steel Design Add-on, steel design is possible according to the AISC 360-22 standard. The following article will compare the result output when calculating lateral torsional buckling according to Chapter F vs. an Eigenvalue Analysis.

Plate girder is an economical choice for long spans construction. I-section steel plate girder typically has a deep web to maximize its shear capacity and flange separation, yet thin web to minimize the self-weight. Due to its large height-to-thickness (h/tw) ratio, transverse stiffeners may be required to stiffen the slender web.
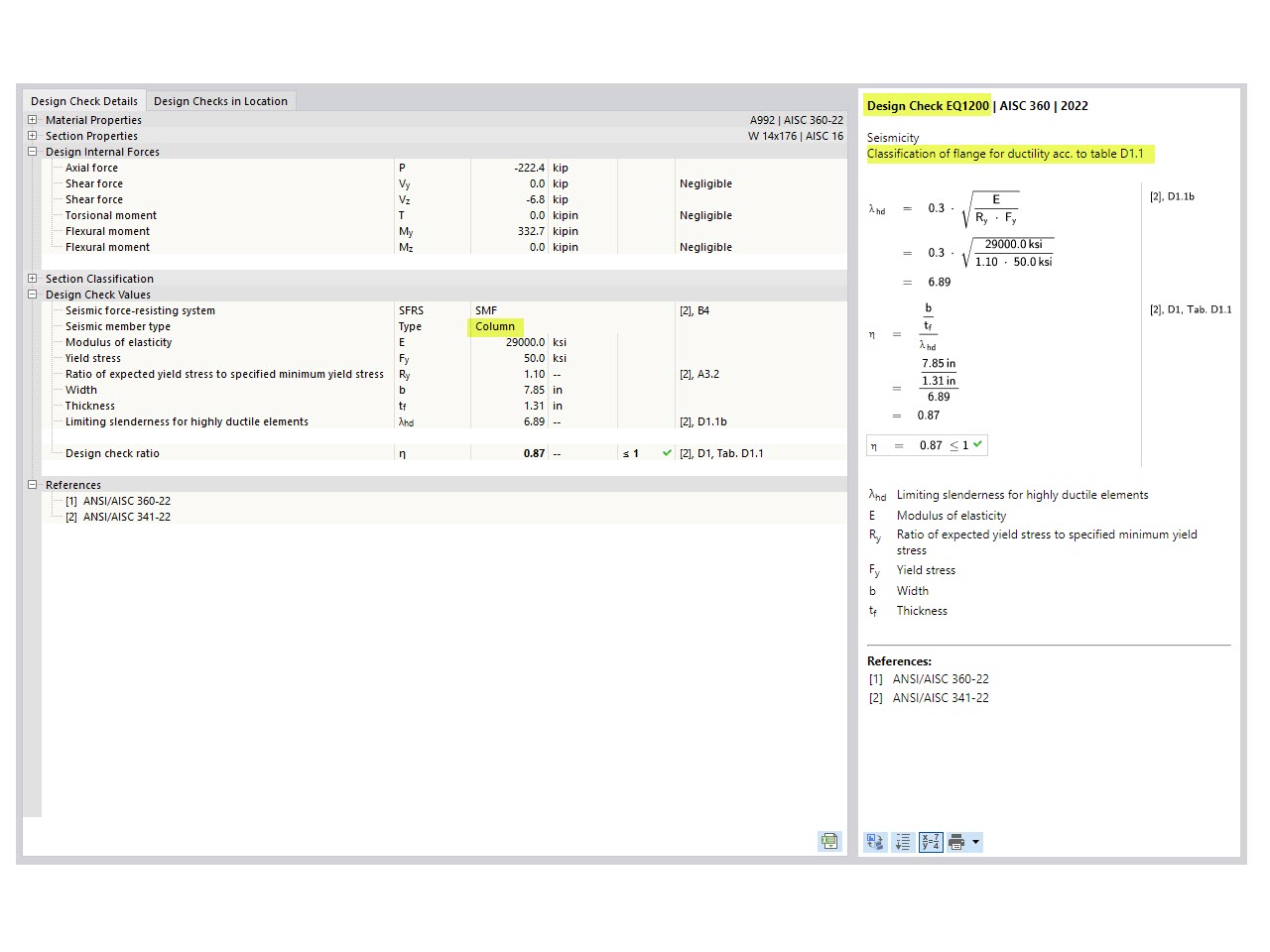
The three types of moment frames (Ordinary, Intermediate, Special) are available in the Steel Design add-on of RFEM 6. The seismic design result according to AISC 341-22 is categorized into two sections: member requirements and connection requirements.
