The following answer refers to the programs RFEM 6 and RSTAB 9.
If you want to use the second-order analysis, you need to define load combinations. In the case of a load combination, the loads of the contained load cases are combined into "one great load case" under consideration of the corresponding partial safety factors, and this load case is then calculated according to the second-order analysis.
In the case of a result combination, on the other hand, the contained load cases are calculated first. Then, the results are superimposed under consideration of partial safety factors. It is not possible to set the calculation method for result combinations. This is only possible for load cases and load combinations.
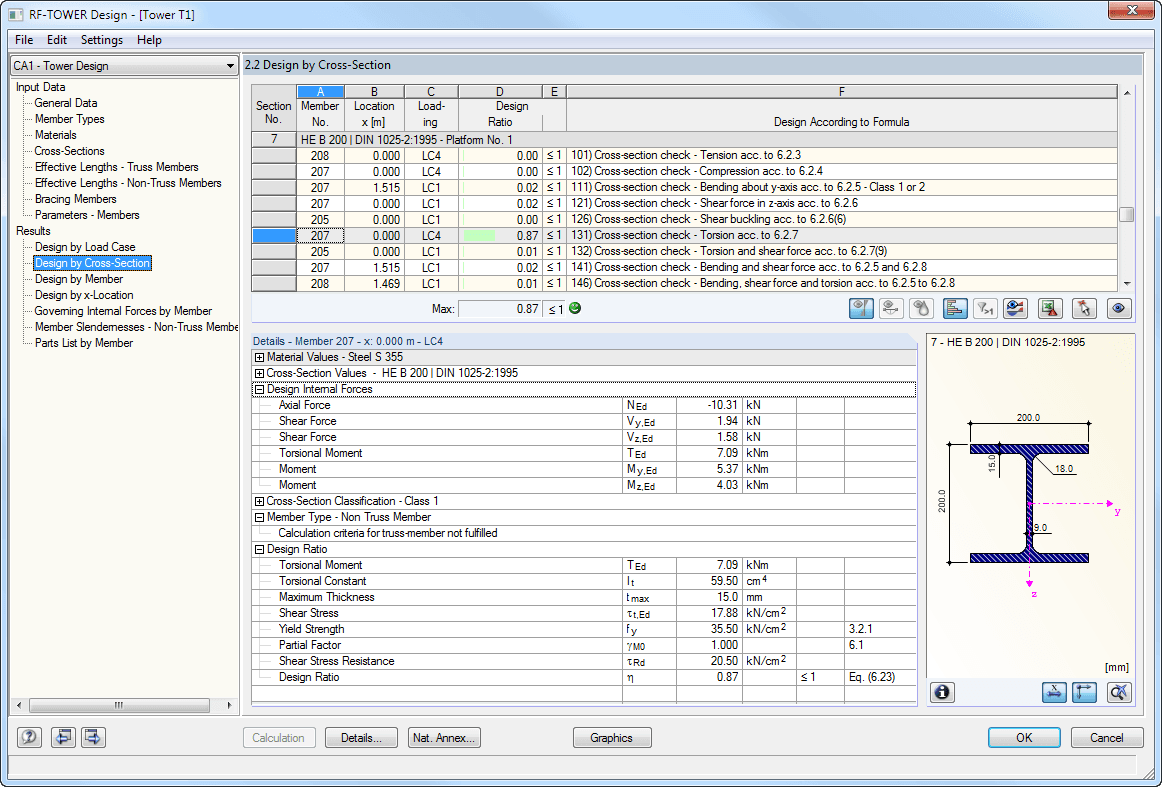
For load cases and load combinations, you can specify the method of analysis in the static analysis settings; for example, the second-order analysis (see Image 01). If the model includes members of the "Cable" type, these elements are calculated according to the large deformation analysis.
For load cases and load combinations, you always obtain unambiguous internal forces. On the other hand, the result combinations include an envelope of the internal forces (max and min values). Since the results of load cases and load combinations are superimposed in the result combinations, the RCs can thus contain results according to the static linear analysis or the second-order analysis.
In your model, you can also combine the defined LCs in a summary RC with the or criterion (for example, RC1 = CO1/permanent or CO2/permanent or CO3/permanent...). Thus, you obtain the maximum internal forces and deformations under consideration of the second-order analysis (see Image 02).
The "permanent or superposition" has the effect that one or both of the COs are used for the results. When connecting the results with "alternatively or superposition", it may also happen that none of the COs are relevant for the results of the RC. The internal forces and deformations may become zero then.



























.png?mw=350&hash=f79867dbf405d536638daef39ee25b113e6e540d)