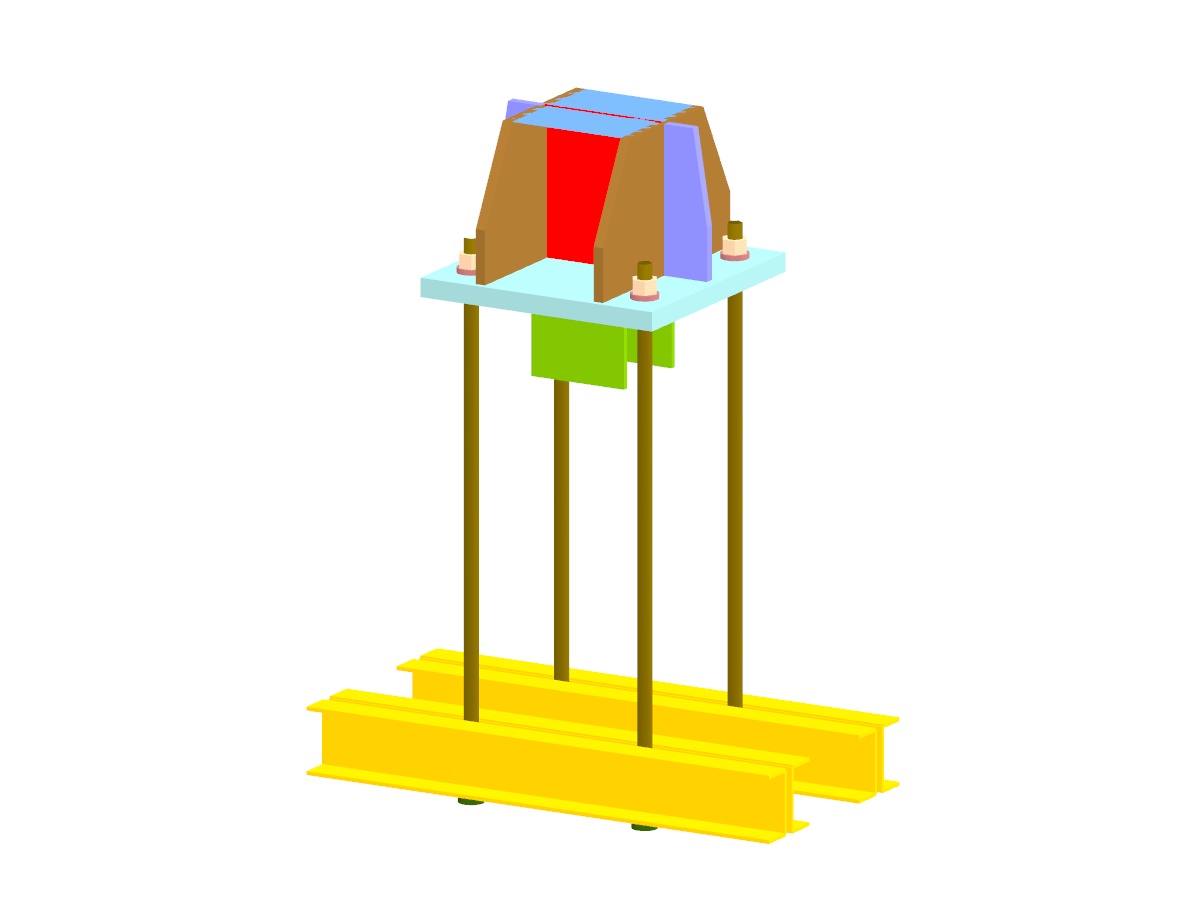
Stress analysis of a column base using an FEA model in RFEM. The bolts are modeled with nonlinear supports that only act under tension. The end plate of the column base has elastic foundations and only acts under compression.
Model Used in
- Online RFEM Training | Basic
- RFEM | Basic
- RFEM for Students | Part 1
- RFEM for Students | Part 2
- RFEM | Basic Steel
- RFEM | Basics
- RFEM for Students
- RFEM | Steel Basics
- RFEM | Structural dynamics and earthquake design according to EC 8
- RFEM | Structural dynamics and earthquake design according to EC 8
- RFEM | Structural Dynamics and Seismic Design According to EC 8
- RFEM | Basics
- RFEM | Basics
- RFEM for Students | Part 1
- RFEM for Students | Part 2
- RFEM | Dynamics | USA
- RFEM | Basics | Arabic
- RFEM | Basics
- RFEM | Structural Dynamics and Seismic Design According to EC 8
- RFEM 6 | Basics
- RFEM 6 | Basics
- RFEM 6 | Dynamic Analysis and Seismic Design According to EC 8
- RFEM 6 | Dynamic Analysis and Seismic Design According to EC 8
- RSECTION | Students | Introduction to Strength of Materials
- RFEM 6 | Basics
- RSECTION | For Students | Introduction to Strength of Materials
- RFEM 6 | Basics
- Most Frequently Asked Questions Answered by Dlubal Support Team | April 2024
- Dlubal RFEM 5 | Introduction to Structural FEA Software
- RFEM 6 for Students | Introduction to Strength of Materials | Apr 26, 2023
- Webinar | Most Frequently Asked Questions Answered by Dlubal Support Team | April 2024
Steel Structure Column Base
| Number of Nodes | 60 |
| Number of Lines | 61 |
| Number of Members | 0 |
| Number of Surfaces | 12 |
| Number of Solids | 0 |
| Number of Load Cases | 2 |
| Number of Load Combinations | 1 |
| Number of Result Combinations | 0 |
| Total Weight | 0.556 tons |
| Dimensions (Metric) | 1,200 x 1,000 x 1,200 m |
| Dimensions (Imperial) | 3.94 x 3.28 x 3.94 feet |
You can download this structural model to use it for training purposes or for your projects. However, we do not assume any guarantee or liability for the accuracy or completeness of the model.
Related Models

.png)