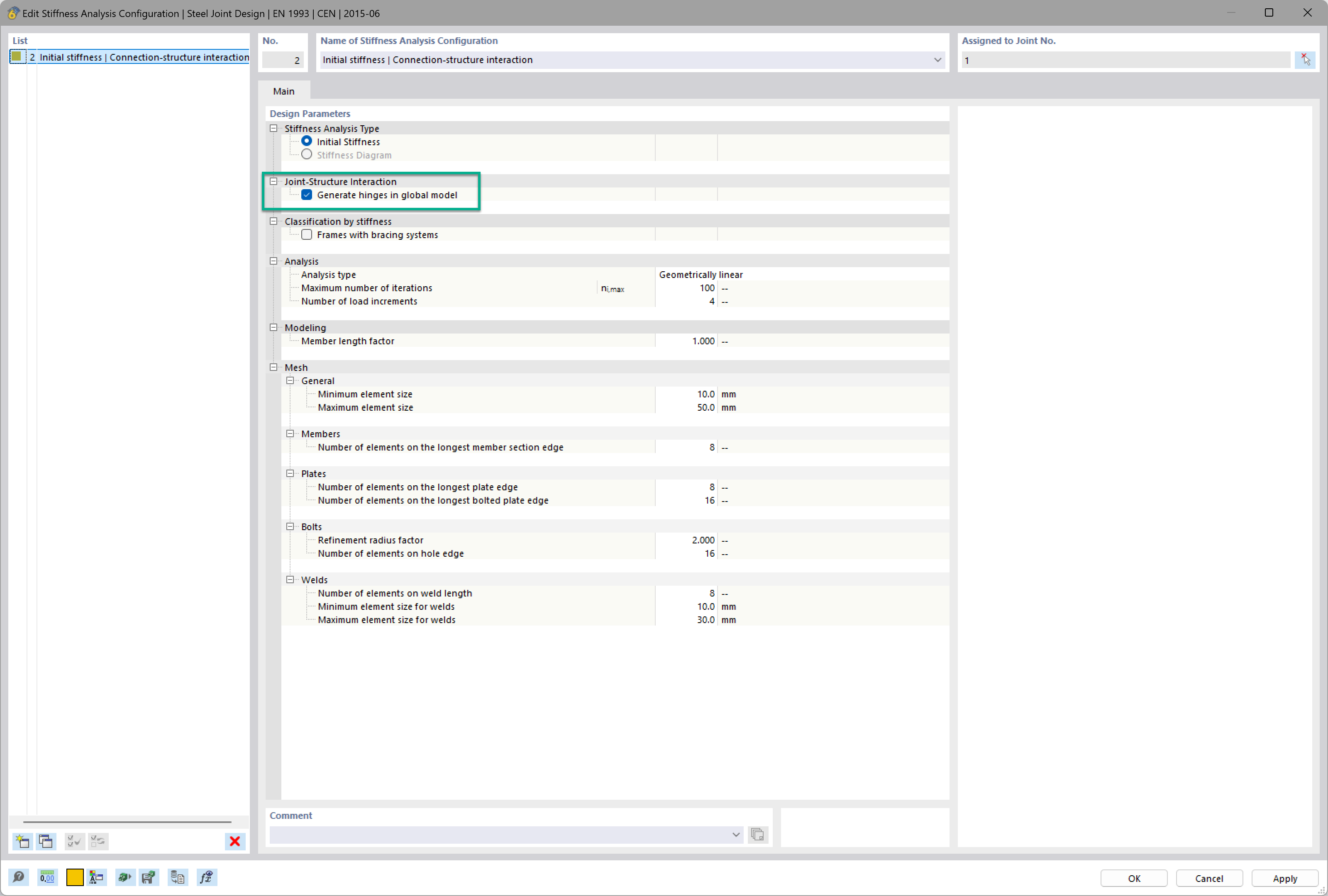
Want to automatically consider steel joint stiffness in your global RFEM model? Utilize the Steel Joints add-on!
