Plate Buckling Analysis for Plates with or Without Stiffeners
RF-/PLATE-BUCKLING | Features
- For the design according to Eurocode 3, the following National Annexes are available:
-
DIN EN 1993-1-5/NA:2010-12 (Germany)
-
SFS EN 1993-1-5/NA:2006 (Finland)
-
NBN EN 1993-1-5/NA:2011-03 (Belgium)
-
UNI EN 1993-1-5/NA:2011-02 (Italy)
-
NEN EN 1993-1-5/NA:2011-04 (Netherlands)
-
NS EN 1993-1-5/NA:2009-06 (Norway)
-
CSN EN 1993-1-5/NA:2008-07 (Czech Republic)
-
CYS EN 1993-1-5/NA:2009-03 (Cyprus)
-
- In addition to the National Annexes listed above, you can also define a specific NA, applying user-defined limit values and parameters.
- Import of all relevant internal forces from RFEM/RSTAB by selecting numbers of members and buckling panels with determination of governing boundary stresses
- Summary of stresses in load cases with determination of governing load
- Different materials for stiffener and plate possible
- Import of stiffeners from an extensive library (flat plate and bulb flat steel, angle, T-section, channel, and trapezoidal sheeting)
- Determination of effective widths according to EN 1993-1-5 (Table 4.1 or 4.2) or DIN 18800, Part 3, Eq. (4)
- Optional calculation of critical buckling stresses according to analytical formulas of annexes A.1, A.2, and A.3 of EC 3, or by means of FEA calculation
- Designs (stress, deformation, torsional buckling) of longitudinal and transverse stiffeners
- Optional consideration of buckling effects according to DIN 18800, Part 3, Eq. (13)
- Photo-realistic representation (3D rendering) of buckling panel, including stiffeners, stress conditions, and buckling modes with animation
- Documentation of all input data and results in a verifiable printout report
RF-/PLATE-BUCKLING | Input
Initially, it is necessary to define material data, panel dimensions, and boundary conditions (hinged, built-in, unsupported, hinged-elastic). It is possible to transfer the data from RFEM/RSTAB. Then, boundary stresses can be either defined for each load case manually or imported from RFEM/RSTAB.
Stiffeners are modeled as spatially effective surface elements that are eccentrically connected to the plate. Therefore, it is not necessary to consider the stiffener eccentricities by effective widths. The bending, shear, strain, and St. Venant stiffness of stiffeners as well as the Bredt stiffness of closed stiffeners is determined automatically in a 3D model.
RF-/PLATE-BUCKLING | Structural Analysis
The designs are carried out step-by-step by the eigenvalue calculation of the ideal buckling values for the individual stress states, as well as the buckling value for the simultaneous effect of all stress components.
The buckling analysis is based on the method of reduced stresses, comparing the acting stresses to a limit stress condition reduced from the yield condition of von Mises for each buckling panel. The design is based on a single global slenderness ratio determined by the entire stress field. Therefore, the design of single loading and subsequent merging using interaction criterion is omitted.
In order to determine the plate buckling behavior, which is similar to the behavior of a buckling member, the module calculates the eigenvalues of the ideal panel buckling values using freely assumed longitudinal edges. Then, slenderness ratios and reduction factors according to EN 1993-1-5, Ch. 4 or Annex B or DIN 18800, Part 3, Table 1. The design is then performed according to EN 1993-1-5, Chapter. 10 or DIN 18800, Part 3, Eq. (9), (10) or (14).
The buckling panel is discretized in finite quadrilateral or, if necessary, triangular elements. Each element node has six degrees of freedom.
The bending component of a triangular element is based on the LYNN-DHILLON element (2nd Conf. Matrix Meth. JAPAN – USA, Tokyo) according to the bending theory of Mindlin. However, the membrane component is based on the BERGAN-FELIPPA element. The quadrilateral elements consist of four triangular elements, while the inner node is eliminated.
RF-/PLATE-BUCKLING | Results
The results are displayed with references to EN 1993-1-5 or DIN 18800. In addition, RF-/PLATE-BUCKLING shows calculation results separately for the action of only one edge load as well as for the simultaneous effect of all edge loads.
In the case of several load cases, the governing load case is displayed separately. Thus, time-consuming comparison of calculation data is not necessary.
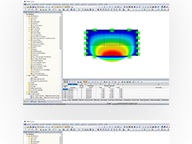
Window 2.5 lists the critical buckling load factors of all load cases and the respective buckling modes.
You can visualize the buckling modes and loads of the buckling panel in the graphic window. This facilitates a quick overview of the buckling modes and loads. Using the animation option, you can clearly represent the buckling behavior of stiffened plates.
Finally, it is possible to export all tables to MS Excel or in a CSV file.
Webshop
Customize your individual program package and find out all the prices online!
Calculate Your Price

The price is valid for United States.






.png?mw=192&hash=f63e4a3f1836233005de32f60201d5392e507cf1)



