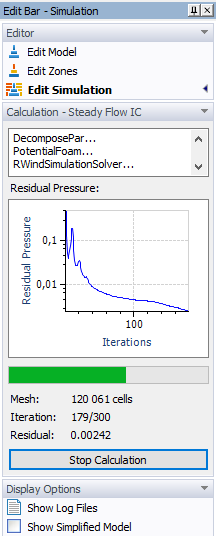
Start Calculation
In the RWIND 2 program, you can start the calculation with the following options:
- Select Start Calculation on the "Simulation" menu.
- Select Calculate Results in the Edit Bar.
You can follow the progression of the mesh generation and calculation in the panel.
The simulation iteratively determines the "Residual Pressure" until either the convergence criterion is satisfied or the maximum number of iterations is reached. These limits are controlled by the "Simulation Parameters" settings (see Chapter Steady Flow).
In RWIND 2 Pro, the simulation of the transient calculation runs the calculation in time layers until the final time, according to the calculation parameters; see Chapter Transient Flow.
Stop Calculation
You can interrupt the simulation at any time by clicking on the
![]() button, for example, to obtain the results at a specific residual pressure or when there is no convergence. The results are then created for the current iteration (that is, the next iteration after the interruption) and will be available for evaluation.
button, for example, to obtain the results at a specific residual pressure or when there is no convergence. The results are then created for the current iteration (that is, the next iteration after the interruption) and will be available for evaluation.
To proceed with the calculation, click "Continue Steady Flow Calculation" in the panel. This function is also available when the simulation is accomplished normally. In the Continue Calculation dialog box, you can then specify the new limit of iterations and/or convergence criterion.
This means that you can interrupt the calculation at any time, look at the intermediate results and continue the simulation if you wish. You can also increase the number of maximum iterations if the calculation was finished without having reached the stated residual. Note that the "Continue Calculation" function is not available after having closed the project.
If the
![]() function does not terminate the calculation within 30 seconds, the text of the button is changed to
function does not terminate the calculation within 30 seconds, the text of the button is changed to
![]() . You can then use this button to abort the simulation. The "Cancel Calculation" function is also available on the Simulation menu. It immediately terminates all running calculation processes and deletes the temporary files. No results will then be available.
. You can then use this button to abort the simulation. The "Cancel Calculation" function is also available on the Simulation menu. It immediately terminates all running calculation processes and deletes the temporary files. No results will then be available.
In the RWIND Pro version, there is a Continue Transient Calculation dialog box. In the "Transient Flow Calculation" section, it is possible to set the target simulation time as "Final simulation time" and the start time for saving the results.
The next part contains the settings for saving transient results (time layers). Here, it is possible to set the saving of results for flow animation and for point probes, in both cases the time step in which the results should be saved is set.
Show Log Files
All calculation steps are recorded in a log file. To open this file, click the "Show Log Files" option, which is available in the Display Options of the panel or in the "Simulation menu." The Log Files dialog box appears where you can check the details of each calculation step. If the calculation is running, the dialog contents and log files are updated continuously.
Pressing the
![]() button opens the "Windows File Explorer." The working directory where the log files are located is shown.
button opens the "Windows File Explorer." The working directory where the log files are located is shown.
Notes
The calculation time largely depends on the global "Mesh Density" (see Chapter Simulation Parameters) and the "Level of Detail" set for the simplified model (see Chapter Edit Model).
For an effective and fast calculation, RWIND applies a parallel approach by using the cores of your computer in an optimal way. You can check the calculation settings in the "Program Options" dialog box which you can access via the "Options" menu.
Interruption and Continuation of the Calculation
Ongoing steady-flow and transient-flow calculations can be interrupted, the current results can be viewed and then the calculation can continue. The results of steady-flow calculation can be used for the continuation of both steady-flow and transient-flow calculations.