Activate joint-structure interaction in the stiffness analysis of your steel joints. Hinges with springs are then automatically generated in the global model and included in subsequent calculations.
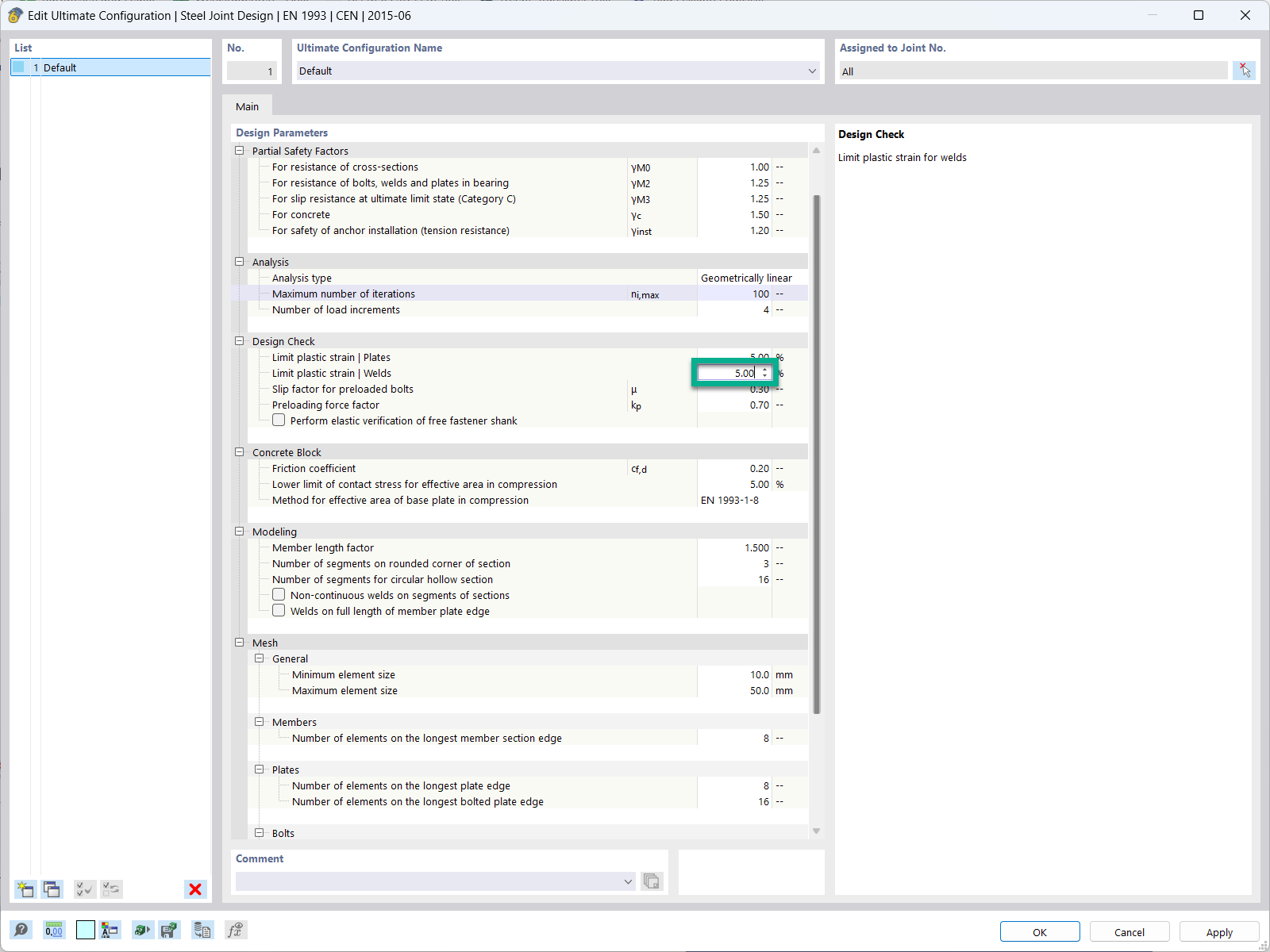
In the ultimate configuration of the steel joint design, you have the option to modify the limit plastic strain for welds.
