One of the key outputs in RWIND is the wind force coefficient (also known as the aerodynamic force coefficient), which helps engineers understand how wind interacts with a structure. This coefficient is essential for optimizing designs to ensure structural stability and efficiency.
In RWIND, the wind force coefficient is typically obtained by running a wind simulation based on the given geometry, wind speed, and environmental conditions. The software then computes the forces acting on the structure and provides coefficient values that indicate the aerodynamic response. This FAQ will walk you through the process of obtaining the wind force coefficient in RWIND.
To illustrate how RWIND determines the wind force coefficient, we can look at a practical example from RWTH Aachen University about Antenna [1] according to image 1.
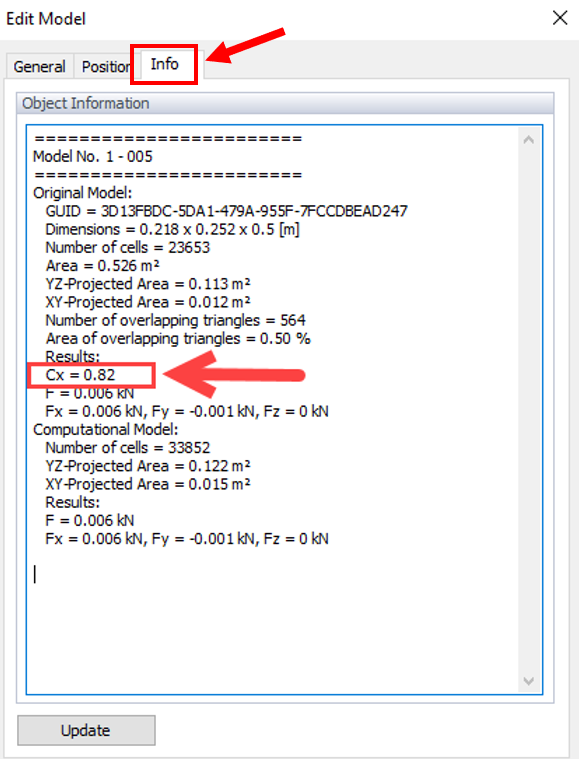
In image 2, the value of wind force coefficient (aerodynamic force coefficient) is calculated in info tab of the edit model data.
Image 3 [1] presents an analysis of force coefficients (Cf) in relation to different structural configurations under wind influence. On the left side, a polar plot titled "Kraftbeiwerte Cf" illustrates the variation of the force coefficients at different angles according to the reference area. A red dot at 0° indicates the force coefficient in RWIND (Cf) = 0.82) as a significant wind-related point in the wind analysis.