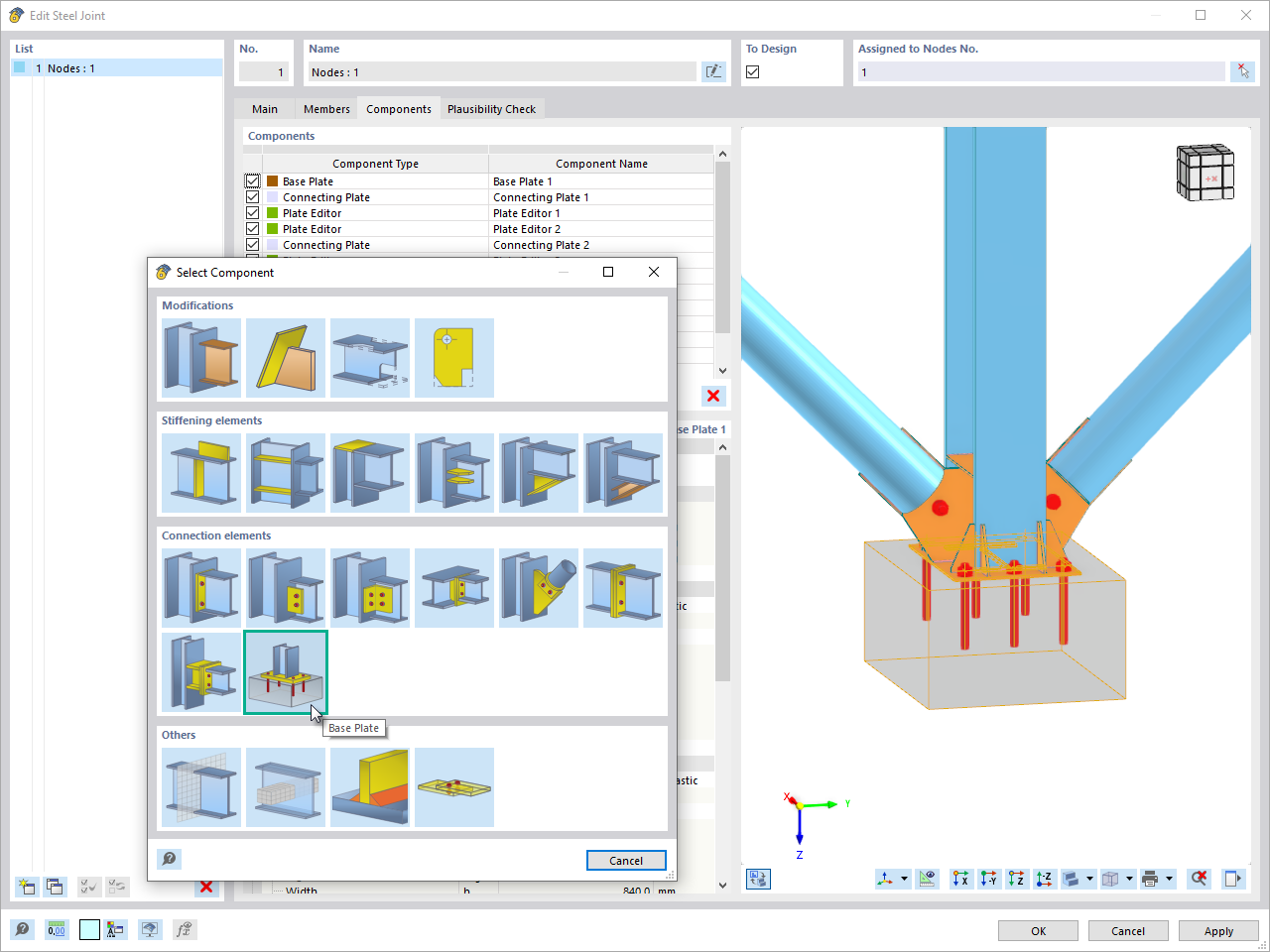
The "Base Plate" component allows you to design base plate connections with cast-in anchors. In this case, plates, welds, anchorages, and steel-concrete interaction are analyzed.
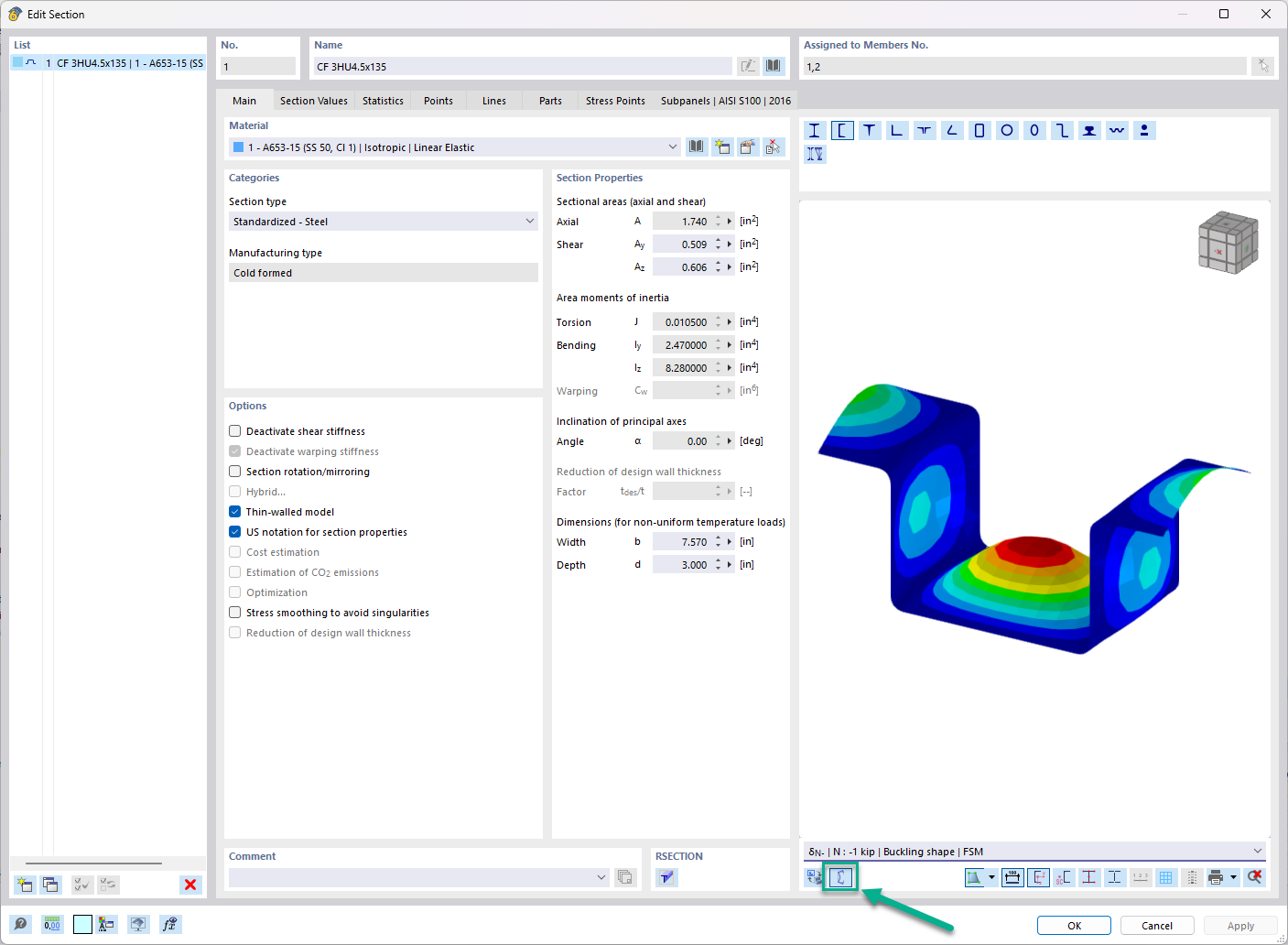
In the "Edit Section" dialog box, you can display the buckling shapes of the Finite Strip Method (FSM) as a 3D graphic.
The lateral torsional buckling (LTB) check looks missing in the Steel Design. What could be the reason?
How can I perform member design by case for different settings in the design configuration?
I would like to analyze temporary structures. Which programs do you recommend?
Which Dlubal programs do I need for tensile membrane structures?
Which programs and add-ons are suitable for the structural analysis and design of steel structures?
Can I design members with Class 4 sections according to CSA S16 in the Steel Design add-on?







































_1.jpg?mw=350&hash=ab2086621f4e50c8c8fb8f3c211a22bc246e0552)



